CIELO
Contents
Introduction 🙏
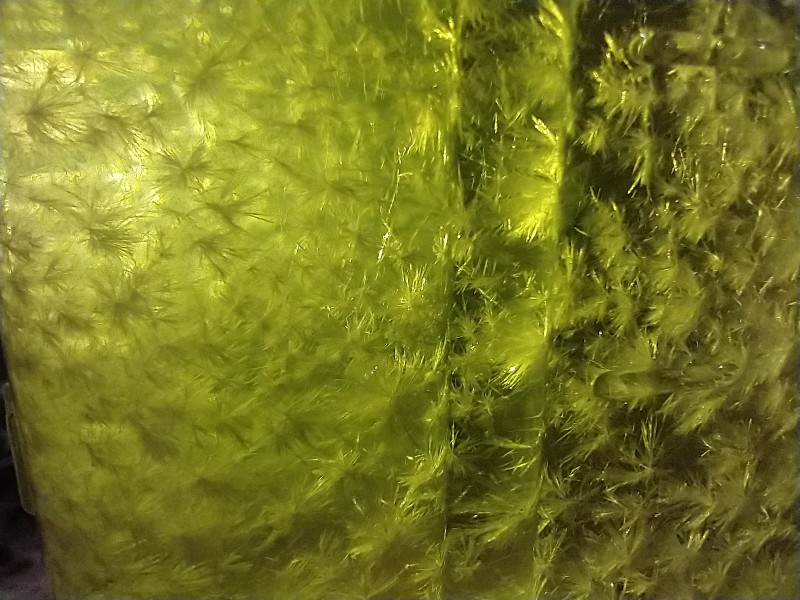
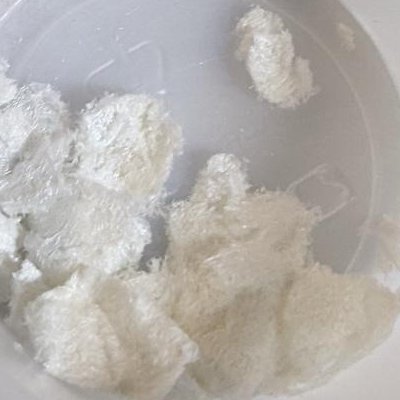
CIELO stands for Crystals In Ethyl-acetate Laizily Over-the-counter. In this process, mescaline from cactus is precipitated in ethyl acetate as monomescaline citrate crystals (see Fig. 1). This technique (TEK) is specialized for catus, simple, and avoids harsh chemicals. The process needs to be followed closely to ensure good results.
Thanks to everyone who contributed to this process: someblackguy, benzyme, shroombee, Metta-Morpheus, Downwardsfromzero, Kash, grollum, Mindlusion, Doubledog, Dreamer042, merkin, _Trip_, Cheelin, Highlightprotein, Loveall, orchidist, BlackRose, and others.
Safety ⛑️
Review ethyl acetate[1] and citric acid[2] safety information. Verify solvent MSDS, plastic compatibility, and clean evaporation.
This TEK is food safe if food grade materials are used.
Following this advice does not guarantee safety. It is up to each adult individual to make their own personal decisions.
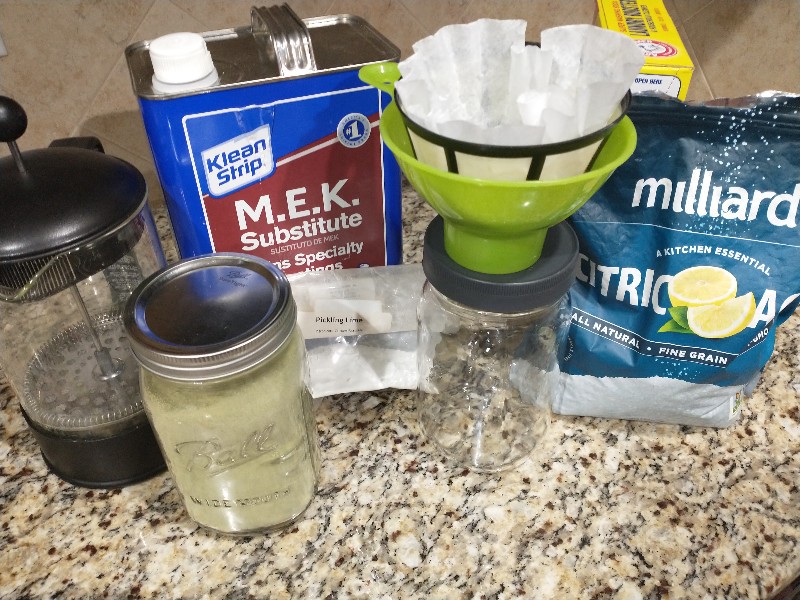
Materials🛒
Consumables👩🌾
- 300g water
- 25g Ca(OH)2 (lime)
- 100g dry cactus†
- 1qt ethyl acetate (sometimes sold as "MEK substitute")††
- 5g of citric acid (~1 tsp)
- Washing soda (Na2CO3) 10% water for solvent reuse
† Ingredients can be scaled down to 5g of cactus powder to perform a TEK test run. This is encouraged for beginners to get a feel for the process before commiting more material[3].
†† Depending on pull technique using two quarts of ethyl acetate may yield a little more mescaline (up to ~+10%). See extraction section for more details.
Equipment🏺
- Knife, paper bag, dehydrator, food processor, and coffee grinder (to harvest plant, store cutting, and make cactus powder)
- Large bowl and spoon (to mix alkaline cactus paste)
- French press (optional, recommended for extraction - all metal model preferred)
- Kitchen scale (to measure ingredients)
- Coffee filters, support basket, and funnel (to first filter extract and to later catch mescaline crystals)
- Quart mason glass jars with lids (to first collect/settle extract and to later salt extract and crystalize mescaline)
- Milligram scale (to measure product)
- Pipette, separatory funnel, or freezer (for solvent reuse water separation)
Process Overview 👀
In short:🌵➠🟢➠🧑🏾🔬➠✨➠💖➠💚, where,
- 🌵: Grow, harvest, store, dry, and grind cactus to a fine powder
- 🟢: Mix cactus powder to a wet alkaline paste
- 🧑🏾🔬: Pull paste with ethyl acetate, rest in fridge, and decant
- ✨: Precipitate mescaline from ethyl acetate with citric acid
- 💖: Collect and wash monomescaline citrate crystals
- 💚: Store ethyl acetate for reuse
Detailed Process 📜
Powder 🌵
Grow[4] and harvest cactus. Store cuttings in a dark place for at least 3 months (e.g. in a paper bag or wrapped in newspaper). Data shows dark storage increases mescaline content[5], and that the top part of the plant contains more mescaline[6]. Chop whole cacti (into for example ~1/4 inch thick slices) and dry them with (for example) a food dehydrator at low temp (~115 F).
All parts of the cactus can be used. Outer green skin yields more than the inner white core for the same dry mass[7], but mescaline is present in both parts of the plant. Outer waxy layers and spines do not yield product, they can optionally be removed but are not detrimental to the extraction.
Grind dry cactus slices to a fine powder. This can be done in two steps, first through a food processor (coarse grind) and then through a coffee grinder (fine grind).
It is very important to make a uniform cactus powder that is dry (<10% moisture) and finely ground. The quick fine grind enables good yields without the need of a long hot water extraction. Clouds of fine dust fly into the air when handling a good powder, reminiscent of flour (but green). Store properly sealed to avoid moisture absorption over time (redry before extracting if needed). Old cactus powder may change to a tan color, and still works well in this process (extract may be tan instead of green).
Paste 🟢
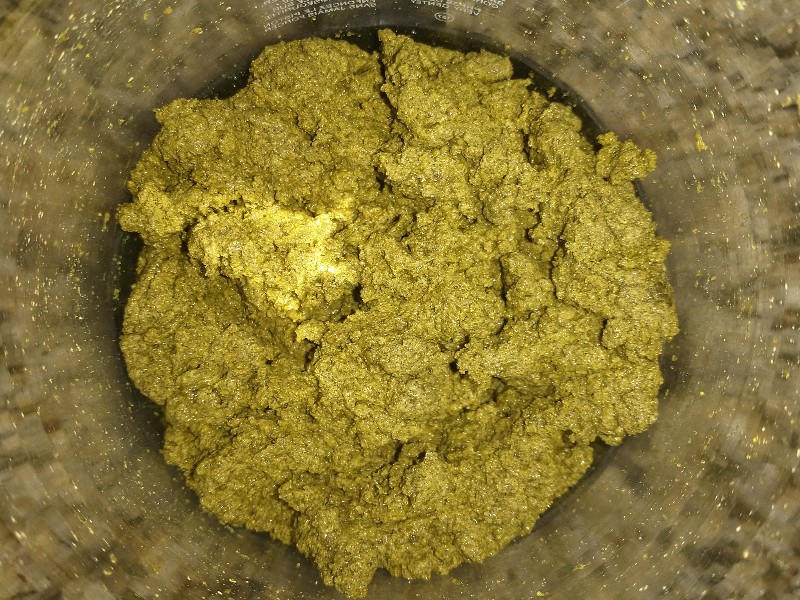
Make milky water in a large mixing bowl by mixing lime with ~270ml of water. Mix so there are no lumps of lime. Without giving lime time to settle, gradually add the cactus powder, stirring thoroughly to ensure the cactus is well incorporated. Toward tbe end, the back of a large spoon pushing down on the paste can be helpful to mix everything well. Goal is to get a "stiff mashed potatoes" consistency (Fig. 3), add the reserved water if needed to achieve this consistency.
If the paste is too dry and clumpy, free base conversion and/or ethyl acetate penetration diminishes lowering yields[8]. If there is too much water the paste will emulsify with ethyl acetate lowering yields and wasting solvent[9] (see FAQ). However, the water process window for a good paste is large, estimated at ±30ml[10], and with attention to detail a good paste can be made. Achieving the right paste consistency is more important than the exact amount of water added (which may vary for different cacti and diameter core-to-skin ratios). Ideal paste consistency is reminiscent of stiff yet fluffy mashed potatoes. The ideal paste also becomes less resistant to mixing. However, drier consistency and more compact paste (~play doh) has been reported to give good yields[11]. Give paste homogeneous texture by stirring vigorously for at least 5 minutes. In case of doubt, mix more.
This paste has the same ratios originally used in 69ron's limonene TEK [12]. However, with ethyl acetate it is very important to mix the paste well and obtain the proper texture. Some elbow grease is required, so mix with intent.
Extract 🧑🏾🔬
Transfer the paste to a french press. Cover paste with ethyl acetate (~200g) and stir for one minute. Do not to stir too aggressively as that may cause plant material to absorb excess solvent. A good paste becomes sandy during extraction and is very easy to handle, but other textures also work. After stirring, rest for two minutes, pour extract into a quart jar. Do not squeeze french press to accelerate the pour because that can release unwanted water into the extract. The pour is complete after a mimute or two, once the trickle turns into drops.
If the paste absorbs all or most of the ethyl acetate during the first pull, that's fine. Just add more ethyl acetate, stir, rest, and pour as explained above. Do NOT add water or aggressively manipulate the paste in an attempt to force out the ethyl acetate. Some solvent absorption during the first pull is common. If an emulsion forms see the FAQ below.
Repeat the extraction with ~125g of ethyl acetate until the extraction jar is full (5-6 total pulls). It is normal for paste to become more sticky as the pulls progress. A small yield boost can be done by optionally doing more pulls into a second jar. This second jar is also a good check on the effectiveness of the pulls in the main jar the first time this TEK is performed. Poor technique will give a larger yield boost in the second jar, <10% boost is considered good[13].
All of the extraction pulls should be completed within 45 minutes. After 45 minutes the paste can begin to congeal, making solvent penetration and recovery more difficult. There is plenty of time to lazily perform the pulls by remaining focused on the task. However, extracting in a warm environment may shorten this time.
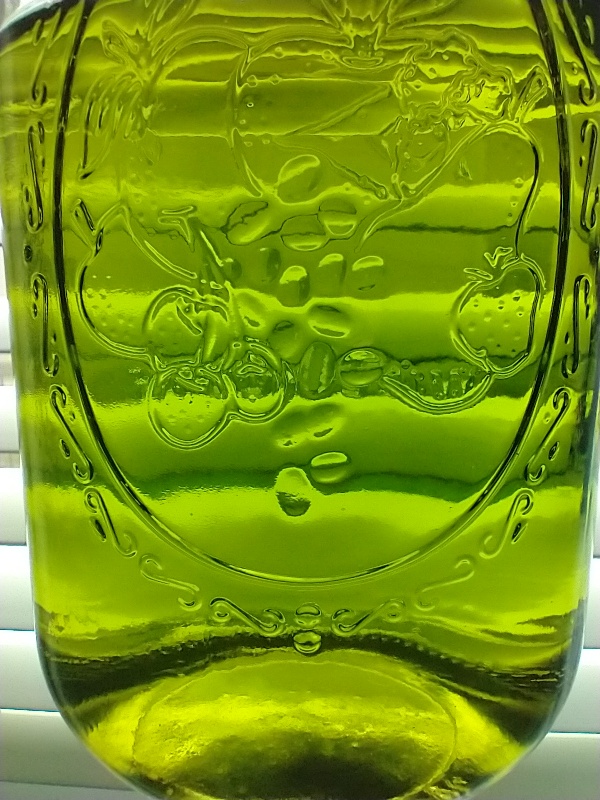
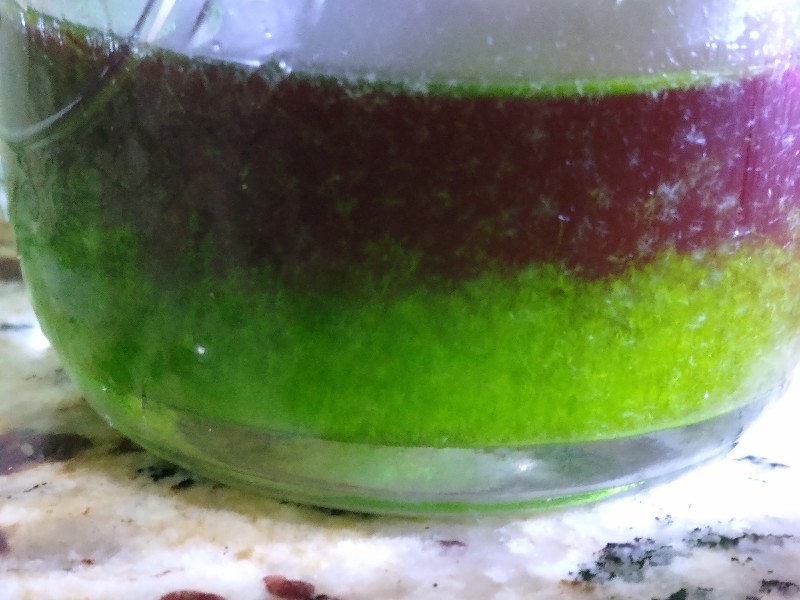
Rest lid sealed extract for 24 hours in a refrigerator. Water solubility in ethyl acetate decreases with temperarure, so this cold resting period is effective at removing some water (see Fig. 4a) and settling debris. Extract may cloud during fridge rest. Decant through a coffee filter leaving any water and debris behind (it is ok to leave a few ml of extract as precise decanting is not possible - the small amounts of liquid can be used in the next extraction if desired), cover, and bring to room temperature. Inspect extract to ensure it is ready for the next step. The extract needs to be clear, particle free, and without water droplets for the crystallization process to happen reliably (see Fig. 4b). If a thick layer of water forms see the FAQ section.
Crystalize ✨
Stir ~5 grams (~1 teaspoon) of citric acid powder granules into extract. Extract should cloud as the citric acid reacts with mescaline free base to form insoluble mescaline citrate. However, cloudiness may be hard to see in darker extracts (a backlight may help). Stir only until citric acid dissolves, which should only take a few minutes. Leave cloudy extract undisturbed. Crystals of monomescaline citrate should begin to appear after a few hours, and take a few days to complete crash out (at least 3 days of wait is recommended). Crystals can have different shapes and can stick to the wall (sometimes looking transparent and difficult to see).
Fast crystalization option: Add up to 15 grams of citric acid powder granules into extract. Use a magnetic stirrer or aggressive shaking to quickly dissolve the citric acid and speed up crystallization. This produces a fast crystalization and minimizes crystals that are stuck to the wall. A stirring vortex will go from visible, to not visible as clouds form, to visible again as mescaline citrate precipitates. If shaking, clouds form and disappear within minutes, leaving product behind. Crystals will be very small with this approach and look like a powder instead of crystals, but the vast majority of them will still be caught by a filter in the next step. They are denser and easier to pack in capsules, but not as pretty to look at.
If no crystals form and goo appears, see FAQ below. Instances of goo have been greatly reduced after the addition of the fridge settling step. If goo results even after settling in the fridge for a known active cactus (>0.3% mescaline expected), please report this on the DMT nexus.
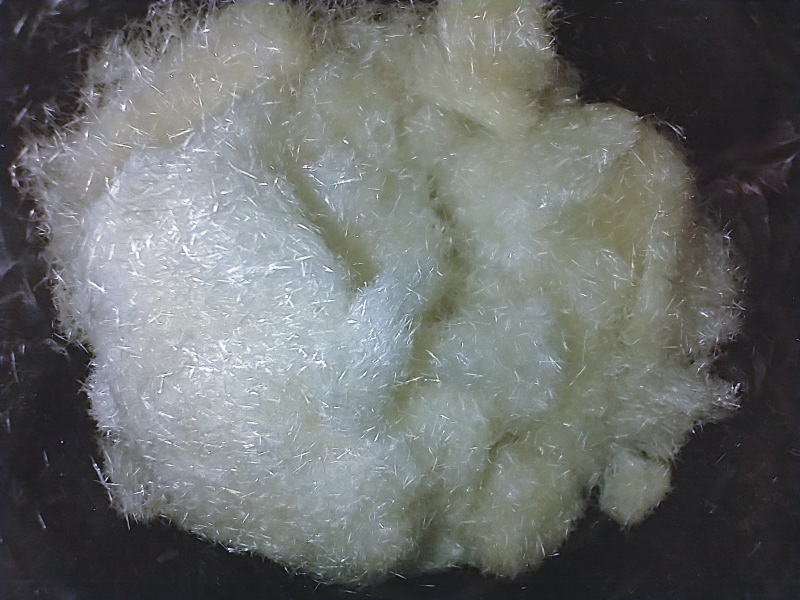
Collect 💖
Swirl ethyl acetate to knock crystals loose. Crystals that cling to the wall can sometimes be dislodged by shaking or with a knife/spoon. Send solvent trough a double coffee filter to catch loose crystals. Rinse any crystals remaining on jar walls with fresh ethyl acetate and send wash through filter to also wash the crystals there and collect any new crystals that are dislodged (repeat ~2-3x until off color is mostly removed).
After the solvent washes are fully dry in the filter and jar:
- Collect crystals in the filter by simply sliding them off. Rubbing the inside of the filter against itself with the palms of the hands can help loosen the last bit of crystals. Do not introduce water into the filter since it could pick up plant matter left behind by ethyl acetate in the filter fibers (or if this is done, keep this water separate from the rest of the product in case it has plant matter).
- Collect crystals that remain stuck on the jar walls (if any) by dissolving them in warm water, evaporating water in a shallow dish, and scraping. When deciding if it is necessary to do this step keep in mind that sometimes the wall crystals form a transparent layer difficult to see.
Combine with the collected crystals to obtain the final product (Fig. 6). Reagent results for the product from this TEK have been published by _Trip_[14].
Yield depends on the cactus and is usually between 0.2% to 2% with ~1.2% being common[15]. However, yields up to 5% and even 9% have been reported (at these extremely high yields verifying the extract is acidic and all the mescaline has been salted is recommended - 5g of citric acid salting capacity is limited to ~10% yield). The product is monomescaline citrate salt, (MesH)H2Cit (see appendix), which is ~61% as strong as MesHCl. Approximate oral dosage recommendations for mescaline [16] roughly converted to monomescaline citrate based on molecular weight and subjective user experience:
- Threshold: 100 - 200 mg
- Light: 200 - 350 mg
- Common: 350 - 700 mg
- Strong: 700 - 1400 mg
- Heavy: 1400 mg+
Attempting to smoke the product is not recommended as potentially unwanted compounds can form [17].
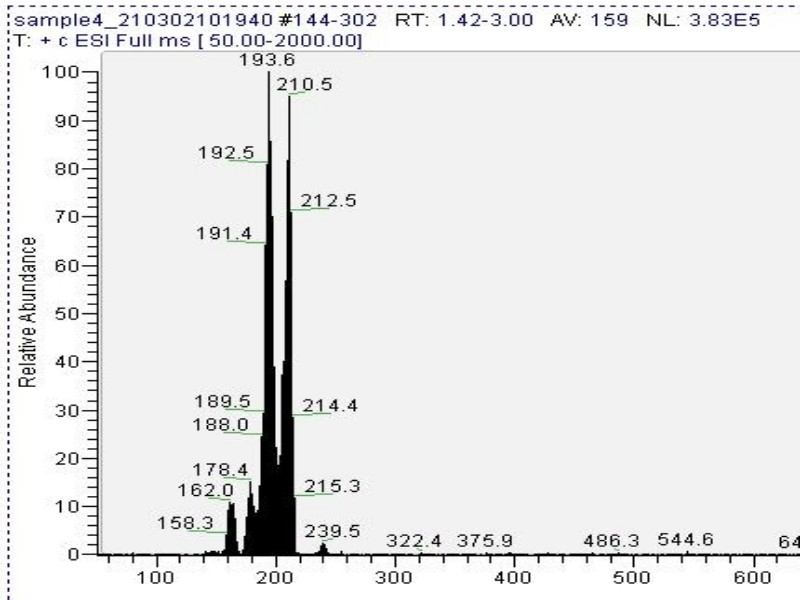
Mass spectrometry (MS) results from solaris analytical[18] indicate the product is very clean mescaline (Fig. 7) in one example where pachanoi was used. It is unknown if cacti with different starting starting alkaloid profiles would give the same result, and more data is needed to make that claim.
Reuse 💚
Reusing solvents is encouraged[19] at the DMT nexus.
Wash spent extract with ~10% sodium carbonate water solution. About 1/3 of the solvent volume is enough for neutralization. Shake vigorously (emulsions do not form). CO2 bubbles may be visible during citric acid neutralization. Keep an eye on any bubbles and release any pressure buildup regularly. Neutralization can be verified with pH paper. Rest washed solution until clear (up to a day or more).
Remove the water layer with a pipette or separatory funnel and filter. Optionally, freeze the solvent and remove the ice slush that forms with a thin mesh metal strainer.
Product from solvent reused multiple times can form flakes along with the usual needles. It can also form smaller crystals, and the product can look like a powder. No difference in effects has been noted between crystal forms; needles, flakes, and powder. However, these are subjective effect observations and not analytically verified at this time.
Frequently Asked Questions ❓
Q: Does increasing the basing time increase the yield?
A: No. Shroombee has tested 15 minute, 24 hour, and 72 hour basing times and there was no difference in yield. Other process variables were 8 minutes incorporating milky water with cactus, 6x3 minute pulls, and 15 mg/gram citric acid added with the fast crystallization method. Loveall has confirmed in his experiments that 10 minute and 24 hour basing times produce the same yield. So we assume that any basing time from 10 minutes through 72 hours will produce the same yield. See a detailed explanation in this post.[20]
Q: I got a en emulsion while pulling, what do I do?
A:If the paste and solvent form an emulsion, it is likely that the paste was too watery. Add lime and dry magnesium sulfate until the paste becomes chunky again and solvent is released. Keep the lime to magnesium sulfate ratio above 1 to ensure paste remains alkaline[21]. Next time, use less water to make the paste.
Q: I have a thick bottom layer in my pulling jar. What is it and what do I do?
A: It is a water layer. This can happen if you squeeze the French press and/or the initial paste is too whet. Separate the layers using a pippete or separators funnel and continue the TEK with the to p ethyl acetate layer. The water layer should also be pulled with theyl actuate incase some mescaline was partitioned into it. The TEK can be continued with these pulls at the fridge rest step.
Q: What’s the difference between the two crystalization methods?
A: In general, adding more citric acid and aggressively stirring or shaking will:
- Force crystals to form faster
- Form smaller and denser crystals less likely to stick to the jar walls
- Cause a negligible amount of tiny crystals to drop through the coffee filter.
Q: What is the upper limit of citric acid that can be added to the extract?
A: The solubility of citric acid monohydrate in ethyl acetate is over 50 mg per gram of ethyl acetate[22]. Note that plant matter or other unwanted extraction products (such as water) may affect the solubility. Stay well under 50 mg/gram limit and do not chemichally dry the extract to ensure no undissolved citric acid is mixed in with the mescaline citrate. Under mostly anhydrous conditions the solubility of anhydrous citric acid in ethyl acetate has been measured as low as 10mg/g [23].
Q: After adding citric acid, I saw clouds followed by precipitation, but the precipitate reminds me of citric acid. How do I know a mescaline salt is precipitating and not citric acid?
A: Citric acid does not precipitate and stays in solution because it is well bellow its solubility limit (50mg/g) in the TEK. The white particles that form from the clouds are salts and not citric acid. A thorough swirl may be needed at the end to make sure all the added citric acid has dissolved. Once it has dissolved it will not come out of solution as citric acid.
Q: After adding citric acid, nothing precipitated, what gives?
A: Check the jar walls, a transparent product may have precipitated there (e.g. this has been reported for whole bridgessi[24]). If product bid not present on walls as a transparent film, bring up the citric acid concentration up to 20mg/g or more (stay below 40mg/g due to solubility concerns) and wait a few days. Keep in mind that if your cactus is not active, no mescaline citrate will form. If all else fails, pulling the salted extract with water, evaporating, and washing citric acid with fresh ethyl acetate should leave behind a residue containing any mescaline in the cactus (dose will be less accurate and can be made proportional to starting cactus amount). The crystallization temperature should not be colder than the previous extraction settling temperature. Water layer formation is sensitive to temperature, and lower temperatures can producte a new water layer.
Q: After adding citric acid, goo/oil precipitated instead of crystals, what gives?
This is the most common issue people encouncer. All the causes are unknown, but there are some theories based loosely on experimental observations:
- Poor TEK execution: This is believed to be the most common issue in general. Make sure the TEK instructions were followed, in particular: well mixed paste, short pull times, clean extract free of debris (including water droplets), citric acid is in range, extract was rested in the fridge for 24h, that any water droplets where left behind when decanting, that the xtalization temperature was higher than the rest temperature, etc. It is worth repeating that, before adding citric acid, rest the extract at a temperature colder than the planned xtalization temperature and ensure any water droplets stay behind when decanting.
- Cactus powder: Some cacti or parts of some cacti may cause goo. orchidist[25] showed that in one case, use of fumaric acid resulted in crystals, while citric acid resulted in goo.
- Xtalization dynamics: A separate water phase presenting as a visible layer on the bottom of the solution with salt/acid could separate before xtals form, resulting in an oily mixture of citric acid and mescaline citrate. One proposed, but not yet tested solution to this problem is to create a saturated solution of citric acid in ethyl acetate, and add that dropwise into the extract, instead of direct addition of solid citric acid crystals. Another suggestion is to chemichally dry the ehtyl acetate before salting. An effective and easy to use drying agent example is K2CO3. Drying the solvent may also be a "guardrail" for people learning how to execute the TEK.
- Rest/decanting and crystalization temperatures: Water solubility in ethyl acetate decreases with temperarure. If the crystalization temperature is lower than the rest/decanting temperature water may crash from solution causing goo.
If you see or overcome goo, please report it on the forum. You could help solve this issue that some workers come across.
Q: I recovered the goo/oil precipitate instead of crystals, what do I do?
A: In one example from Cheelin the goo was 65% mescaline citrate[26]. There are four main options. (1) Do an A/B extraction on the goo, (2) If a TEK execution is suspect, add the goo to cactus paste and do the TEK properly, increasing citric acid by the amount of expected mescaline present in the goo, (3) decant off the solvent and cover the goo in fresh EA, it has been observed that crystals can grow out of the goo after a few days sitting in fresh solvent and stirring can help the process move along[27] if crystal formation stops and there is still goo left, discard the solvent and add more (4) if goo forms repeatedly, retry the TEK using fumaric acid instead of citric acid (fumaric may be more robust at forming xtals)
Q: How quickly can the extraction process be done?
A: With experience, and by skipping the fridge rest step (xtalizaton temperature should be warmer than extraction temperature) it is possible to go go from raw cactus powder to dry crystals in under an hour by choosing the fast crystalization method shaking the salted extract vigorously. Current documented world record is 48 minutes to go from cactus powder to dry mescaline crystals ready to use.[28]. However, there is an increased risk of obtain goo without the fridge rest step. The express process is not recommended for newcomers.
Q: The cactus paste turned to goo in ethyl acetate very quickly and I couldn't finish the timed pulls with a sandy consistency. How can I give myself more time?
A: Try using less water next time amd keep resting powder time to 10 minutes. Excess water can accelerate 'goofication' of the cactus paste and decrease yield as it is harder to extract from goo due to poor solvent penetration. Not all cactus powder is the same, so a 'feel' is needed to achieve the right paste consistency before pulling. The initial water ammount is only a starting guideline, the consistency is the goal and water amount should be adjusted as needed. Higher summer temperature pulls in the summer can also accelerate the paste to goo change.
Appendix: Development Notes 🔬
Paste 🌵
No improvements were seen with longer basing time, paste oven drying, or increasing the ionic strength with CaCl2. Microwave treatment or boiling water resulted in a small yield loss.
Paste made with sodium carbonate saturated water congeals over time and requires long solvent soaks which are darker and don't crystallize to large loose crystals (small sticky crystals were obtained).
Use of lime and boiling water causes the saponification of chlorophyll over time [29]:
Chlorophyll is soluble in Ethyl Acetate, but Chlorophyllin and Phytol are not[30]. Saponification in hot water gives an extract with less plant matter and lighter color, however yields where slightly lower with this approach.
Extract 👨🏾🔬
Tests with longer/warmer pulls resulted in darker extract, smaller crystals, solvent paste absorption, congealing of paste, and no yield benefit.
Chemically drying the extract with anhydrous CaCl2 had no benefits, while drying with MgSO4 was problematic. However, depending on the worker and techniques used, a chemical dry with CaCl2 pellets (available commercially as de-icer) could reduce water content in the solvent and possibly make crystallization easier. Washing soda (when sold as Na2CO3 in monohydrate form, or when making the anhydrous form from baking soda with an oven) may also dry the extract and be beneficial in such cases (but that is currently an assumption based on other lab techniques).
Crystalize ✨
During crystallization, excess citric acid (H3Cit) reacts with free base mescaline (Mes) to form to form the monomescaline citrate salt (MesH)H2Cit:
Monomescaline citrate salt's strength relative to mescaline HCl is 61% (assuming no hydrate formation)[31]. By not using excess citric acid, different salt forms can be precipitated[32], but that process is more complex than the simpler excess citric acid approach.
There is a lot room for excess citric acid in solution since its solubility is 50mg/g in ethyl acetate. In extracts with crystallization issues, adding more citric acid can help force precipitation: in one example with whole cactus powder 20mg/g was used [33].
Several factors can make crystals smaller: Reusing ethyl acetate, longer/warmer pulls, higher citric acid concentration, mechanical agitation, and other potential variables. Small crystals can look like a fine powder. Potency does not seem affected by the crystallization appearance, and a powdery precipitate is not a problem unless it becomes difficult to decant/filter.
After the initial crystallization, adding more citric acid and/or moving the extract to the refrigerator does not result in any more precipitation. Moving the extract to the freezer produced ice crystals.
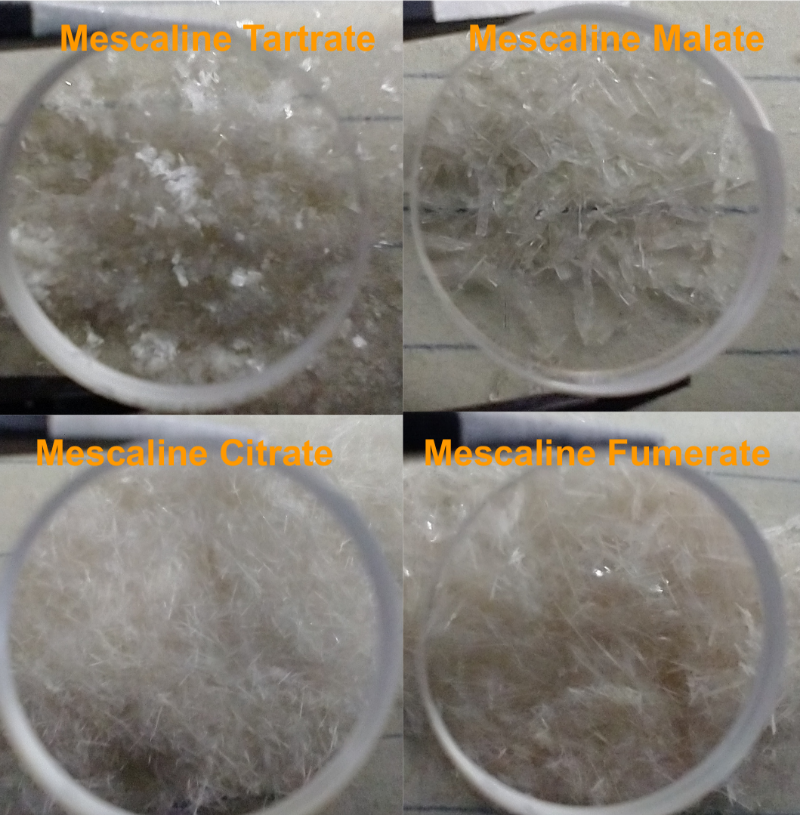
Other dry organic acids have been tested[34],[35]. Fumaric and tartaric crystalized well as monomescaline and could be a substitute for citric. Malic also crystallized but took longer to do so, and a crude mass measurement indicated the dimescaline form. See Fig. 8 for resulting citrate, tartrate, fumarate, and malate crystals. Succinic also crystalized from a chemichally dried extract (without drying xtals did not form[36]) as the monomescaline form (see Fig. 9). Ascorbic, and benzoic did not crystalize well. Other organic acids (lactic, oxalic, etc) have not been tested yet at the time of this writing. For the organic acids that crystalized, Mescaline HCl equivalent is (assuming no hydrate formation):
- Monomescaline Citrate: 61%
- Monomescaline Tartrate: 69%
- Monomescaline Fumarate or Succinate: 75%
- Dimescaline Malate: 89%
For a comprehensive reference of mescaline salt weight conversion see orchidist's calculator[37].
10% sulfuric acid was tested and while some crystals formed, a separate liquid layer also appeared making the process not practical. HCl has not been tested as it may break down ethyl acetate.
Collect 💖
Washing crystals in a filter appears to wick away plant colors and is superior to decanting if the goal is white xtals.
The washed crystals in the filter can be dissolved in warm water after collecting them
(do not "pull" filter with water as that can be a source of plant matter) along with any wall crystals. This will give then final product a uniform appearance with large needles forming during slow water evaporation.
Reuse 💚
Dark extract can be cleared up with activated carbon (also called activated charcoal). Use dustless pellets (typically rinsed with water and dried before use).
While it is easier to work with a solvent that is not dark, a quantifiably benefit of using activated charcoal to decolor the used solvent is not clear (pun intended). The environmental benefit of regenerating a colorless solvent is in question since ethyl acetate is easy to produce and activated charcoal requires resources to manufacture.
References 🗝️
- ↑ Ethyl acetate safety[1]
- ↑ Citric Acid Safety[2]
- ↑ Cheelin's beginner recommendation[3]
- ↑ Cactus growing guide[4]
- ↑ Dark storage data[5]
- ↑ Paper with vertical signal[6]
- ↑ Result for different cactus parts[7]
- ↑ Minimum water paste[8]
- ↑ Excessive water paste[9]
- ↑ Cheelin paste making skews[10]
- ↑ Drier paste example[11]
- ↑ 69ron's Limonene TEK[12]
- ↑ Second set of pulls [13]
- ↑ Reagent results[14]
- ↑ Cactus analysis thread[15]
- ↑ Mescaline Oral Dosage[16]
- ↑ Citric acid heat degradation[17]
- ↑ Solaris analytical service[18]
- ↑ On reusing non polar solvent[19]
- ↑ Basing time tests results[20]
- ↑ Lime and magnesium sulfate ratio vs pH[21]
- ↑ Citric acid solubility[22]
- ↑ Anhydrous citric acid solubility test[23]
- ↑ Whole bridgessi precipitate on jar walls [24]
- ↑ orchidist fumaric goo fix[25]
- ↑ Goo conversion to crystals[26]
- ↑ Crystallization from oil after solvent washing[27]
- ↑ Plant to crystal record [28]
- ↑ Hot water saponification with lime[29]
- ↑ Phytol not present in Ethyl Acetate plant extract[30]
- ↑ Mescaline citrate vs HCl[31]
- ↑ Trimescaline citrate candidate[32]
- ↑ Ethyl acetate approach[33]
- ↑ Organic acid tests[34]
- ↑ Succinic test[35]
- ↑ Wet solvent succinic salting[36]
- ↑ Orchidist's mescaline salt calculator[37]