Difference between revisions of "BW's Bufotenine Dry Tek"
(→Base) |
(→Base) |
||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
| − | <font color=" | + | <font color="green"> Alternatively (Experimental still-but works well): |
One can do a few pulls with Ethyl Acetate and then place it in a small glass dish with xylene 1:3 ratio (amount still being confirmed). And start to evaporate it. | One can do a few pulls with Ethyl Acetate and then place it in a small glass dish with xylene 1:3 ratio (amount still being confirmed). And start to evaporate it. | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
Note: The alternative method is safer than boiling xylene and may pull more efficiently than EA/Naphtha mix. Note MS-LC data on this method has not be compiled. | Note: The alternative method is safer than boiling xylene and may pull more efficiently than EA/Naphtha mix. Note MS-LC data on this method has not be compiled. | ||
| − | <font color="white"> | + | <font color="white"> |
== Crash/ Filter TEK Complete == | == Crash/ Filter TEK Complete == | ||
Revision as of 02:44, 20 June 2022
Contents
Introduction
This Tek was created by Brennendes Wasser.
Thanks to everyone who has contributed or helped experiment to aid in refining/ improving this process:
This Tek is more or less completed. Lab and test results have been confirmed and are very promising. Feel free to contribute. More photo's to follow soon.
Please take your time with your first extraction, although this is an easy Tek you don't want to rush it and make a mistake.
Forum Link[1]
Safety
Review Acetone [1] ethyl acetate[2] and citric acid[3] safety information. Verify solvent MSDS, plastic compatibility, and clean evaporation.
This TEK is food safe if food grade materials are used.
Following this advice does not guarantee safety. It is up to each adult individual to make their own personal decisions.
Consumables
- 100g of anadenanthera peregrina seeds or Anadenanthera colubrina
- 25g Sodium Carboante/ additional 1.85g for later
- 150ml water (spray bottle)
- 25ml Water for later
- 450ml Naphtha
- 450ml Acetone or alternatively 450 Ethyl Acetate
- 3g of citric acid or furmaric acid
- Sodium Carbonate
- Jars
- Coffee filter, lab filter or cotton balls (with funnel)
- 3x 100ml 1:3 Ethyl Acetate:Naphtha
Equipment
- Blender
- Kitchen scale
- Coffee filters, support basket, and funnel Or lab filter and vacuum pump.
- Glass jars with lids
- Fridge
- Milligram scale
- Spray Bottle
- Fry Pan and stove
Detailed Process
Heat Seeds
-Place seeds on minimal heat on fry pan, bring it up to heat until they start popping, lower the heat and turn it off once the seeds have stopped popping.
Powder
-Get 100g seeds and 25g of sodium carbonate grind them with a glass blender into a powder. (Check weight on scales and take note).
Add water
-Add 150ml of water by spraying the seeds/ sodium carbonate mix with a spray bottle. Do this until the paste becomes doughy. Mix well.
Dry Paste
-Dry the paste with a fan and optionally low heat.
Defatting
When dry (check by comparing weight previously noted), defat with 3 x 150 ml boiling Naphtha, then decant.
Pull
Extract and pull with 3 x 150 ml DRY Acetone, filter. Alternatively Ethyl Acetate can be used and may be a better option.
Boiling the solvent should increase solubility so a hot water bath is recommended. You should be using glass jars, ensure glass containers have lids to minimize evaporation of solvent.
Salting
-Add Fumaric acid or citric acid at least 3 g, slowly, then stir vigorously. Let it rest for 12 h, then decant and watch if the Acetone precipitates more, also check if adding more FASA causes further clouding and let the Alkaloid-Fumarate crystals dry off any remaining Acetone. Note using citric acid may negate the need to wait 12h.
Decant
-Decant Acetone (or Ethyl Acetate if using that)
Dissolve Goo
- Dissolve the Alkaloid-Fumarate crystals (or citrate) in 25 ml hot water. Slowly pour another a solution of 1,85 g Na2CO3 (0,5:1 Na2CO3:Alkaloid-Fumarates) in 25 ml water. This will form impure freebase bufotenine (either as a blob or crystal if you defatted adequately enough). Decant water.
If the ratio's are off and a blob or crystals do not form you can evaporate the water with the freebase and proceed to next step-Note if you evap results will be more impure.
Base
-Extract the brown precipitating freebase alkaloid blob with 100 ml portions of 1:3 Ethyl Acetate:Naphtha. Do this until the freebase blob does not shrink anymore. Black powder will remain. Dont combine the pulls, but put them in the fridge separately. The freebase blob may solidify to a ball upon stirring within this process. Break it apart, if it becomes hard, to speed up extraction. If it remains a goo, still just proceed extracting. Place decanted solvent mix from each pull in the fridge for fridge-frecipitation.
Alternatively (Experimental still-but works well): One can do a few pulls with Ethyl Acetate and then place it in a small glass dish with xylene 1:3 ratio (amount still being confirmed). And start to evaporate it.
So the idea here is to pull the freebase bufotenine with EA (EA may pick up some impurities) and place it with xylene. Bufotenine wont dissolve in room temp xylene (or even heated bufotenine <139 celcius).
Since EA boils at 70 degrees and xylene at 140 degrees celcius, the idea is to let half the EA/ Xylene mix evaporate. At this point majority if not all the EA should have evaporated out leaving behind xylene only. Xylene won't hold bufotenine freebase so it crashes out as a white residue/ crystal. The majority of the impurities stay in the xylene as it is quite a large spectrum solvent. Once the bufotenine crashes out one can decant the xylene and dry the dish for bufo crystals. Cystals will be white but as you scrape can become slightly brown (it sometime stays white). The browning that can occur is believed to do with xylene and EA ratios as well as how well the de-fatting was performed.
Note: The alternative method is safer than boiling xylene and may pull more efficiently than EA/Naphtha mix. Note MS-LC data on this method has not be compiled.
Crash/ Filter TEK Complete
Collect your precipitated freebase Bufotenine (decant solvent). The solvent mix itself will still contain Bufotenine. Evaporate the rest to get all the remaining Bufotenine with a slightly lower purity.
Bufotenine yield: 1-3 % to seed weight This is very pure bufotenine 96%+ purity/
Bufotenin recrystalization (optional)
Bufotenin recrystalization for 99.99% purity
The best solvent to form crystaline Bufotenin is Xylene. Actually it would be way too unpolar to ever dissolve Bufotenine.
As you can heat Xylene above the melting point of Bufotenin, the latter suddenly becomes soluble while liquifying, while the more polar 2 % dark impurities will remain undissolved. This way you can create 100 % purity Bufotenin from 98 % purity Bufotenin retrieved by the former mixture. See the following :
1 = Break up crude Bufotenine chunks (if even solid) 2 = Heat in Xylene > 140 °C until only brown powder is leftover (see solubility table how much to use) 3 = transfer surfactant Xylene into new Jar and let it sit until surfactant is clear 4 = dry crystaline Bufotenine - much faster if you wash it with low-boiling Naphtha
Note the fumes are highly dangerous for your health and combustible. You should use the required PPE and have very good ventilation (as in outdoors).
Lab Analysis
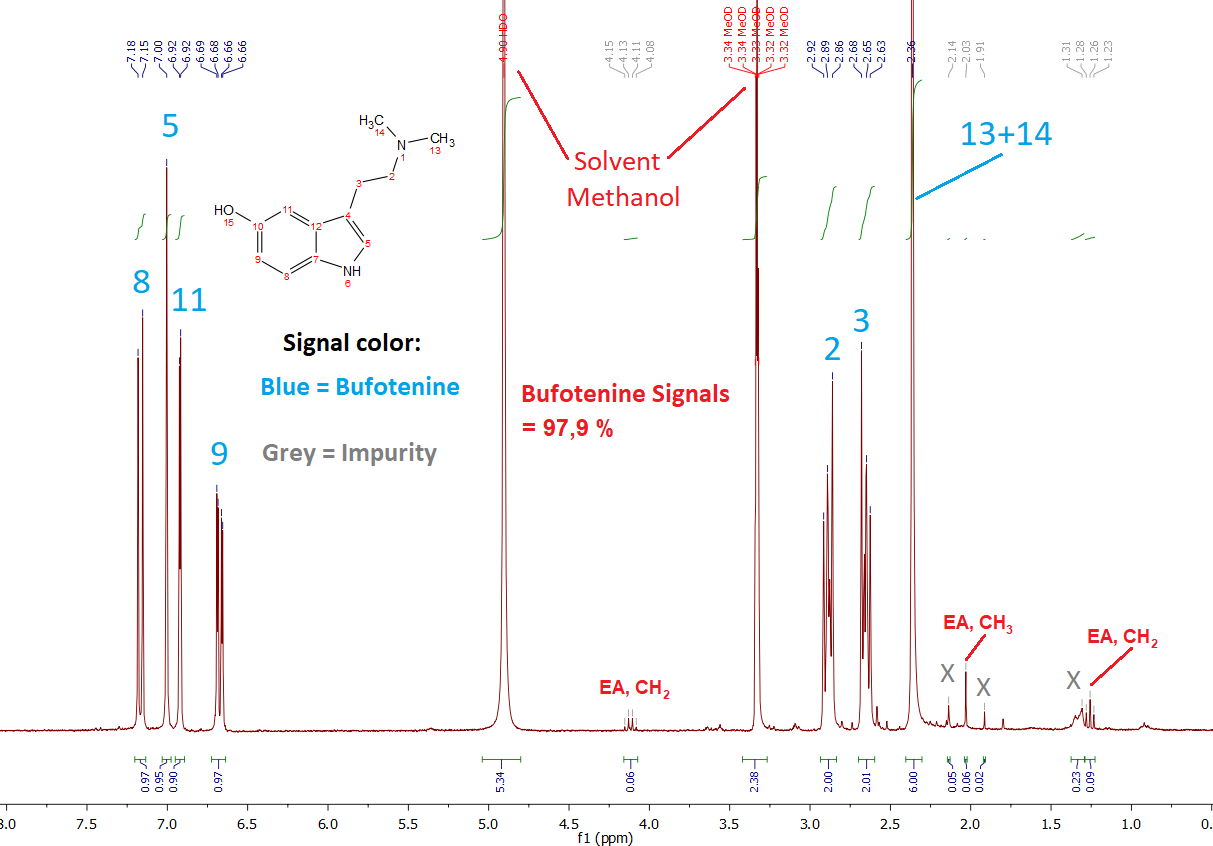
Not much to say, all the signals are there (and the big Methyl signal is indeed like DMT of course, not like the wrong simulation). As it is measured in MeOD you can see 2 big solvent peaks. These are marked red, so you can just ignore them. Also there are traces of EA present. The only unidentified peaks are marked gray and these are just traces. In total their integral is just 0,30 and the peak fraction of Bufotenine derived from this number is 97,87 %. Now this does not automatically translate into a purity of 97,87 %, but I may say that still the purity is somewhere between 96 - 99 %.
Further investigations
-Sodium Carbonate is the only base you should use do not use calcium hydroxide or caustic soda/lye.
-Drying the product in the microwave has been tested to a limited compacity and should work.
-Furmaric or citric acid should work and have been successfully tested.
-Ethyl acetate instead of acetone for the initial pull should work.
-Warming the EA or acetone for the first pull should increase yield.
Reuse
Reusing solvents is encouraged[4] at the DMT nexus.
Wash spent extract with sodium carbonate saturated water (35% by weight). About 1/5 of the solvent volume as saturated water is enough. Shake vigorously (emulsions do not form). CO2 bubbles may be visible during citric acid neutralization. Keep an eye on any bubbles and release any pressure buildup regularly. Neutralization can be optionally verified with pH paper. Rest washed solution until clear (up to a day or more).
Remove the water layer with a pipette or separatory funnel. Freezing the solvent and filtering the ice slush that forms with a metal strainer is also an option. Finally, decant off any excess solid sodium carbonate/citrate. CaCl2 (sold as deicer, calcium hardener for pools and sometimes is the only ingredient in moisture absorbers tubs) can be used to ensure there is no water still left in the EA.
References
Ethyl Acetate Safety[2] Citric Acid Safety [3] Reusing Solvent [4]
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found