Category:DMT
Contents
Brief overview - What is DMT?
NN-Dimethyltryptamine or DMT for short is an short acting psychedelic entheogen which allows a persons consciousness to voyage into the most incredible dimensions, visions, thoughts and experiences imaginable.
It is without doubt one of the most powerful yet mysterious psychedelics in existence but to classify DMT as merely a drug would be doing it a great injustice as DMT is more a trans dimensional key into places and vistas so profound and awe inspiring that it raises many new questions regarding the nature of reality and our place within it.
DMT exists naturally in every human being and also throughout the plant and animal kingdoms. It occurs naturally in many mammals, marine animals, trees, grasses, flowers and shoots.
DMT is closely related to serotonin, the naturally occurring neurotransmitter that psychedelics affect so widely. The pharmacology of DMT is similar to that of other well-known psychedelics. It affects receptor sites for serotonin in much the same way that LSD, psilocybin, and mescaline do. These serotonin receptors are widespread throughout the body and can be found in blood vessels, muscle, glands, and skin.
There are a number of ways to acquire this entheogen. The first and most difficult way is to have some substantial chemistry knowledge and experience and actually synthesize pure DMT in a laboratory. This a rather tricky and time consuming process and requires access to some rather obscure and hard to acquire chemicals.
The most common and easiest method to acquire DMT is to extract it from the various plant species that contain the compound. The various plants and extraction techniques can be found on this wiki at the extraction teks.
Chemical and physical properties
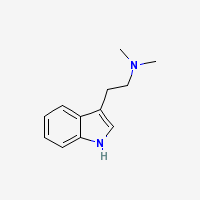
DMT = N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
Freebase DMT
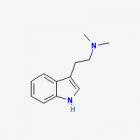 |
- Appearance: White/Transparent crystals
- CAS Registry Number: 61-50-7
- Composition: C12H16N2
- Molecular Weight: 188.26884 g/mol
- Melting point: 44-68°C (Conflicting reports in literature, as mentioned in TIHKAL)
- Boiling point: Theoretically 360-380°C
- XLogP: 2.0
- XLogP3: 2.5 (PubChem)
- pKa: 8.68 (Merck Index)
- Colorimetric reagent results: Here
- Stability/Degradation: Oxidation to DMT N-Oxide (yellow oil) in prolonged exposure to open air (unknown rate). N-oxide may be reverted back to the parent compound by reduction, as described in the N-Oxide to Freebase Wiki.
- Solubility:
Very Soluble in Xylene, Toluene, Limonene, acetone, Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA), methanol, ethanol, Dichloromethane (DCM), chloroform, ether, Butanone (also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK)) and butanol. Soluble in dilute acids (form salts with these acids), soluble in acidified alcohols (forms salts) (Trout's notes)
Soluble in naphtha, hexane, heptane but almost insoluble in these solvents at freezing temperatures
Almost insoluble in water.
DMT N-Oxide
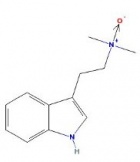 |
- Appearance: Yellow oil
- XLogP3: 2
- Colorimetric reagent results: Here
- Solubility:
Soluble in Xylene, Toluene, Limonene
Slightly soluble in basic water
Insoluble in naphtha/heptane/hexane but soluble in these solvents that have fats/oils dissolved in them (Trout's notes)
DMT Fumarate
- Molecular Weight: 492.608 g/mol
- Solubility:
Very soluble in water
Soluble in methanol (~10mg/ml)
Soluble in boiling IPA, Practically insoluble in room temp IPA (~1mg/ml), Insoluble in freeze-cold IPA.
Slightly soluble in ethanol (~5mg/ml)
Insoluble in cold acetone
Insoluble in FASI (Fumaric Acid Saturated IPA)
Insoluble in FASA (Fumaric Acid Saturated Acetone)
Effects
Depending on the dosage and form of ingestion, the effects of DMT can range from a multitude of sensations, from light, subtle perceptual changes, to bizarre, beautiful and even 'impossible' visions , and to literally jaw hanging awe as one is propelled into other dimensions of existence where human language and logic cannot even begin to describe or comprehend.
There have been a few attempts to define different levels and types of experience. Psychedelic Monographs and Essays[1] discusses different levels of a DMT experience.
The Hyperspace Lexicon project is an attempt to create a new vocabulary to try to describe the DMT realm
Pharmacology, toxicity and general safety
Pharmacology
DMT is inactive when taken orally, unless if ingested together with MAOI.
After intramuscular injection it is rapidly metabolised primarily into indol-3-ylacetic acid. About 33% of the dose is excreted in urine in 6 hours as free and conjugated (glucoronide) indol-3-ylacetic acid. Less than 0.1% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine in 24 hours (Clarke's second, 1986)
DMT is an agonist of serotonin 5-HT2a, 5-HT2c and 5-HT1a
For specific information about DMT/Ayahuasca pharmacology, read these papers:
Ayahuasca pharmacology part 1 Jordi Riba
Ayahuasca pharmacology part 2 Jordi Riba
Human pharmacology ayahuasca
DMT psychopharmacology
Safety
For info on DMT safety, please reffer to Health and Safety section
Plants containing DMT
The following is a list of plants known to contain tryptamines. In some, the DMT content may be very small or it may be present together with other potentially unwanted alkaloids. Please research well before extracting from some plant, and be sure you have your desired alkaloids only when bioassaying from a new plant.
Acacia
- DMT in the leaf (Trout's Notes)
- 0.2% tryptamine in bark, leaves, some in flowers, phenylethylamine in flowers (Hegnauer 1994)
- DMT in plant (Lyceaum)
- Bark of A. maidenii contains 0.6% of N-methyltryptamine and DMT in the proportions approx. 2:3 (Fitzgerald & Sioumis 1965)
- DMT in the bark and leaf, less than 0.02% total alkaloids (Hegnauer 1994)
- DMT in the leaf (Trout's Notes)
- DMT in the leaf (Trout's Notes)
- 0.4 to 0.5 % DMT/NMT in the dried bark (Csiro 1990)
- 0.15-0.6% DMT,NMT(2:1)plus trace betacarboline in bark, 0.06-0.2% leaves (Southern Cross University comissioned test 2001)
- 5-MeoDMT & bufotenine in some loctations (E., Entheogen Review 1995-6; Trout's Notes 2005-10) Is not fast growing in the wild and is under threat of serious overharvesting. Is NOT considered a weed as previously stated here, and will become rarer if wild seed populations exploited further.(Nen, original bioassay subject)
- Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf (Ott)
- 0.3% DMT in leaf, NMT (Trout's Notes)
- Tryptamine in the leaf (Trout's Notes)
- 0.5% to 2% DMT in fresh bark, phenethylamine trace amounts (Hegnauer 1994)
- DMT in leaf (Trout's Notes)
- DMT and MMT (www.factorey.ch/Eins.htm)
- Less than 0.02% total alkaloids found (Hegnauer 1994)
- DMT, NMT, tryptamine, amphetamines, mescaline, nicotine and others (Phytochem. 199
- DMT, in the leaf
- DMT and NMT, in the leaf, stem and trunk bark, 0.81% DMT in bark, MMT
- DMT, NMT, and other tryptamines
- DMT in the leaf (Trout's Notes)
Anadenanthera
- Seed pods contain dimethyltryptamine and the seeds bufotenin, bufotenin oxide, and oxide of dimethyltryptamine (GRANIER-DOYEUX 1965)
Grasses
- Entire Plant contains 5-MeO-DMT (Shulgin, TIHKAL)Flowers contain DMT, 5-MeO-DMT, and 5-MeO-NMT (Shulgin, TIHKAL)Roots contain DMT, 5-MeO-DMT, 5-MeO-NMT, Bufotenine, bufotenidine, dehydrobufotenidine (Shulgin, TIHKAL)
- Plants analyzed in india were found with alkaloids, others from USA where not found to contain DMT based alkaloids (Trout notes)
- Root contains DMT - 0.200% (Ott)Root Bark contains DMT - 0.340% (Ott)
- Leaves and seedlings contain DMT, 5-MeO-DMT, and related compounds (Smith 1977)DMT - 0.100% (erowid)5-MeO-DMT - 0.022% (erowid)5-OH-DMT - 0.005% (erowid)
Delosperma
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT (Trout's Notes)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT (Trout's Notes)
- DMT (Trout's Notes)
- DMT (Trout's Notes)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT (Trout's Notes)
- DMT (Trout's Notes)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT (Trout's Notes)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT (Trout's Notes)
- Traces of DMT (Trout's Notes)
- DMT (Trout's Notes)]]
Desmanthus
- Root contains DMT - 0.200% (Ott)Root Bark contains DMT - 0.340% (Ott)
Desmodium
- Roots: 0.087% DMT, Bufotenine-N-oxide 0.03% (Trout's Notes)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT, whole plant, roots, stems, leaves (Ott)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT, leaves, roots (Ott)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT, whole plant, roots, stems, leaves, flowers (Ott)
- 5-MEO-DMT (Ott)
- DMT-N-oxide, roots (Ott)
Lespedeza bicolorvar. japonica
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in leaves and root bark (Ott)
Petalostylis
- 0.4-0.5% tryptamine, DMT, etc. in leaves and stems (Johns et al 1966)
Mimosa
- 1.6% DMT in rootbark
- DMT in bark (Ott)
- DMT (Schultes 1969)
- Leaves, seeds, stems and roots contain L-Dopa, Serotonin, 5-HTP, and Nicotine, as well as N,N-DMT, Bufotenine, and 5-MeO-DMT (Erowid)
Petalostylis labicheoidesvar. casseoides
- DMT in leaves and stems (Ott)
- DMT
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark (Ott)
Virola
- Leaves 0.149% DMT (Ott)
- DMT in leaves (Ott)
- DMT in leaves (Ott)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark and leaves (Ott)
- DMT in bark (Ott)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark and leaves (Ott)
- DMT in leaves (Ott)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark (Ott)
- Alkaloids in bark and root, 95% of which is 5-MeO-DMT (Shulgin, TIHKAL)
- DMT in bark (Ott)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark, roots, leaves and flowers (Ott)
- DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in roots and leaves (Ott)
- 0.2% average DMT in dried leaves (Ott)
Extraction Teks
A/B
STB
STB-A/B hybrid
Dry tek
Dosages and consumption methods
http://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/Ingestion_Methods
Smoked / Vaporized
Extracted DMT freebase can be vaporized for very potent effects that last around 10 minutes. DMT is ideally vaporized, as opposed to smoked. Vaporization is achieved by a controlled temperature that does not burn/combust DMT material (and potential impurities), but instead just makes DMT evaporate and be inhaled.
Vaporization is much smoother than smoking. Smoking leads to break down of DMT (and impurity) molecules into potential toxic nitrogen oxides (Trout's notes), so not only it is harsher but also there is a significant loss of actives.
Vaporizing can be achieved with improvised vaporizers such as The Inspirator mkII, or commercially sold vaporizing pipes such as the VaporGenie.
Some methods, such as The Machine, if very carefully done with lighter farther away, can also vaporize DMT but due to lack of adequate buffer between fire and the alkaloids, so often will also generate combustion.
Smoking is nonetheless still a popular way of ingesting DMT, and is often done by infusing herbs with the DMT, or smoking in a bong, with the DMT sandwhiched between thick layer of ashes or thin layer of herbs that serve to protect the DMT from fire (though there is still combustion, specially when using herbs).
Dosages are around 20-30mg for efficient vaporization methods, and with smoking methods can be around 50-60mg or even more....
Oral
DMT is only active orally when taking together with a MAOI. (FAQ for more info)
Dosages for DMT, considering MAOs are fully inhibited, vary wildly depending on person, probably due to metabolism in great part. They can go from 30 to 250mg! If its your first time, start on the lower end!
Another factor is whether one is ingesting a whole plant brew or purified extracts. Often in ayahuasca analysis the amount of DMT found is very small (20-30mg), but also often there is redosing in ayahuasca sessions, but also its possible other trace amount of beta-carbolines and alkaloids can improve MAO inhibition, or that other inactive plant substances can help protecting DMT from fast breakdown by any potential active MAO.
Snorted
This is a method that gets very opposite responses for different people. For many, it hurts too much and isn't effective. For others it works well and pain/discomfort is tolerable, and the effects are worth it. It is unknown what possible health consequences snorting a basic alkaloid such as DMT can have on nasal passages, specially long term use, so we advice caution. There are some attempts to find less harsh ways, check threads below for more info:
Snorting Works! Preparations to make snorting more tolerable
History of usage
Analysis of DMT
To learn how analytical processes work, follow this link
Colorimetric reagents
DMT
- α-Nitroso-β-naphthol-nitrous acid - Negative - (silica gel) - (23)
- - Weak brown (on paper) - (18 )
- Chloranil - No Reaction - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- CNTF - Gray (light) - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- Diazotized p-Nitroaniline - Very weak yellow - (on paper) - (18 )
- Dragendorff's - positive with spray - (silical gel) - (5)
- Red-Brown - (paper) - (18 ) - Orange - (silica gel) - (23)
- Ehrlich - Reddish purple - (as acetate on paper) - (26)
- Fluoranil - Purple - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- Fluorescence with PENE - Violet under 254nm UV - (silica gel with PENE) - (24)
- HNS - No reaction - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- HNO3 atmosphere - yellow - (silica gel) - (25)
- Iodine vapor - Red-Brown - (paper) - (18 )
- Iodoplatinate - Purple - (silica gel) - (25)
- Blue (silica gel) - (17)
- Iodoplatinate, acidified - Positive - (silica gel) - (5)
- Marquis - Yellow - (NA) - (13)
- Marquis - GreenYellow - (silica gel) - (7)
- Marquis - Orange->red - (NA) - (5)
- Mecke - Brown->red over time time. - (NA) - (13)
- Mandellin - yellow - (NA) - (13)
- Ninhydrin, acetic acid - No UV fluorescence - (acetate on paper) - (26)
- No visible color - (acetate on paper) - (26)
- NNCD - Weak orange - (on paper) - (19)
- p-DMAB, ethanol:sulphuric - Red solution, Violet when diluted with water - (5)
- p-DMAB-TS - Yellow - (pure compound) - (3, 27)
- p-DMAB, ethanolic - Purple - (pure compound) - (3)
- TACOT - Purple (light) - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- TCBI - Brown-green - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- TCNE - Brown (light and fading) - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- TetNF - Brown (light) - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- TNB - Yellow->Brown - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- TNF - Brown (light) - (silica gel) - ( 8 )
- Van Urk - Blue - (silica treated with 0.1M KOH) - (16)
- Xanthydrol - Purple - (silica gel & celulose) - (15)
- Purple - (tlc & on paper) - (5, 20) - Pink - (on paper) - (21) - Lavender - (on paper) - (22)
LC / GC-MS
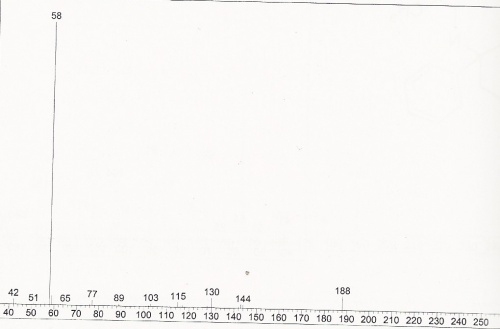
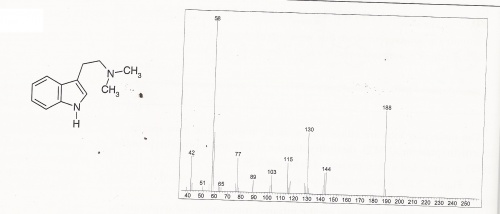
DMT Mass Spectra
DMT Mass Spectra (expanded)
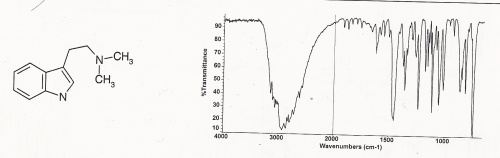
IR - Infrared
Other IR data (Clarke's second): Principal peaks at wavenumbers 743, 1113, 1235, 1050, 812, 1010 (KBr disk)
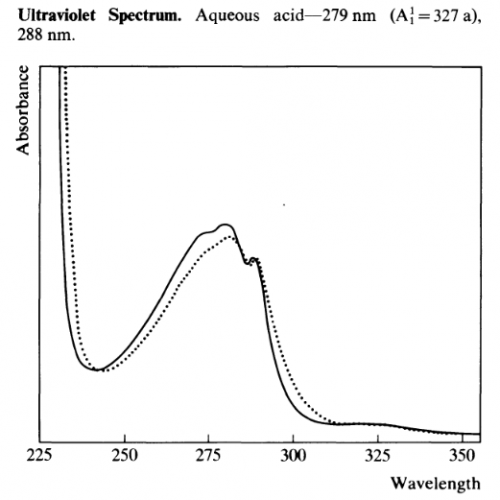
UV-Vis
Other UV-Vis data:
- λmax 222nm (log e 4.48), 277 (3.77) and 288 (3.75) Ghosal et al 1969
- λmax 222-224, 274 & 294nm Banergee & Ghosal 1969
- λmax 222, 277, 287 & 294 nm Ghosal & Banergee 1969
- λmax 274, 283, 291nm (refernce material) 275, 283, 291nm (isolated material) Fish et al 1955
- λmax (CH3OH): 220, 280, 290 (= 5500, 5600, 5000) De Moraes et al 1990
- λmax (EtOH): 226, 275 (sh), 279, 284, 293nm Grina et al 1982
- λmax 276, 282, 290nm
λmin 278, 287nm Martin & Alexander 1968
- λmax 275, 219 (0.1N NaOH)
- λmax 290, 276, 282 (EtOH) Sunshine 1981
- λmax of Xanthydrol reactive product (CHCl3): 510nm
λmin of Xanthydrol reactive product (CHCl3): 400nm Gander et al 1976
Scientific publications
Links of interest
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Pages in category "DMT"
The following 40 pages are in this category, out of 40 total.