Difference between revisions of "Dissociative"
Mindlusion (Talk | contribs) (→Others) |
Mindlusion (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
2-EMSB | 2-EMSB | ||
| + | |||
2-MMSB | 2-MMSB | ||
| + | |||
Alazocine | Alazocine | ||
| + | |||
Bremazocine | Bremazocine | ||
| + | |||
Butorphanol | Butorphanol | ||
| + | |||
Cyclazocine | Cyclazocine | ||
| + | |||
Cyprenorphine | Cyprenorphine | ||
| + | |||
Dezocine | Dezocine | ||
| + | |||
Enadoline | Enadoline | ||
| + | |||
Herkinorin | Herkinorin | ||
| + | |||
HZ-2 | HZ-2 | ||
| + | |||
Ibogaine [[Iboga]] | Ibogaine [[Iboga]] | ||
| + | |||
Ketazocine | Ketazocine | ||
| + | |||
Metazocine | Metazocine | ||
| + | |||
Nalbuphine | Nalbuphine | ||
| + | |||
Nalfurafine | Nalfurafine | ||
| + | |||
Nalorphine | Nalorphine | ||
| + | |||
Noribogaine | Noribogaine | ||
| + | |||
Phenazocine | Phenazocine | ||
| + | |||
Pentazocine | Pentazocine | ||
| + | |||
Salvinorin A (found in Salvia divinorum)[[Salvia]] | Salvinorin A (found in Salvia divinorum)[[Salvia]] | ||
| + | |||
Spiradoline | Spiradoline | ||
| + | |||
Tifluadom | Tifluadom | ||
| + | |||
U-50488 | U-50488 | ||
Revision as of 22:33, 9 December 2012
Contents
What is it?
Dissociatives are a class of hallucinogen, which distort perceptions of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment - dissociation - from the environment and self. This is done through reducing or blocking signals to the conscious mind from other parts of the brain. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include sensory deprivation, dissociation, hallucinations, and dream-like states or trances. Some, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria. Many dissociatives have general depressant effects and can produce sedation, respiratory depression[citation needed], analgesia, anesthesia, and ataxia, as well as cognitive and memory impairment and amnesia.
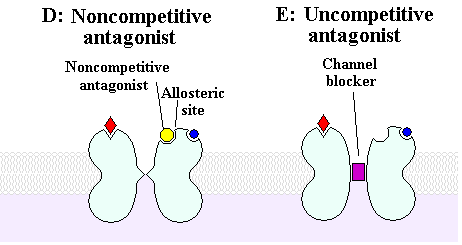
The primary area of activation for dissociatives is blockade of the Ca++ ion in the NDMA receptor. Also known as uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists.
Noncompetitive antagonists result in the same effect on the receptor, but achieve it in a slightly different way.
Dissociatives can also be classified by molecular structure. The most well known dissociatives used recreationally and in medicine are known as arylcyclohexylamines 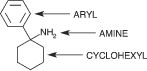
Another well known dissociative Dextromethorphan (DXM) has a very opioid like structure. It is classified as a morphinan
NMDA receptor antagonists
Adamantanes
Amantadine
Memantine
Rimantadine
Arylcyclohexylamines
Dieticyclidine
Esketamine
Eticyclidine
Gacyclidine
Metaphit
Neramexane
Phenylhexylcyclopyrrolidine
Rolicyclidine
Tenocyclidine
Tiletamine
Methoxydine (4-MeO-PCP)
Morphinans
Dextromethorphan
Dextrorphan
Methorphan
Morphanol
Others
2-MDP
8A-PDHQ
Aptiganel
Dexoxadrol
Diethyl ether
Dizocilpine
Etoxadrol
Midafotel
NEFA
Nitrous oxide
Noribogaine
Perzinfotel
Remacemide
Selfotel
Xenon
κ-opioid agonists
kappa-opioid agonists are an entirely different type of drug that can have dissociative effects.
Very little is known about this receptor and its effects on the body.
2-EMSB
2-MMSB
Alazocine
Bremazocine
Butorphanol
Cyclazocine
Cyprenorphine
Dezocine
Enadoline
Herkinorin
HZ-2
Ibogaine Iboga
Ketazocine
Metazocine
Nalbuphine
Nalfurafine
Nalorphine
Noribogaine
Phenazocine
Pentazocine
Salvinorin A (found in Salvia divinorum)Salvia
Spiradoline
Tifluadom
U-50488