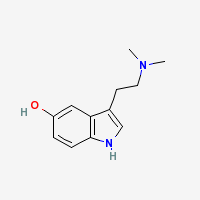
Bufotenin
From DMT-Nexus Wiki
Revision as of 13:23, 15 November 2011 by Endlessness (Talk | contribs)
| Note: | This page has been transcluded to The Nexian DMT Handbook under the Bufotenin section or other locations within or without the handbook. Please markup in consideration of this. The top section header is to remain in place as a reference for subsequent section headers and to allow easy editing directly from the handbook. |
Contents
- 1 Brief overview - What is Bufotenine?
- 2 Chemical and physical properties
- 3 Effects
- 4 Pharmacology, toxicity and general safety
- 5 Plants containing bufotenine
- 6 Extraction teks
- 7 Dosages and consumption methods
- 8 History of usage
- 9 Analysis of bufotenine
- 10 Scientific publications
- 11 Other links of interest
Brief overview - What is Bufotenine?
Bufotenine (5-HO-DMT) is a psychoactive alkaloid found in several plants and animals, also in humans. It is known specially for it's presence in the skin and venom of some toads (Bufo species, hence the name BUFOtenine)
Chemical and physical properties
For solubility, melting point, etc, check the Bufotenine Chemical and Physical Properties WIKI
Effects
Pharmacology, toxicity and general safety
Jonathan Ott - Pharmañopo (bufotenine activity article)
Plants containing bufotenine
Amanita spp.
(Generally low concentration. Ref Trout's Notes)
- Wieland & Motzel 1953 (European specimens) 0.045% bufotenine (Stijve
1979 noted their inefficient procedure may have only recovered 10% of what was there.)
- Bufotenine presence. Catafolmo & Tyler 1961 (North American specimens)
- Bufotenine presence. Tyler 1961 (North American specimens)
- Bufotenine presence.Tyler & Groger 1964 (Gennan specimens) Identified chromatographically. (Mycelium shown to contain 0.03%)
- Stijve 1979 (German, Dutch & Swiss specimens). Bufotenine was the major alk. Bufotenine concentrations were estimated from 0.70- 1.5% using GLC and from 0.4-1.3% using tlc. Isolation: 0.8% in cap. 1.5% iu stalk & 0.065% in bulb. Wurst et al. 1992 (0.0 - 1.899%)
- Bufotenine presence. Wieland & Motzel 1953 (observed)
- Catalfomo & Tyler 1961 could not verify
- Stijve 1979 could not detect it
- Wieland & Motzel 1953 (Bufotenine observed)
- Brady & Tyler 1959 could not detect.
- Stijve 1979 could not detect it
- Bufotenine presence. Catafolmo & Tyler 1961 (North American specimens)
- Bufotenine presence. Tyler 1961 (observed)
- Bufotenine presence. Tyler & Groger 1964 (German specimens) Identified chromatographically.
- Bufotenine presence. (0.374 & 0.617%) Wurst et al. 1992
- Bufotenine presence(0.018-0.020%). Wurst et al. 1992
- Stijve 1979 could not detect it
- Tyler 1961 (Bufotenine presence observed)
- Overview & summary: see Catalfomo & Eugster 1970
Arundo spp.
- Bufotenine In leaf and rhizome. 180 mg from 700 grams of rhizome. Ghosal et al. 1969 ref Trout's Notes
- Bufotenine 128 mg from 200 grams of dry plant. 110 plus 18 mg. Dutta & Ghosal 1967 ref Trout's Notes
- Bufotenine In flowers. Ghosal et at. 1971 ref Trout's Notes
Phalaris spp.
- Bufotenine present in all fresh samples they examined but not in all dried samples and if so was present in considerably reduced amounts. Culvenor et at. 1964
- Bufotenine traces both in commercial material and in AQ-1 (Italy). HPLC by Fabio Calligris. Festi & Samorini 1994b ref trout's Notes
- (France) Bufotenine traces reported (HPLC) Festi & Samorini 1994b ref Trout's Notes
- (Portugal) Bufotenine Traces reported (HPLC) Festi & Samorini 1994b ref Trout's Notes
- (Portugal) Bufotenine Traces reported (HPLC). Festi & Samorini 1994b ref Trout's Notes
- (Romania) Bufotenine Traces reported (HPLC) Festi & Samorini 1994b ref Trout's Notes
- (France) Bufotenine Traces reported (HPLC) Festi & Samorini 1994b ref Trout's Notes
Phalaris tuberosa ( see P aquatica)