The FASA Method
From DMT-Nexus Wiki
| Note: | This page has been transcluded to The Nexian DMT Handbook under the The FASA Method section or other locations within or without the handbook. Please markup in consideration of this. The top section header is to remain in place as a reference for subsequent section headers and to allow easy editing directly from the handbook. |
The FASA Method
| Materials Required | |
|---|---|
Source Material:
|
|
Solvents:
|
|
Reagents/Desiccants:
|
The FASA, or fumaric acid saturated acetone, method is a method employed to render DMT Fumarate.
Considerations:
- DMT Fumarate is reportedly quite stable and resistant to oxidization or other forms of degradation. It is notably resistant to heat, and as such is able to withstand low-temperature oven-drying. Certain other related compounds, such as jungle-spice and bufotenine are also able to crystallize as a fumarate. Defatting is not required prior to employing FASA methods, as oils and most other impurities should not interfere with this method's procedure or the yield
- Because DMT Fumarate is water-soluble, it is also well-suited for oral administration in conjunction with harmaloids, either mixed into a beverage or encapsulated.
Methods:
- The FASA method employs the firstly, the solubility of fumaric acid in acetone, and secondly, solubility of freebase DMT in acetone, and thirdly, the insolubility of DMT Fumarate in acetone or the non-polar solvents commonly utilized for extraction. The solubility of both DMT and fumaric acid in acetone facilitates their reaction to produce a crystalline DMT salt which is completely insoluble in acetone or non-polar solvents.
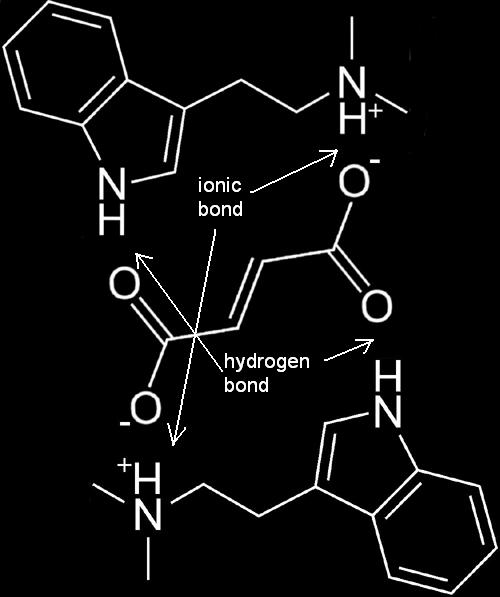
FASA Molecule
One fumaric acid molecule attaches to two DMT freebase molecules.
Procedure
| Rendering Crystalline DMT Fumarate | |
|---|---|
|