Difference between revisions of "CIELO"
(→Paste 🟢) |
(→Extract 🧑🏾🔬) |
||
| (439 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = Introduction | + | = Introduction 🔆= |
| − | + | ||
| + | '''CIELO''' stands for '''C'''rystals '''I'''n '''E'''thyl-acetate '''L'''azily '''O'''ver-the-counter. In this process, mescaline from cactus is precipitated in ethyl acetate as crystals (see Fig. 1). This technique (TEK) is specialized for cactus, simple, and avoids harsh chemicals. With less than an hour of labor, very pure mescaline can be extracted. However, the process needs to be followed closely to ensure good results. | ||
| − | |||
| + | '''Please''' grow your own cacti <ref name=seeds>Sowing Cactus Seeds[https://misplant.net/SeedGrow.html]</ref>, <ref name=guide>Cactus growing guide (PDF)[https://trichocereus.net/wp-content/uploads/Trichocereus%20Culture%20First%20Published%20Edition%20Cactus%20Cultivation.pdf]</ref>. San Pedro cacti in Peru (Echinopsis pachanoi and Echinopsis peruviana) are being over-harvested in the wild in a non sustainable way <ref>Huachuma Collective Talk[https://youtu.be/xKWHJFzAFAk]</ref>, <ref>Huachuma Collective statement 2023 (PDF)[https://www.huachumacollective.org/_files/ugd/7cb3ef_bff49300ccbd4af0a821d0cec05631e4.pdf]</ref>. '''Never''' purchase dry cactus powder. Online powders are normally of poor quality and their purchase funds endangered plant harvest and destruction, with less of 1/4 of wild habitats being well stocked as of 2024<ref>Huachuma Collective statement 2024 (PDF)[https://www.huachumacollective.org/_files/ugd/7cb3ef_396ebb81f67740ba869724937523065c.pdf]</ref>. Obtain and grow live seeds, cuttings, or rooted plants. With patience and love, we can all extract the essence of the plant sustainably 🌵💚 | ||
| − | |||
| + | This process was developed in a collaborative open source effort at the DMT nexus website<ref>DMT nexus website[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/]</ref> and refined with community input from the subreddit r/mescaline<ref>Reddit community [https://www.reddit.com/r/mescaline]</ref>. No parts of this procedure may be patented or used for profit. The information presented here and any modifications to it may be distributed freely with a reference to this source and with love. | ||
| − | |||
| + | Thanks to everyone who contributed to this process: someblackguy, benzyme, shroombee, Metta-Morpheus, downwardsfromzero, Kash, grollum, Mindlusion, Doubledog, Dreamer042, merkin, _Trip_, Cheelin, Highlightprotein, Loveall, orchidist, BlackRose, endlessness, Madhattress, reptivity, wowitsbabygirl, roundtripfarm, bobcollege, starbob, aizoaceous, and many others. | ||
| − | [[File:IMG 20211220 095906809 copy 800x600.jpg|center]]<center>''Fig. 1: | + | |
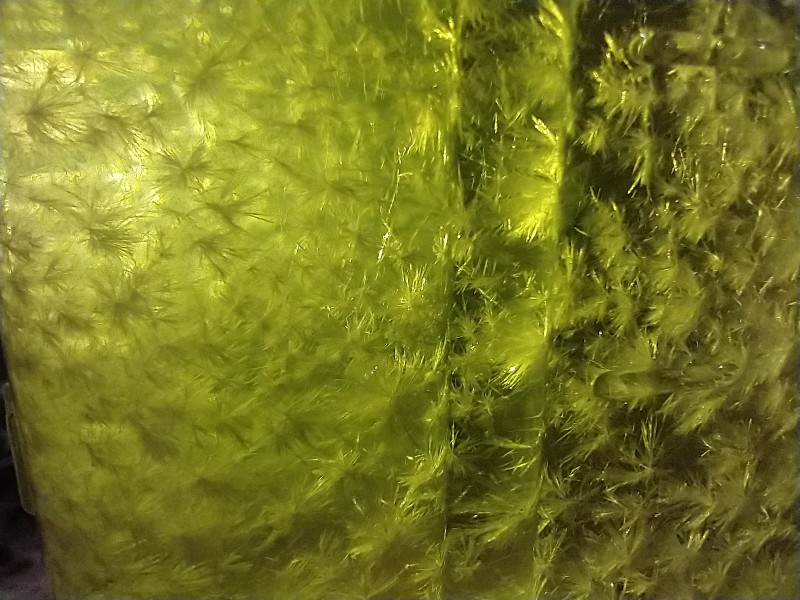
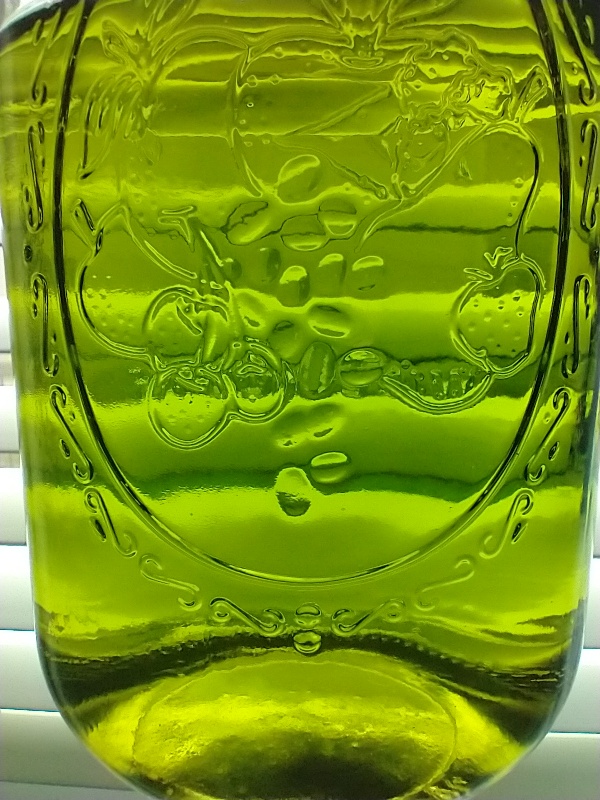
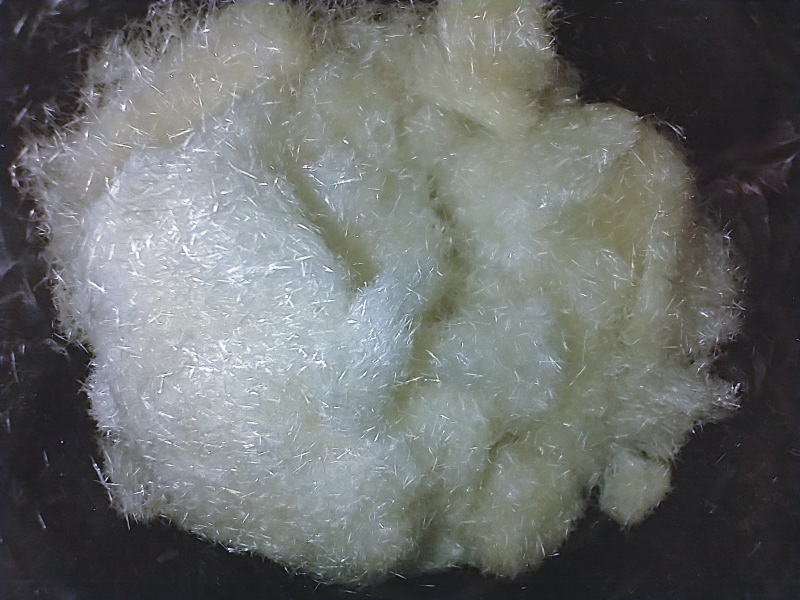
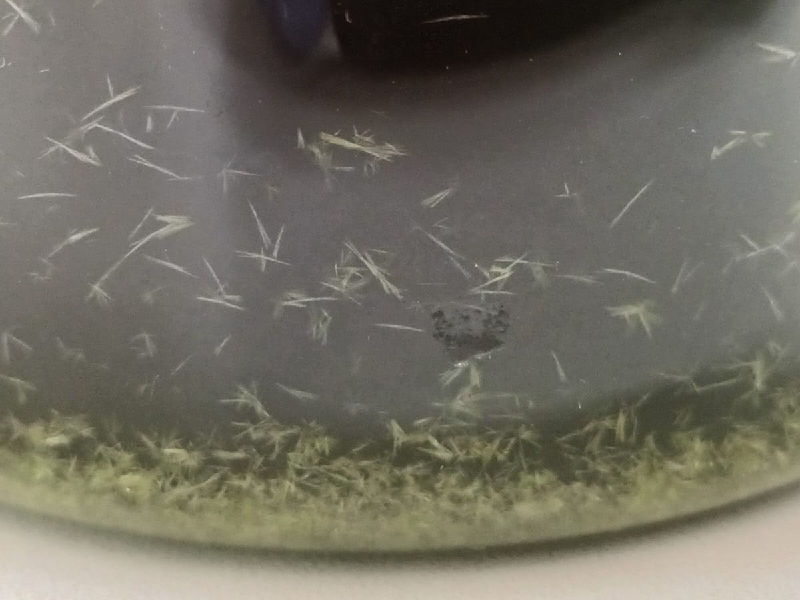
| + | [[File:IMG 20211220 095906809 copy 800x600.jpg|center]]<center>''Fig. 1: Mescaline crystals in ethyl acetate. Nubes del cielo transformadas en estrellas. General appearance can vary depending on the crystallization option used. Credit: Loveall.</center> | ||
= Safety ⛑️= | = Safety ⛑️= | ||
| − | Review ethyl acetate<ref>Ethyl acetate safety[https://www.msdsonline.com/2015/04/10/ethyl-acetate-a-sweet-smelling-safety-hazard/#:~:text=Ethyl%20acetate%20is%20highly%20flammable,with%20the%20eyes%20or%20skin.]</ref> and citric acid<ref>Citric Acid Safety[https://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/Citric_Acid_Safety#Process_.F0.9F.A5.9E]</ref> safety information. Verify solvent MSDS, | + | Review ethyl acetate<ref>Ethyl acetate safety[https://www.msdsonline.com/2015/04/10/ethyl-acetate-a-sweet-smelling-safety-hazard/#:~:text=Ethyl%20acetate%20is%20highly%20flammable,with%20the%20eyes%20or%20skin.]</ref> and fumaric or citric acid<ref>Citric Acid Safety[https://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/Citric_Acid_Safety#Process_.F0.9F.A5.9E]</ref> safety information. Verify solvent MSDS, material compatibility, and clean evaporation. |
| − | This TEK is food safe if food grade materials are used. Use food grade citric acid since some of it will be in the final product as mescaline citrate. | + | Ethyl acetate has a relatively low flash point of 38F. Ensure no open flames (e.g. cigarette, candle, gas heater) during extraction and work in a well ventilated area. It is a serious eye irritant. Safety googles are recommended. Flush with water for 15 minutes if any ethyl acetate gets in your eye. The information in this paragraph is not a substitute to reading the safety information mentioned above. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This TEK is food safe if food grade materials are used. Use food grade fumaric or citric acid since some of it will be in the final product as mescaline fumarate or citrate. | ||
Following this advice does not guarantee safety. It is up to each adult individual to make their own personal decisions. | Following this advice does not guarantee safety. It is up to each adult individual to make their own personal decisions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In one example, an individual used aluminum vessels to store salted (acidic) ethyl acetate <ref>Al vessel issue[https://www.reddit.com/r/mescaline/s/cCoNYvu0Up]</ref> and did not check for compatibility of aluminum with citric acid, causing the metal to corrode from the acid. | ||
=Materials🛒= | =Materials🛒= | ||
| Line 27: | Line 34: | ||
==Consumables👩🌾== | ==Consumables👩🌾== | ||
| − | *100g dry fine cactus powder | + | *100g dry fine cactus powder |
| − | * | + | *130g water + another 70g water as reserve |
| − | * | + | *25g Ca(OH)<sub>2</sub> (lime) |
| − | *1L | + | *1L (~1 qt) ethyl acetate (sometimes sold as "MEK substitute") |
| − | * | + | *'''Optional:''' pH testing strips<ref> Suitable pH strips [https://www.amazon.com/Strips-Professional-Indicator-Cosmetics-Acidity/dp/B0BNGTRCKP]</ref> |
| − | * | + | *3g of fumaric acid. |
| + | **Alternatively, 5g citric acid can be used (both anhydrous or monohydrate are suitable). However the fumaric acid is more robust and HIGHLY recommended for beginners due to multiple advantages, especially if working with low yielding cacti. | ||
| + | *'''For solvent reclaim:''' Washing soda (monohydrate Na2CO3 which is sold as arm and hammer super washing soda, or anhydrous). | ||
| − | '' | + | '''Important note''': Avoid combining PC cactus with citric acid. This combination has the risk of not precipitating anything if the yield is low (<0.15%). |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
==Equipment🏺== | ==Equipment🏺== | ||
| − | *Knife, paper bag, dehydrator, food processor, | + | *Knife, paper bag, dehydrator, food processor, coffee grinder (or grain mill), and flour sifter (to harvest plant, store cutting, and make cactus powder) |
| − | *Large bowl and spoon ( | + | *Gram scale (to measure ingredients) |
| − | *French press ( | + | *Large bowl and spoon (or gloves) for wet crumb mixing |
| − | + | *French press (stainless steel, 34 oz. or larger preferred) | |
| − | *Coffee filters, | + | *Coffee filters, filter basket, and funnel |
| − | *Quart | + | *Quart mason glass jars with lids (to collect and salt extract) |
*Milligram scale (to measure product) | *Milligram scale (to measure product) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Recommended Upgrades🪬 === | ||
| + | *Stand mixer with flat beater | ||
| + | *Magnetic stirrer | ||
[[File:IMG 20210608 223040865 copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | [[File:IMG 20210608 223040865 copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | ||
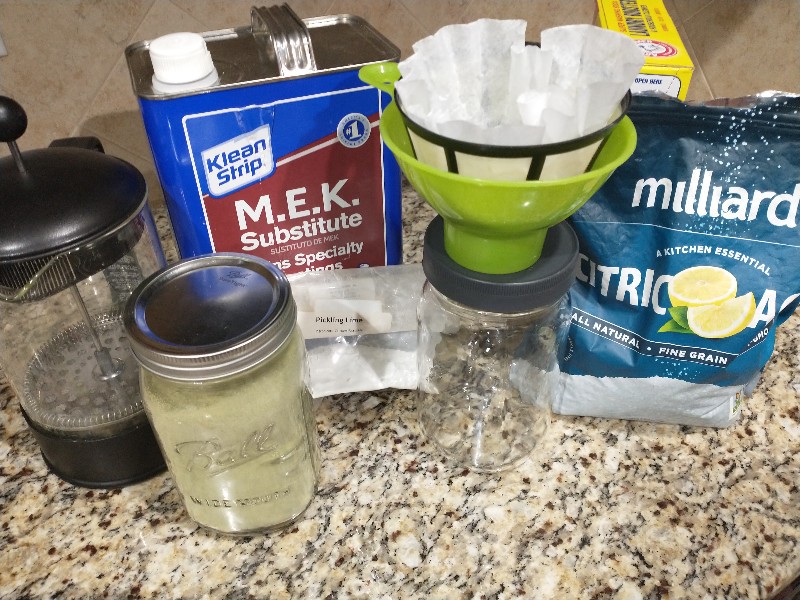
| − | <center>''Fig. 2: Some of the over the counter materials. While a glass/plastic french press is show, an all metal model is | + | <center>''Fig. 2: Some of the over the counter materials. While a glass/plastic french press is show, an all metal model is preferred. Credit: Loveall.</center> |
= Process Overview 👀 = | = Process Overview 👀 = | ||
In short:🌵➠🟢➠🧑🏾🔬➠✨➠💖➠💚, where, | In short:🌵➠🟢➠🧑🏾🔬➠✨➠💖➠💚, where, | ||
| − | *🌵: Grow, harvest, store, dry, and grind cactus | + | *🌵: Grow, harvest, store, dry, and grind cactus |
| − | *🟢: Mix cactus powder | + | *🟢: Mix wet crumbs with cactus powder, lime, water |
| − | *🧑🏾🔬: Pull | + | *🧑🏾🔬: Pull wet crumbs with ethyl acetate |
| − | *✨: | + | *✨: Crystallize mescaline with fumaric acid |
| − | *💖: Collect and | + | *💖: Collect, rinse, and dry mescaline citrate crystals |
| − | *💚: | + | *💚: Reclaim ethyl acetate for reuse |
| − | |||
| + | There is a good overview video of the process at https://youtu.be/-uQo7Xka8_c. This could be especially useful for visual learners intimidated by detailed text instructions alone. | ||
| − | + | There is also a good printable guide from experienced reddit extractor u/roundtripfarm at https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/t9020yx7oizpg5o08mmvt/cielo-workbook.pdf . | |
| − | + | ||
| + | = Detailed Process 📜= | ||
| − | + | == Cactus Powder 🌵 == | |
| − | + | Grow <ref name=seeds/>, <ref name=guide/> and harvest cactus. It is recommended to not harvest young plants that are under 3 feet tall to avoid stunting. One way to harvest is to cut the top half for processing and leave the bottom half to grow Note: the top part of the plant contains more mescaline<ref>Paper with vertical signal[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1146358&#post1146358]</ref>. For growing collections, Make two cuts at 1/3 and 2/3 height. Replant the top third (la cabeza) after the cut is calloused (~1 week), and process the middle third. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [ | + | |
| − | < | + | |
| + | Some data shows that dark storage (stressing) of the cuttings can increase mescaline content<ref>Dark storage data[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=739806]</ref>. However, it has also been argued that with optimal growing conditions, stressing is not necessary. The optimal growing conditions are uncertain so stressing is recommended even though it many not always be needed. To stress the cacti, store live cuttings in a dark place for at least 3 months (e.g. in a paper bag or wrapped in newspaper). | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | All parts of the cactus can be used. Outer green skin yields more than the inner white core for the same dry mass<ref>Result for different cactus parts[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1127854#post1127854]</ref>, but mescaline is present in both parts of the plant. Outer waxy layers and spines do not yield product, they can optionally be removed but that is not necessary because they are not detrimental to the extraction. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Chop whole cacti (into for example ~1/4 inch thick slices) and dry them with (for example) a food dehydrator at low temp (~120 F). Low drying temperature is recommended because chlorophyll begins to break down at 140F and it's byproducts have a yellow/tan color that can end up in the final product (although this is a cosmetic issue only). | |
| − | + | Grind dry cactus slices to a fine powder. This can be done in two steps, first through a food processor (coarse grind) and then through a coffee grinder or grain mill (fine grind). See Fig. 2a for representative images going from seed to powder. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[File:IMG 20230213 104225336 HDR copy 800x648.jpg|center]] | |
| + | [[File:IMG 20230213 103910895 HDR copy 800x720.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:20230203 085108 copy 800x1215.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:8iwkwZzHmA copy 643x502.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:RDT 20250312 1126232053354350690903250 copy 800x800.jpg|center]] | ||
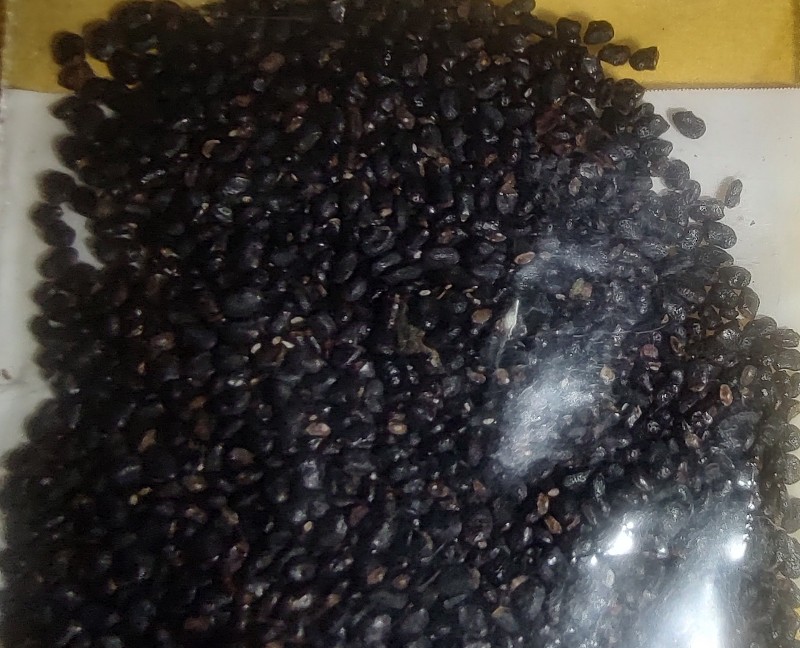
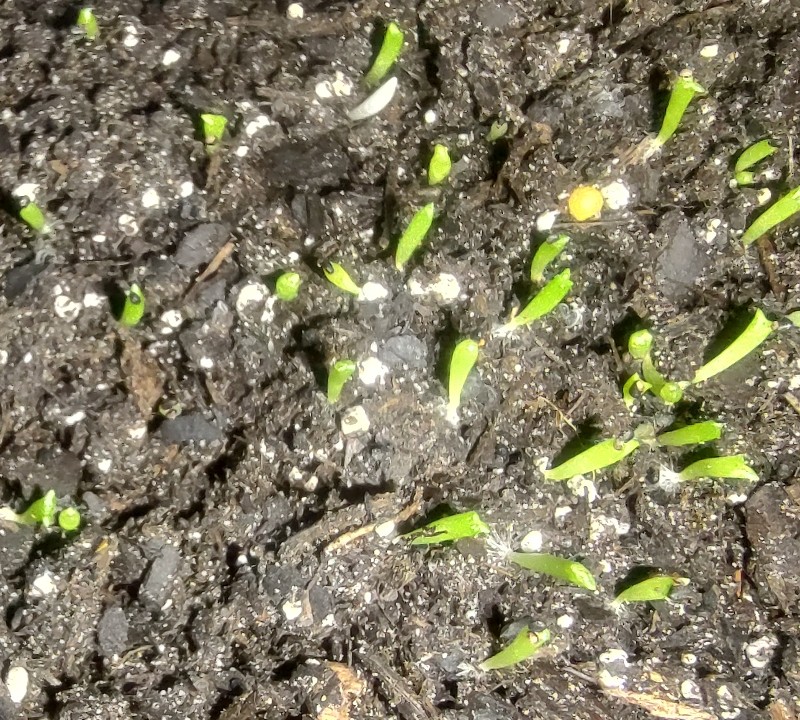
| + | <center>''Fig. 2a: Cactus life stages. Seed (top), seedling (second from top), mature specimen (middle), dried chunks (second from bottom), and powdered (bottom). After this life cycle the plant is ready for CIELO. Credits (top to bottom): Loveall, Loveall, Madhattress, Endlessness, BioHackedRomulan.</center> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Run the powder through a flour sifter and regrind any course material caught by the sifter. It is '''very important''' to make a uniform cactus powder that is dry and finely ground. The fine grind enables good yields and proper crystallization. Clouds of fine dust fly into the air when handling a good powder, reminiscent of flour (but green). Store powder in a sealed container to avoid moisture absorption over time. Old cactus powder may change to a tan color because chlorophyll slowly breaks down over time, and still works well in this process, however same as with tan powder from excessive dry heat, the tan color may make it to the product. No differences in subjective effects have been noticed for different off-white product colors (green/yellow/tan). | ||
| − | + | == Wet Crumb Mix 🟢 == | |
| − | + | Mix the '''finely ground''' cactus powder and lime together until uniform. Add ~130ml of water, '''mix well for at least 10 minutes'''. Mixing can be done with a spoon or gloved hands. Alternatively, a stand mixer at low speed and is a great upgrade. | |
| − | + | Mix well enough to have a uniform | |
| + | mix with '''no dry spots'''. If dry spots remain after thoroughly mixing, add small amounts of water until no dry spots remain. Mix well after the last water addition to make sure there are no pockets of '''wet spots''' either. | ||
| − | + | A "wet crumb" consistency should be reached (see Fig 3. Top). These wet crumbs are wet enough to stick together when cupped (see Fig 3. Bottom), and dry enough to crumble back to crumbs when broken apart. | |
| − | |||
| + | [[File:IMG20250304234250 copy 800x799.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:20250304234306 copy 798x799.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | <center>''Fig. 3: Ideal wet crumb consistency (top). When crumbs are squeezed together they join into a single mass (bottom). The joined mass can easily be broken apart back to the wet crumb consistency. Credit: Loveall.''</center> | ||
| − | |||
| + | If by mistake the mix becomes too wet the crumbs will congeal into a dough or even a paste. The extraction process will still work for wetter mixes, but excess water requires a water removal step from the solvent: See the sodium carbonate fridge rest in the appendix. | ||
| − | + | == Extract 🧑🏾🔬== | |
| + | Transfer the wet crumbs to a french press. A food scale is recommended to keep track of the ethyl acetate. Cover wet crumbs with ethyl acetate (~225g = 250ml), stir for three minutes, and rest for one minute (see Fig. 4). The wet crumbs will break up into a sandy consistency allowing ethyl acetate to easily access all the mescaline in the plant matter. Do not stir too aggressively, such as using an electronic hand mixer, to avoid changing the pull consistency. Press extract into a clean quart jar trough two stacked coffee filters. Do not press too aggressively and watch the final trickle of liquid closely to avoid water from the crumbs being squeezed into the solvent. Some of the solvent will remain trapped in the crumbs matrix, but aim to get back at least 125g (~ 137ml) of Ethyl acetate in the first pull. Since the mix is now saturated with solvent, aim for getting al of the add mass of ethyl acetate back out in subsequent pulls. | ||
| − | + | It is normal for some plant mass to be caught by the filters, but if loose particles appear in the extract and/or the filter clogs, the wet crumbs had some dry spots from insufficient water mixing. The process will still work after putting in the extra effort to filter/decant all particles in the extract before salting in the next step. Next time, mix the crumbs thoroughly with enough water so they are uniformly sticky and properly hydrated. | |
| − | + | [[File:IMG 20230210 115119600 HDR copy 800x558.jpg| center]] | |
| − | + | <center>''Fig 4. Ethyl acetate pull in metal french press ready to be covered and easily poured out. Credit: Loveall.''</center> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| + | Repeat the extraction with ~160g (~175ml) of ethyl acetate until the extraction jar is full (~5 total pulls). All of the added ethyl acetate in these pulls can be recovered. Optionally, the alkaloid content can be roughly tracked with pH paper (see Fig 4b.). | ||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:IMG20250305010724 copy 800x426.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | <center>''Fig 4b. Alkaloid monitoring across 5 pulls using pH paper. The wet solvent becomes neutral as mescaline is depleted. A post salting pH check (next section) is also shown and should be acidic from excess citric (or fumaric) acid. The pH strips work in the solvent due to the presence of water, and reading is done after strips dry out. Credit: Loveall.''</center> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | All of the extraction pulls should be completed within 45 minutes and combined (see Fig. 4b). After ~45 minutes the sandy plant matter will begin to congeal, making solvent penetration and recovery more difficult. Hours after the last standard pull, the congealed plant matter will have released a few ml of solvent which can be optionally added to the extraction for a minimal yield boost and increased solvent recovery. Over 90% of the solvent should be recovered. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
[[File:IMG_20210601_122315740_copy_600x800.jpg| center]] | [[File:IMG_20210601_122315740_copy_600x800.jpg| center]] | ||
| − | <center>''Fig. | + | <center>''Fig. 4b: Ethyl acetate extract. Color may vary (darker green is normal), but extract must be clear and free of debris. Credit: Loveall</center> |
| − | The spent | + | The spent wet crumbs can be dumped in a compost pile when not raining (avoid introducing ethyl acetate into waterways). Alternatively, allow the spent plant material to dry in a ventilated area and dispose of it in the trash. |
== Crystallize ✨== | == Crystallize ✨== | ||
| − | Drop | + | Drop fumaric acid (~3 grams) in the extract. Alternatively, 5g of citric acid cam also be used. Extract will cloud as the dissolved organic acid reacts with mescaline freebase to form an insoluble monomescaline salt. Cloudiness may be hard to see in darker extracts (a backlight may help).There are two recommended options to complete the crystallization: |
| + | *Slow crystallization option: Allow the organic acid to dissolve by diffusion without stirring. Leave cloudy extract undisturbed and sealed with a lid. Crystals of monomescaline fumarate (or citrate) should begin to appear after a few hours, and take a few days to completely crash out (at least 3 days of wait is recommended). Crystals will sometime grow large with this method (>2mm, see Fig. 5), but not always. | ||
| − | + | *Fast crystallization option: Turn on the magnetic stirrer for faster crystallization. Monomescaline fumarate crystalizes will form quickly (typically in 30 minutes or less), while monomescaline citrate will take more time (up to two hours). The crystals will be very small and will form a powder. | |
| + | The crystallization time can vary a lot, especially for beginners, so give extra time to ensure the crystallization is complete until familiar with the process. See appendix for other crystallization options. | ||
| − | + | The mescaline salt crystals cam sometimes look like undissolved organic acid to beginners. However, all the acid granules are reliably dissolved. The mescaline salt floats in the extract long enough to make a "snow globe" when shaken/stirred. Organic acid will not. | |
| + | If citric acid was used and no crystals form and goo appears, the ethyl acetate contained too much water. See FAQ below for simple recovery options. If goo still results after taking the FAQ suggestions into account, please report this on the DMT nexus or the reddit forum r/mescaline. | ||
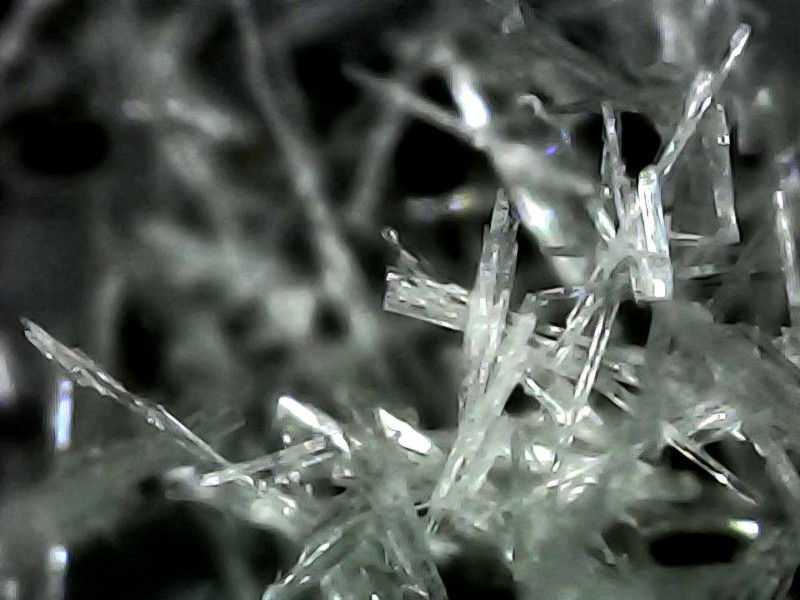
| − | [[File:IMG 20230211 145228076 HDR copy 800x800.jpg|center]]<center>''Fig. 5: Monomescaline citrate crystals growing in ethyl acetate. When light is shining in front of the extract it | + | |
| + | [[File:IMG 20230211 145228076 HDR copy 800x800.jpg|center]]<center>''Fig. 5: Monomescaline citrate crystals growing in ethyl acetate. When light is shining in front of the extract, it appears a dark red due to chlorophyll emission (see Fig. 1 for an example with back light). Mescaline salt precipitate appearance can vary alot, and can even appear to look like the original acid granules. Credit: Loveall.</center> | ||
== Collect 💖== | == Collect 💖== | ||
| − | Swirl ethyl acetate to knock crystals loose. | + | Swirl ethyl acetate to knock crystals loose. Citrate crystals that cling to the wall can sometimes be dislodged by shaking or with a knife/spoon. Fumarate crystals do not tend to stick to the wall and are easier to pour out. Send solvent through a coffee filter to catch crystals (note: do not store the filtered salted solvent in a metal can because excess acid can corrode metal). Rinse any crystals remaining on jar walls with a small amount of fresh ethyl acetate and send wash through the collection filter (a good practice to protect the metal filters basket from corrosion). Repeat ~1-2x until off color is mostly removed). |
| − | + | Let the filter dry and collect crystals by sliding them off the filter. Folding and rubbing the inside of the filter against itself with the palms of the hands can help loosen the last bit of crystals. This is the final product (Fig. 6). | |
[[File:IMG 20210603 130102387 copy 600x800 copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | [[File:IMG 20210603 130102387 copy 600x800 copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | [[File:RDT 20240718 1333511883143029882510217 copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | ||
[[File:WIN 20230329 22 04 26 Pro copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | [[File:WIN 20230329 22 04 26 Pro copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | ||
[[File:WIN 20230329 22 05 46 Pro copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | [[File:WIN 20230329 22 05 46 Pro copy 800x600.jpg|center]] | ||
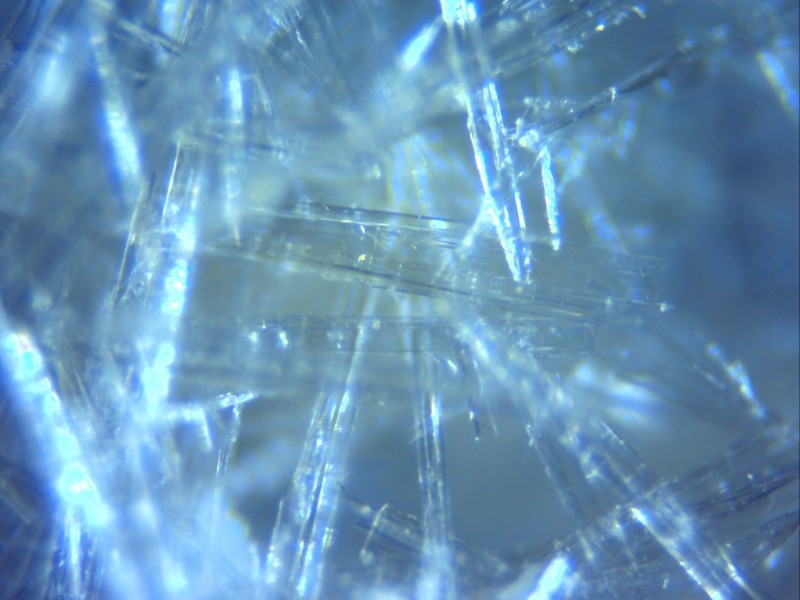
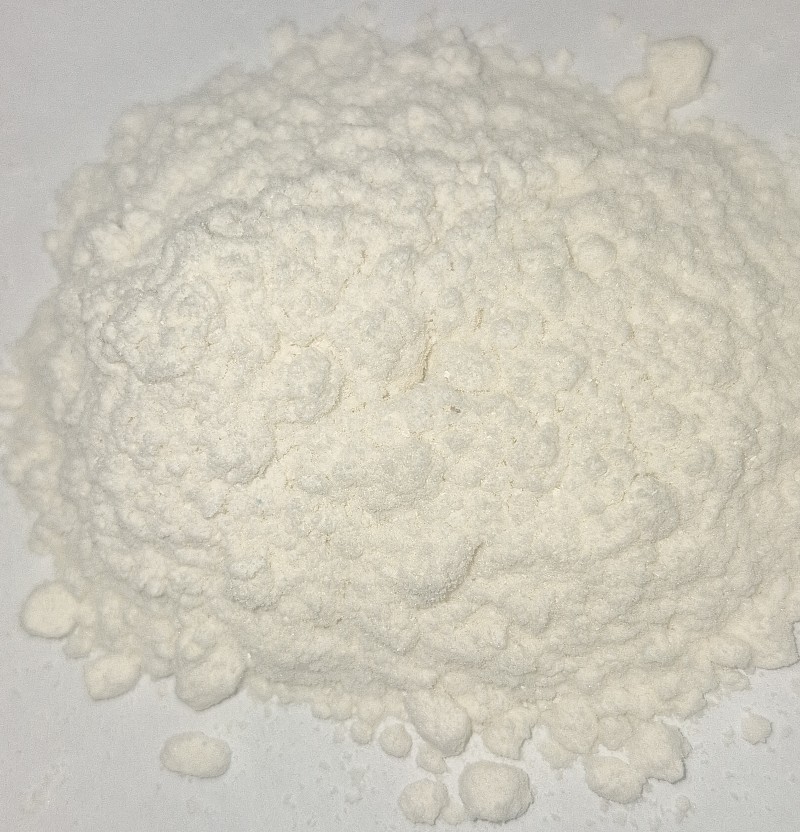
| − | <center>''Fig. 6: | + | <center>''Fig. 6: Images of mescaline citrate. Appearance can vary and crystals may be smaller to the point of looking like a powder. Top without magnification, second from top macro lens image, second from bottom at 50x microscope magnification, and bottom at 100x microscope magnification. Credit: Loveall, Madhattress, and Vincent.</center> |
| + | |||
| + | Yield depends on the cactus and is usually between 0.3% to 3% with ~0.6% to 1.5% being common<ref>Cactus analysis thread[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&t=71353]</ref>. However, yields up to 8.2%<ref>High bridgesii yield[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1180912#post1180912]</ref> (5.0% mescaline HCl equivalent) have been reported. The large mescaline variability cannot be explained by genetics alone and understanding the environmental factors is a fertile scientific question waiting for new discoveries to be made. In general, healthy home grown bridgesii cacti tend to yield more than pachanoi, while peruvians have a wide range of yields and less data. | ||
| − | |||
| + | Depending on the organic acid used, the product is (1) monomescaline fumarate (anhydrous), or (2) hydrated monomescaline citrate with 1.5 molecules of water per molecule of salt (see fig 6a). | ||
| − | The | + | The monomescaline fumarate contains 645mg/g of mescaline and is 76% as strong as mescaline HCl. In previous versions of the TEK before we had more analysis, the dimescaline salt was believed to form. However, titration showed that product was much more consistent with the monomescaline salt. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | The citrate hydrated salt has been analyzed well, since it was used in the early TEK before the benefits of fumaric were known. It contains 491mg/g of mescaline which was verified separately by Altitude Consulting measuring 492mg/g of mescaline | ||
| + | (anonymous source). The rest of the hydrated salt is 447mg/g citric acid 63mg/g of water. The product is therefore ~58% as strong as Mescaline HCl which contains 853mg/g mescaline. | ||
[[File:4118 089df672-6b60-4a76-a6d8-6a467e8c398b Captura de tela 2023-02-11 220537 copy 800x398.jpg|center]] | [[File:4118 089df672-6b60-4a76-a6d8-6a467e8c398b Captura de tela 2023-02-11 220537 copy 800x398.jpg|center]] | ||
| − | <center>''Fig. 6a: NMR results | + | <center>''Fig. 6a: NMR results of 93.1% monomescalone citrate with the remaining 6.9% being water, consistent with the hydrated salt form '''(MesH)H<sub>2</sub>Cit·1.5H<sub>2</sub>O''' (see appendix for notation description) within the detector resolution. Credit: endlessness.</center> |
| Line 197: | Line 205: | ||
| − | Testing the product with marquis reagent gives a bright orange color as expected<ref>Marquis reagent result[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1180894#post1180894]</ref> (see Fig. 7b). Several reagent results for the product from this TEK have been published by _Trip_<ref>Reagent results[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1165913#post1165913]</ref>. | + | Testing the product with fresh or well stored marquis reagent gives a bright orange color as expected<ref>Marquis reagent result[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1180894#post1180894]</ref> (see Fig. 7b). Several reagent results for the product from this TEK have been published by _Trip_<ref>Reagent results[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1165913#post1165913]</ref>. Note that marquis reagent may expire after a few months depending on storage conditions after which the reaction color is invalid/brownish. |
| Line 203: | Line 211: | ||
| − | Tip: The coffee filter used to collect the crystals can be re-used upside-down before salting. Any small crystals not collected may be forced into the extract and subsequently act as seed crystals for the next extraction<ref>Filter reuse[https://www.reddit.com/r/mescaline/comments/14kot72/free_cielo_salting_tip_come_can_get_it/?utm_source=share&utm_medium=android_app&utm_name=androidcss&utm_term=1&utm_content=share_button]</ref>. | + | Tip: The coffee filter used to collect the crystals can be re-used upside-down before salting the next extract. Any small crystals not collected may be forced into the extract and subsequently act as seed crystals for the next extraction<ref>Filter reuse[https://www.reddit.com/r/mescaline/comments/14kot72/free_cielo_salting_tip_come_can_get_it/?utm_source=share&utm_medium=android_app&utm_name=androidcss&utm_term=1&utm_content=share_button]</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | == Dosage ⚕️== | ||
| + | The mescaline experience is subjective. It can vary by individual and can be affected by the environment. Natural settings usually go well with the mescaline experience. | ||
| + | A small group of trusted loved ones or close friends also goes well with the experience. When deciding on a dose for a desired experience classification<ref>Experience Classification[https://en.psychonautwiki.org/wiki/Dosage_classification]</ref>, the results of several non-scientific poll results indicate the following for monomescaline citrate 1.5H2O (see Fig 7c): | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Threshold''': 100 - 165 mg, average '''133mg''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Light''': 165 - 485 mg, typically '''350mg''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Common''': 485 - 860 mg, typically '''650mg''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Strong''': 860 - 1370 mg, typically '''1000mg''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Heavy''': '''>1370mg''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | For monomescaline fumarate, divide these doses by a factor of | ||
| + | 1.3. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Mplotc.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | <center>''Fig. 7c: Reddit mescaline citrate dosage poll summary of 112 responses. Salt form is monomescaline citrate with 1.5 H2O molecules of hydration (unfortunately the .5 did not show up on the plot axis). Poll is non-scientific and subjective. Respondents participate in a mescaline forum and had previous experience. Note the overlap in poll responses. For example, while at 350mg a light experience is expected, but there are some chances of having a threshold or common experience. Percent of answers are normalized by each subjective effect category. To convert to mescaline HCl multiply dosage by 0.58, and to convert to mescaline fumarate multiply by 0.76. Credit: Loveall.''</center> | ||
== Reuse 💚== | == Reuse 💚== | ||
| Line 209: | Line 237: | ||
| − | + | To reuse, the excess organic acid will be removed. The green chlorophyll does not interfere with the process and will remain. There is no limit to the number of reuses. | |
| − | + | Before washing solvent, check for new crystal grown and collect any new product if present. Sometimes, a small amount of product precipitates after the main collection. | |
| − | + | It is not necessary to remove the green/dark color present in the solvent because it does not affect the TEK and remains stable after many reuses (chlorophyll saturation). Also, any mescaline that does not crystallize in the main extraction will mostly remain in the ethyl acetate during regeneration. | |
| − | + | ''Do not store salted solvent in metal cans''. The excess citric acid can make them rust. It is ok to store neutralized/washed solvent back in the original metal can long term. Another long term storage solution is a mason jar sealed with a plastic lid resistant to ethyl acetate<ref>Plastic lid resistant to ethyl acetate[https://www.ballmasonjars.com/products/essentials-accessories/jar-lids-bands/ball®-regular-mouth-leakproof-storage-lids-6pk/SAP_1440010812.html]</ref>. | |
| − | + | There are two options to regenerate the solvent. The option that uses a magnetic stirrer is a lot less work and is recommended. | |
| − | + | ===With Magnetic Stirrer=== | |
| + | Add a tablespoon of sodium carbonate and a teaspoon of water to the solvent, cover loosely, and magnetically stir until pH strips roughly match fresh EA after. The reaction is very quick for fumaric acid (seconds), but can take up to half a day for citric acid. If no pH strips are available, 12 hours of magnetic stirring should be enough. | ||
| − | + | If citric acid is being removed, a cloudy haze of sodium citrate from the neutralization reaction will appear over time (best seen by shining a light). If the solvent has enough water, hydrated sodium citrate subsequently forms and drops out of solution as a wet white solid layer. If cloudiness persists after 12 hours, remove the washing soda, add a tablespoon of water, and check again after another 12 hours. Repeat until cloudiness disappears. | |
| − | + | Once the neutralized extract is clear (a backlight can be seen through the solvent), stop the magnetic stirrer, rest the solvent for a few minutes, and pour off the neutralized clear extract from the wet clumped up solids (sodium carbonate and sodium fumarate/citrate) through a coffee filter. Wet salts can be sticky and that is normal. The solvent is now reclaimed and ready to use. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Note: if the xtalization during the main TEK did not completely finish (impatience, mistake, etc), the reclaimed solvent will carry any residual mescaline to the next extraction and pH paper could be slightly green (see Fig. 4b). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Without Magnetic Stirrer=== | ||
| + | Are you sure you don't want a magnetic stirrer? Regeneration of one quart of solvent is done in two steps: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 1) Add a tablespoon of sodium carbonate and 50ml of water to the extract. Shake vigorously, releasing CO2 gas as citric acid reacts with sodium carbonate. Neutralization can be verified with pH paper matching fresh EA and/or the absence of pressure buildup. If excess citric acid is used (above the TEK's main recommendation) more sodium carbonate may be needed for neutralization (0.83 parts sodium carbonate neutralize 1 part citric acid). It is important to remove all the citric acid and it can take 5 minutes or more of shaking to fully neutralize the extract. A water layer may form above the excess sodium carbonate and the extract will cloud. After resting for at least an hour, decant neutralized extract into new jar (you may need to leave a small amount of solvent behind when decanting: it can be added to the next extraction's neutralization). Optionally, use a separatory funnel to recover all of the neutralized extract. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 2) Wash neutralized solvent with a tablespoon of salt and ~50ml of water. The solvent cloudiness will change after shaking for a few minutes. Rest the solvent in the fridge for a few hours until a backlight shines through clearly. Decant into a long term storage container (e.g. original solvent can if empty). As before, you will need to leave some solvent behind which can be added to the next brine wash). Optionally, use a separatory funnel to recover all of the washed extract. | ||
= Frequently Asked Questions ❓ = | = Frequently Asked Questions ❓ = | ||
| − | '''Q: I froze my cuttings, is ok to proceed with the TEK?''' | + | '''Q: I froze my cuttings on the freezer, is ok to proceed with the TEK?''' |
| + | |||
| + | A: Probably not. Fully freezing the cuttings will change the consistency of the cactus/lime/water mix during the pull, resulting in a pancake-like batter mixture and low yield <ref>Freezing cutting result[https://www.reddit.com/r/mescaline/s/gr2yeqm5bR]</ref>. If you can still produce a fine powder and find a way to make the process work please share your result with the community on the dmt nexus. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Q: My plants died. Can I extract them with this process?''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | A: Dead dry plants have been used successfully as long as they can be dried well and ground to a fine powder. Moldy parts have also worked with no apparent issue, but users need to assess the possibility of mycotoxins for their case. In extreme cases such as a deep freeze to the core they may not be usable (see previous FAQ). | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | Dead plants will have some chlorophyll degradation which can give the final product a tan color. This is only cosmetic. | |
'''Q: I bought cactus powder only and I'm getting a low yield, is this normal?''' | '''Q: I bought cactus powder only and I'm getting a low yield, is this normal?''' | ||
| − | A: Yes. Online powders typically yield below 1%, with 0.5% being common. Buying powders online is | + | A: Yes. Online powders typically yield below 1%, with 0.5% or less being common. Buying powders online is strongly discouraged as it can finance poaching and plant destruction in natural habitats. Instead, grow your own cacti if possible. If not possible, go out there and make it possible. However, be warmed that mescaline is a gateway drug to gardening. |
| Line 253: | Line 302: | ||
'''Q: I got an emulsion while pulling, what do I do?''' | '''Q: I got an emulsion while pulling, what do I do?''' | ||
| − | A:If | + | A:If an emulsion forms, the cactus/lime/water mix was too watery. Add lime, dry magnesium sulfate, and more ethyl acetate until solvent is released. Keep the lime to magnesium sulfate ratio above 1 to ensure cactus mix remains alkaline<ref>Lime and magnesium sulfate ratio vs pH[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=942484#post942484]</ref>. Next time, use less water to make the cactus mix. |
| − | '''Q: | + | '''Q: Why is fumaric acid recommended over citric acid?''' |
| − | A: It is a water layer. This can happen if you squeeze the French press aggressively and/or the initial | + | A: The main reason is that fumaric acid is leas sensitive the water in the EA. The process window for water content is much larger. Other benefits include: |
| + | |||
| + | - Faster crystallization | ||
| + | - Less sticking of the salt to the jar walls | ||
| + | - More complete precipitation of the last traces of mescaline salt (needs analytical confirmation a | ||
| + | - Less likely to keep the color of brown powder from chlorophyll breakdown (but this is only cosmetic) | ||
| + | - Stronger by weight than the citrate salt by a factor of 1.3 | ||
| + | - Faster regeneration reaction | ||
| + | |||
| + | Downsides are (1) fumaric is more difficult to find in stores than citric, but homebrew shops do carry it sometimes, and (2) there is less analytical data confirming purity and stoichiometry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Q: I have a bottom separate layer in my pulling jar. What is it and what do I do?''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | A: It is a gunky water layer. This can happen if you squeeze the French press aggressively and/or the initial cactus mix is too wet. Remove the bottom layer using a pipette/syringe, separatory funnel, or decanting. Do a sodium carbonate partial dry, and continue the TEK. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Q: I have citric acid which contains <2% SiO2 anti-caking agent. Can I use it in the TEK?''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Yes, it should work despite the unwanted additional chemical. It is usually a lot less than 2% SiO2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If used as is, there will have a small amount of SiO2 in the product, <100mg if 5g were used for salting <2%), but it is probably a lot less. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alternatively, the adulterated citric acid can be dissolved in water. Any SiO2 won't dissolve and can be separated out. Evaporate the water to recover purer citric acid. Note that this citric acid will be hydrated and mass may increase slightly, but that is not an issue. | ||
| Line 274: | Line 346: | ||
| − | '''Q: After adding citric acid, I saw clouds followed by precipitation, but the precipitate reminds me of citric acid. How do I know a mescaline salt is precipitating and not citric acid?''' | + | '''Q: After adding citric (or fumaric) acid, I saw clouds followed by precipitation, but the precipitate reminds me of citric (or fumaric) acid. How do I know a mescaline salt is precipitating and not citric acid?''' |
| − | A: Citric acid | + | A: Citric (or fumaric) acid is not part of the precipitate after 3 days. It goes in solution because it is well bellow its solubility limit in wet Ethyl Acetate (~50mg/g for citric and ~10mg/g for fumaric). The white particles that form from the clouds after the organic acid is added and dissolved are mescaline salts. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Only exception to this is if one deviated from the TEK (e.g. by doing a freezer reset or used a chemical drying agent), and dried the Ethyl Acetate too much. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Note that product crystal morphological can vary a lot and sometimes look like acid granules. Do not allow this to confuse you. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Some beginners still doubt that all the solid organic acid dissolves. To verify solubility directly, add 1mg/g of acid to the used extract after product collection and verify it all dissolves. | ||
'''Q: After adding citric acid, nothing precipitated, what gives?''' | '''Q: After adding citric acid, nothing precipitated, what gives?''' | ||
| − | A: | + | A: Some water is needed for the salting crystals to form. Add a few drops of water and check for clouding. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If the drops of water initiate clouding, add 0.5% water and check for xtalization after a few days. If no xtalization repeat the drop test and add another 0.5% water if new clouds form. Next time you perform the TEK, think about how you may have made the extract too dry or ask on the online forums. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If clouds do not form, check the jar walls, a transparent product may have precipitated there (e.g. this has been reported for whole bridgesii<ref>Whole bridgesii precipitate on jar walls [https://mycotopia.net/topic/111136-lets-talk-about-cactus-extractions/#entry1487992]</ref>). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If product did not precipitate on walls as a transparent film, bring up the citric acid concentration up to 20mg/g and wait a few days. Higher citrate concentration can help a initiate xtalization, but this borderline case is rare. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If your cactus does not contain mescaline, no mescaline citrate will form. It is possible to have bunk cactus, especially if bought as powder online (which should never be done). Under certain conditions, PC cacti can struggle to yield anything significant. | ||
'''Q: After adding citric acid, goo/oil precipitated instead of crystals, what gives?''' | '''Q: After adding citric acid, goo/oil precipitated instead of crystals, what gives?''' | ||
| − | + | There was an issue with the citric/water/mescaline ratio in the solvent when salting. For most people, too much water was their issue, but too little citric acid or not enough water can also cause problems. Low yielding plants have narrower process windows for xtalization. However, an issue with ratios can be reliability avoided with good cacti (>0.4% mescaline) and good TEK execution. | |
| − | * | + | |
| + | In one example from Cheelin the goo was 65% mescaline citrate<ref>Goo conversion to crystals[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1133388#post1133388]</ref>. In another example, goo was measured to be roughly equal parts water, citric acid, and mescaline citrate <ref>Goo measurements[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1218686#post1218686]</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Tips to reduce changes of goo: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ensure you are using an active cactus (>0.4% mescaline). Low mescaline concentrations can fall outside the proper crystallization process window. People may encounter this when using low potency PC plants (note that not all PC plants are low potency for unknown reasons). | ||
| + | *Good wet crumb consistency | ||
*Not excessively squeezing the French press | *Not excessively squeezing the French press | ||
| − | * | + | *Perform the sodium carbonate partial dry. |
| − | + | ||
| − | Before salting it is important to ensure water and debris are present. Tilting the extract and shining a flashlight are needed for a good check. Take your time, especially the first time you try the TEK. | + | Before salting it is important to ensure water and debris are not present. Tilting the extract and shining a flashlight are needed for a good check. Take your time, especially the first time you try the TEK. |
| − | |||
| − | + | Alternatively, to reduce the water percentage before salting, , Shroombee suggests to add fresh ethyl acetate (usually relatively dry from the manufacturer) to the extract <ref>Fresh ethyl acetate to lower water content before salting[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1181802#post1181802]</ref>. This can increase robustness if any water is missed by a novice. For example, by adding ~100g of fresh ethyl acetate to a quart of extract. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Some people recommend a freezer rest followed by filtering off the ice crystals that form. This is very effective at removing large amounts | ||
| + | of water if the TEK has not been done properly. However, if a lot of water is removed with this technique, about 1% water needs to be added back before salting for good crystallization dynamics. This is a gross sledgehammer for water removal, and may be useful for those who don't trust their cactus mix skills or have fridge/ambient temperature issues (e.g. fridge is set to warm and/or crystallization environment is set too cold). | ||
| Line 308: | Line 408: | ||
'''Q: I recovered the goo/oil precipitate instead of crystals, what do I do?''' | '''Q: I recovered the goo/oil precipitate instead of crystals, what do I do?''' | ||
| − | A: A simple | + | A: A simple recrystallization with 99% IPA is recommended. |
| + | |||
| + | *Dissolve the goo in minimal heated 99% IPA (using a hot water bath and a covered but unsealed small mason jar jar) until only white solid mescaline citrate remains undissolved (will look like small fine particles). Note: If a lot of IPA is used all the mescaline citrate may dissolve, while unnecessary, this is not detrimental. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Seal/tighten the bar and move the IPA to the freezer for 24h where more mescaline citrate will precipitate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Collect the precipitate in a filter and rinse with a small amount of freezer cold 99% IPA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Immediately''' press the outsides of the folded collection filter into absorbent paper towels until dry so the cold product does not have a chance to absorb air moisture and liquify. | ||
'''Q: How quickly can the extraction process be done?''' | '''Q: How quickly can the extraction process be done?''' | ||
| − | A: With experience, and by skipping the fridge rest step | + | A: With experience, and by skipping the fridge rest step it is possible to go from raw cactus powder to dry crystals in under an hour by choosing a fast crystallization method. The first documented world record is 48 minutes to go from cactus powder to dry mescaline crystals ready to use.<ref>Plant to crystal record |
[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1134986#post1134986]</ref>. However, there is an increased risk of obtain goo without the fridge rest step. The express process is not recommended for newcomers. | [https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1134986#post1134986]</ref>. However, there is an increased risk of obtain goo without the fridge rest step. The express process is not recommended for newcomers. | ||
| − | + | The world record was beat in October 2024 with a time of 32 minutes by an anonymous contributor. | |
| − | A: Try using less water | + | |
| + | Example CIELO process for record seekers (raw cactus powder to pure mescaline citrate): | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Prepare ingredients for world/personal record and start timer | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Turn on stand mixer with 1 part cactus and add in order 0.22 parts lime until uniform (seconds), 1.33 parts ice cold water (seconds), and finally 2.22 parts fridge cold ethyl acetate. Stand mix for a few minutes | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Strain/filter mixing bowl solvent into jar over mag stirrer with mag stirrer rod (a fine metal pasta strainer pushed down into the mixing bowl can be helpful) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Add another 2.22 parts fridge cold ethyl acetate to sand mixer for second pull for a few minutes (go to next step before this one finishes) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *While stand mixer runs with second pull, turn on magnetic stirrer with first pull and add 0.055 parts of citric acid | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Strain second pull into xtalizing extract | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Decide if any more pulls are needed | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Decide when to stop the xtalization | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Collect xtals in coffee filter, rinse with fresh EA, and dry quickly (e.g. with a paper towel press followed by hot hair from a hair dryer). | ||
| + | |||
| + | To make the record official the following conditions must be met: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 1) Total yield must be above 1.1% | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2) Another pull needs to done after the timer stops and must yield less than 0.06% | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3) Original dry yield must be measured again after two hours with no weight loss detected from solvent evaporation | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4) Magnetically stir the salted extract for two more hours. Any new mescaline citrate must be below 0.06% yield. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Q: The cactus mix congealed in ethyl acetate very quickly and I couldn't finish the timed pulls with a sandy consistency. How can I give myself more time?''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | A: Try using less water and/or lower temperature ethyl acetate next time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 1) Excess water can accelerate congealing and decrease yield as it is harder to extract. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 2) Higher summer temperature pulls in the summer can also accelerate congealing. Keep ethyl acetate in a cool place. Consider using fridge cold ethyl acetate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Q: Why do I need to neutralize the extract before re-use?''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | A: Salted extract is acidic due to excess citric acid. The citric acid will react with the lime in the cactus mix releasing small particles of calcium citrate into the extract, making a cloudy mess. While it is possible to rest/settle/decant these particles off with time, neutralizing the extract and washing it is recommended by default. | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, if the operator would rather deal with calcium citrate as part of the extraction process, reclaiming the solvent is not needed. The resulting calcium citrate can be used as a supplement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Q: I have old resin and/or tea and would like to extract mescaline for a measured dose, can CIELO be used?''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | A: Yes! Adding resin or even tea to the cactus mix works. Increase the amount of citric acid accordingly (e.g. 50% if 50g of dry cactus is added). | ||
| Line 331: | Line 493: | ||
''St. Peter saw clouds transform into stars in the sky'' | ''St. Peter saw clouds transform into stars in the sky'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Q: Is there a video example of this TEK?''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Yes, see for example https://youtu.be/-uQo7Xka8_c. The video does not wash the product with fresh EA, which leaves a light cosmetic green color behind. | ||
= Appendix: Development Notes 🔬= | = Appendix: Development Notes 🔬= | ||
| − | == | + | == Wet Crumbs 🌵== |
| − | No improvements were seen with longer basing time, | + | No improvements were seen with longer basing time, oven drying, or increasing the ionic strength with CaCl2. Microwave treatment or boiling water resulted in a small yield loss. |
| − | + | Mix made with sodium carbonate failed. Material congeals very quickly and requires long solvent soaks which are darker and don't crystallize to large loose crystals (small sticky crystals were obtained). | |
| Line 351: | Line 518: | ||
== Extract 👨🏾🔬== | == Extract 👨🏾🔬== | ||
| − | Tests with longer/warmer pulls resulted in darker extract, smaller crystals, solvent | + | Tests with longer/warmer pulls resulted in darker extract, smaller crystals, more solvent absorption by cactus mix, faster congealing of plant mix, stickier crystals and no yield benefit. |
| − | + | Colder ethyl acetate (e.g. fridge temperature) the works fine with no yield loss and less smell. It can be used if desired. It is not mentioned as an option in the main TEK for brevity. | |
| + | |||
| + | Chemically drying the extract with anhydrous CaCl2 had no benefits, while drying with MgSO4 was problematic. However, depending on the worker and techniques used, a chemical dry with CaCl2 pellets (available commercially as de-icer) could reduce water content in the solvent and possibly make crystallization easier. Washing soda (when sold as Na2CO3 in monohydrate form, or when making the anhydrous form from baking soda with an oven) also dried the extract and can be beneficial in cases where the cactus/lime/water mix was made improperly with too much wetness, and this process is now detailed in the next section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Ethyl acetate has been shown to not as strong as chloroform in LLE extractions<ref>LLE extractions with Ethyl Acetate[https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.3c01048]</ref>. However, it is great for our purposes here because of wet crumbs penetration and citric acid (or fumaric acid) solubility. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Partial Dry (required if mix became a dough instead of wet crumbs) 🧐=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Beginners may use too much water in their cactus/lime/water mix, making it a dough instead of wet crumbs. The additional water can make it into the extract and interfere with xtalization, causing goo (a brown syrupy mix of mescaline citrate, citric acid, and water) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | If a dough was made during the mixing step, to ensure water levels are correct, add a tablespoon of washing soda to the extract, shake for a few minutes, and rest overnight in the fridge. The washing soda will absorb some water and partially clump<sup>''*'' ''♡''</sup>. Filter the extract and proceed to the next step. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''*If all the washing soda clumps up or a water layer forms, the extract is still too wet. You are at a risk of goo. Isolate the extract and repeat the partial dry until some washing soda does not clump. Next time, improve your mixing process (fine grind of well dried cactus and mix thoroughly adding water slowly giving it time to fully incorporate before adding more).'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''♡If none of the washing soda clumps, congrats! This is an indication that your extract was not excessively wet and you could have salted it directly. | ||
== Crystallize ✨== | == Crystallize ✨== | ||
| Line 361: | Line 548: | ||
| − | *''' | + | *'''Fast crystallization option:''' Use a magnetic stirrer to dissolve the citric acid and speed up crystallization. This produces a fast crystallization and minimizes crystals that are stuck to the wall. A stirring vortex will go from visible, to not visible as clouds form, to visible again as mescaline citrate precipitates (see Vid. 1). Crystallization is complete within two hours for almost all situations, but can vary a lot depending on the starting conditions (mescaline percent, water content, temperature, stirring speed, etc). Crystals will be very small with this approach and look like a powder. The crystals should still be large enough to be caught by a filter in almost all situations, but if some are not caught, slowing down the magnetic stirrer will produce larger granules in subsequent runs. The resulting powder is dense and easier to pack in capsules compared to the long needles, but not as pretty to look at (see Fig. 8aa). |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:YouCut 20240110 125804737 (1).gif|center|800x800px]]<center>Vid. 1: Fast crystallization. Magnetic stirrer speed was dropped after citric acid was dissolved so crystals would be slightly larger and caught by the filter. Credit: Loveall.''</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:20231212 042235 copy 800x832.jpg|center]]<center>Fig. 8aa: Powdery product from fast crystallization. Credit: Loveall</center> | ||
| − | *''' | + | *'''Shaken''': After adding the citric acid, shake the sealed jar vigorously. The citric acid will dissolve quickly and small crystals will precipitate as the shaking continues. After 15 minutes, shaking will crystallize most (but not necessarily all) of the product out of solution quickly. |
| Line 384: | Line 577: | ||
| − | + | By not using excess citric acid, different salt forms can be precipitated<ref>Trimescaline citrate candidate[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1131459#post1131459]</ref>, but that process is more complex than the simpler excess citric acid approach, and the other salt forms can form goo. | |
| Line 396: | Line 589: | ||
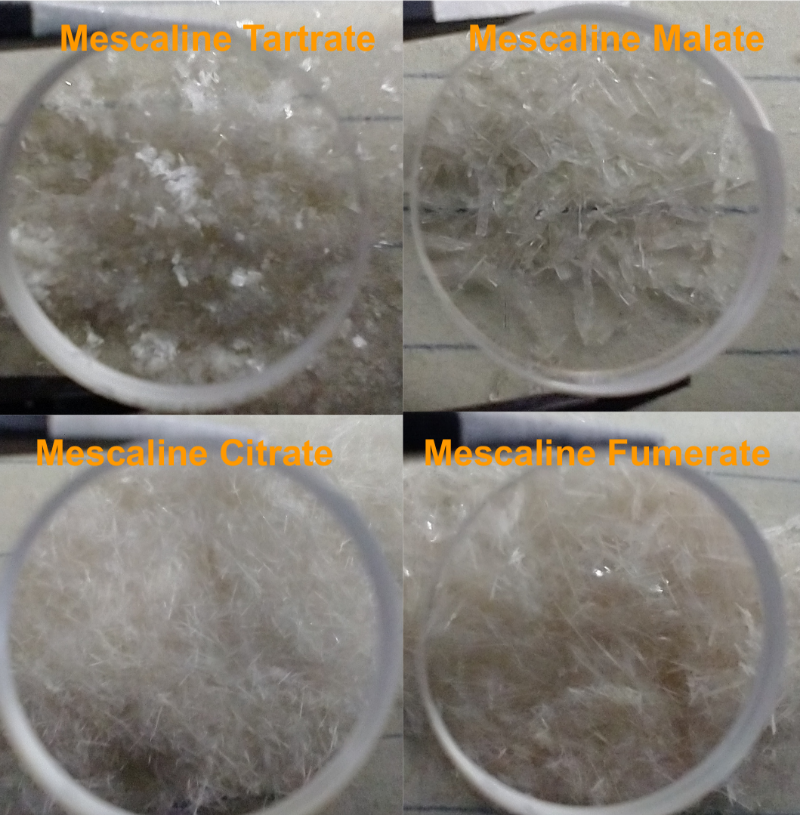
| − | Other dry organic acids have been tested<ref>Organic acid tests[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1136570#post1136570]</ref>,<ref>Succinic test[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1144986#post1144986]</ref>. Fumaric and tartaric crystallized well as | + | Other dry organic acids have been tested<ref>Organic acid tests[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1136570#post1136570]</ref>,<ref>Succinic test[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1144986#post1144986]</ref>. Fumaric and tartaric crystallized well as and could be a substitute for citric. Malic also crystallized but took longer to do so. Crude mass measurement indicated the anhydrous monomescaline form for the fumarate salt. See Fig. 8b for resulting citrate, tartrate, fumarate, and malate crystals. Succinic also crystallized from a chemically dried extract (without drying crystals did not form<ref>Wet solvent succinic salting[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1145951#post1145951]</ref>) as the monomescaline form (see Fig. 8c). Ascorbic, did not crystalize well. Other organic acids (lactic, oxalic, etc) have not been tested yet at the time of this writing. For the organic acids that crystallized, Mescaline HCl equivalent is: |
| − | *Monomescaline Citrate: | + | *Monomescaline Citrate 1.5 H2O: 58% |
| − | * | + | *Dimescaline Fumarate 92% (Titration analysis from Nov 2025 indicates this is NOT the salt that forma with CIELO <ref>Titration showing monomescaline fumarate[forum.dmt-nexus.me/threads/ethyl-acetate-approach-cielo.363620/post-3975576]</ref> |
| − | + | Monomescaline Fumarate:76% | |
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | A good alternative to citric acid is fumaric acid, which is also used in the food industry. Since the fumarate salt does not interact with water, it has a larger process window: less prone to form goo or stick in excess water conditions. It is also more concentrated, with 1.60 times more mescaline per gram compared to the citrate salt (monomescaline citrate 1.5H2O). | ||
| Line 408: | Line 603: | ||
| − | [[File:Screenshot 20220129-133134-447 copy 800x815.png|center]]<center>''Fig.8b: CIELO results using citric, tartaric, fumaric, and malic acids. No | + | [[File:Screenshot 20220129-133134-447 copy 800x815.png|center]]<center>''Fig.8b: CIELO results using citric, tartaric, fumaric, and malic acids. No chemical drying of the solvent was done in all cases. Credit: Loveall.''</center> |
| − | [[File:Succinate-fumarate-comparison copy 400x400.png|center]]<center>''Fig.8c: CIELO results using succinic acid after | + | [[File:Succinate-fumarate-comparison copy 400x400.png|center]]<center>''Fig.8c: CIELO results using succinic acid after chemically drying the extract with K2CO3. No xtals formed from succinic in an example where chemical drying was not done. Credit: _Trip_''</center> |
| − | 10% sulfuric acid was tested and while some crystals formed, a separate liquid layer also appeared making the process not practical. HCl has not been tested as it may break down ethyl acetate. | + | 10% sulfuric acid was tested and while some crystals formed, a separate liquid layer also appeared making the process not practical. HCl has not been tested as it may break down ethyl acetate, but a careful titration of a dry extract with concentrated HCl may work (however this is not considered lazy or a low hazard and committed from CIELO options). |
== Collect 💖== | == Collect 💖== | ||
| Line 420: | Line 615: | ||
| − | Any product | + | Any product stuck to the jar walls tends to be small. Minor amounts of xtals on the wall are normal, but if a lot of it sticks to the wall, the cactus mix could have been too wet and/or the ethyl acetate was too warm. The laziest way to collect this small amount of product is to dissolve it in water used in the next extraction. |
== Reuse 💚== | == Reuse 💚== | ||
| − | Dark extract can be cleared up with activated carbon (also called activated charcoal). Use dustless pellets (typically rinsed with water and dried before use). | + | Dark extract can be cleared up with activated carbon (also called activated charcoal). Use dustless pellets (typically rinsed with water and dried before use). Use the pellets statically so they don't release difficult to filter carbon powder. Clearing process takes time, especially for dark solvents used many times and saturated with plant matter. It may take several days to notice a change in very dark solvent, and weeks to completely clear it. |
| + | |||
| + | Manually passing the EA through a home made carbon filter a few times won't work. A recirculation system at 1000 GPH would time and pass the quart of EA through the filter thousands of times before beginning to clear the EA. | ||
| − | Any benefit to using activated charcoal to decolor the used solvent is not ''clear'' (pun intended). | + | Any benefit to using activated charcoal to decolor the used solvent is not ''clear'' (pun intended). Also, the environmental benefit of regenerating to a colorless solvent is in question since ethyl acetate is easy to produce and activated charcoal requires resources to manufacture. However, if the activated charcoal itself can be regenerated (e.g. in a hot oven) it may be economical to use it if a colorless solvent is wanted. However, there is no benefit to this other than aesthetics since the final product is the same regardless of the color of the starting solvent (provided some fresh ethyl acetate is available for the rinse). |
= References 🗝️= | = References 🗝️= | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:13, 26 February 2026
Contents
Introduction 🔆
CIELO stands for Crystals In Ethyl-acetate Lazily Over-the-counter. In this process, mescaline from cactus is precipitated in ethyl acetate as crystals (see Fig. 1). This technique (TEK) is specialized for cactus, simple, and avoids harsh chemicals. With less than an hour of labor, very pure mescaline can be extracted. However, the process needs to be followed closely to ensure good results.
Please grow your own cacti [1], [2]. San Pedro cacti in Peru (Echinopsis pachanoi and Echinopsis peruviana) are being over-harvested in the wild in a non sustainable way [3], [4]. Never purchase dry cactus powder. Online powders are normally of poor quality and their purchase funds endangered plant harvest and destruction, with less of 1/4 of wild habitats being well stocked as of 2024[5]. Obtain and grow live seeds, cuttings, or rooted plants. With patience and love, we can all extract the essence of the plant sustainably 🌵💚
This process was developed in a collaborative open source effort at the DMT nexus website[6] and refined with community input from the subreddit r/mescaline[7]. No parts of this procedure may be patented or used for profit. The information presented here and any modifications to it may be distributed freely with a reference to this source and with love.
Thanks to everyone who contributed to this process: someblackguy, benzyme, shroombee, Metta-Morpheus, downwardsfromzero, Kash, grollum, Mindlusion, Doubledog, Dreamer042, merkin, _Trip_, Cheelin, Highlightprotein, Loveall, orchidist, BlackRose, endlessness, Madhattress, reptivity, wowitsbabygirl, roundtripfarm, bobcollege, starbob, aizoaceous, and many others.
Safety ⛑️
Review ethyl acetate[8] and fumaric or citric acid[9] safety information. Verify solvent MSDS, material compatibility, and clean evaporation.
Ethyl acetate has a relatively low flash point of 38F. Ensure no open flames (e.g. cigarette, candle, gas heater) during extraction and work in a well ventilated area. It is a serious eye irritant. Safety googles are recommended. Flush with water for 15 minutes if any ethyl acetate gets in your eye. The information in this paragraph is not a substitute to reading the safety information mentioned above.
This TEK is food safe if food grade materials are used. Use food grade fumaric or citric acid since some of it will be in the final product as mescaline fumarate or citrate.
Following this advice does not guarantee safety. It is up to each adult individual to make their own personal decisions.
In one example, an individual used aluminum vessels to store salted (acidic) ethyl acetate [10] and did not check for compatibility of aluminum with citric acid, causing the metal to corrode from the acid.
Materials🛒
Consumables👩🌾
- 100g dry fine cactus powder
- 130g water + another 70g water as reserve
- 25g Ca(OH)2 (lime)
- 1L (~1 qt) ethyl acetate (sometimes sold as "MEK substitute")
- Optional: pH testing strips[11]
- 3g of fumaric acid.
- Alternatively, 5g citric acid can be used (both anhydrous or monohydrate are suitable). However the fumaric acid is more robust and HIGHLY recommended for beginners due to multiple advantages, especially if working with low yielding cacti.
- For solvent reclaim: Washing soda (monohydrate Na2CO3 which is sold as arm and hammer super washing soda, or anhydrous).
Important note: Avoid combining PC cactus with citric acid. This combination has the risk of not precipitating anything if the yield is low (<0.15%).
Equipment🏺
- Knife, paper bag, dehydrator, food processor, coffee grinder (or grain mill), and flour sifter (to harvest plant, store cutting, and make cactus powder)
- Gram scale (to measure ingredients)
- Large bowl and spoon (or gloves) for wet crumb mixing
- French press (stainless steel, 34 oz. or larger preferred)
- Coffee filters, filter basket, and funnel
- Quart mason glass jars with lids (to collect and salt extract)
- Milligram scale (to measure product)
Recommended Upgrades🪬
- Stand mixer with flat beater
- Magnetic stirrer
Process Overview 👀
In short:🌵➠🟢➠🧑🏾🔬➠✨➠💖➠💚, where,
- 🌵: Grow, harvest, store, dry, and grind cactus
- 🟢: Mix wet crumbs with cactus powder, lime, water
- 🧑🏾🔬: Pull wet crumbs with ethyl acetate
- ✨: Crystallize mescaline with fumaric acid
- 💖: Collect, rinse, and dry mescaline citrate crystals
- 💚: Reclaim ethyl acetate for reuse
There is a good overview video of the process at https://youtu.be/-uQo7Xka8_c. This could be especially useful for visual learners intimidated by detailed text instructions alone.
There is also a good printable guide from experienced reddit extractor u/roundtripfarm at https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/t9020yx7oizpg5o08mmvt/cielo-workbook.pdf .
Detailed Process 📜
Cactus Powder 🌵
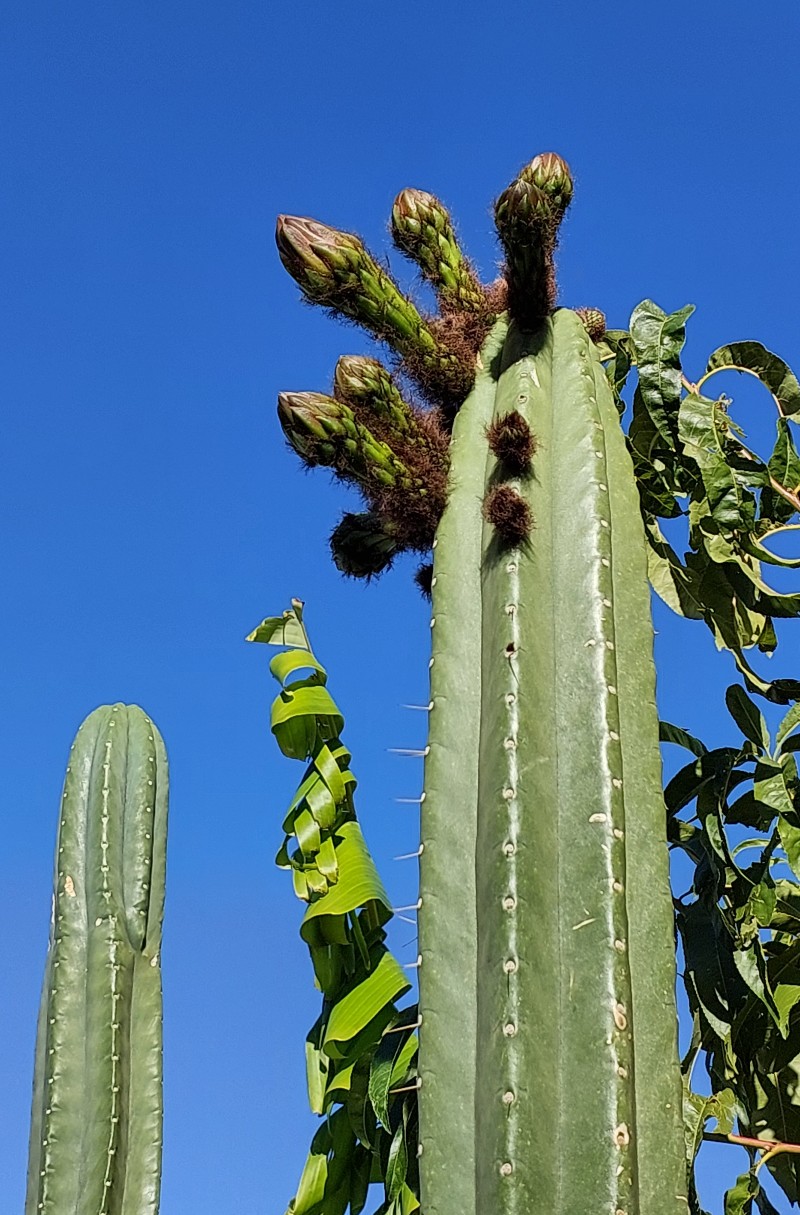
Grow [1], [2] and harvest cactus. It is recommended to not harvest young plants that are under 3 feet tall to avoid stunting. One way to harvest is to cut the top half for processing and leave the bottom half to grow Note: the top part of the plant contains more mescaline[12]. For growing collections, Make two cuts at 1/3 and 2/3 height. Replant the top third (la cabeza) after the cut is calloused (~1 week), and process the middle third.
Some data shows that dark storage (stressing) of the cuttings can increase mescaline content[13]. However, it has also been argued that with optimal growing conditions, stressing is not necessary. The optimal growing conditions are uncertain so stressing is recommended even though it many not always be needed. To stress the cacti, store live cuttings in a dark place for at least 3 months (e.g. in a paper bag or wrapped in newspaper).
All parts of the cactus can be used. Outer green skin yields more than the inner white core for the same dry mass[14], but mescaline is present in both parts of the plant. Outer waxy layers and spines do not yield product, they can optionally be removed but that is not necessary because they are not detrimental to the extraction.
Chop whole cacti (into for example ~1/4 inch thick slices) and dry them with (for example) a food dehydrator at low temp (~120 F). Low drying temperature is recommended because chlorophyll begins to break down at 140F and it's byproducts have a yellow/tan color that can end up in the final product (although this is a cosmetic issue only).
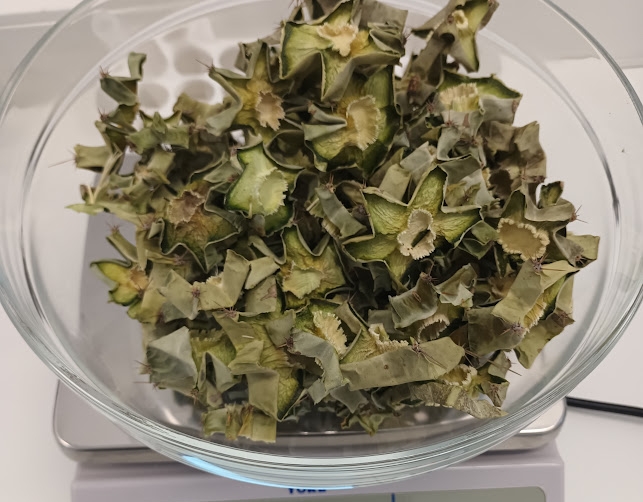
Grind dry cactus slices to a fine powder. This can be done in two steps, first through a food processor (coarse grind) and then through a coffee grinder or grain mill (fine grind). See Fig. 2a for representative images going from seed to powder.
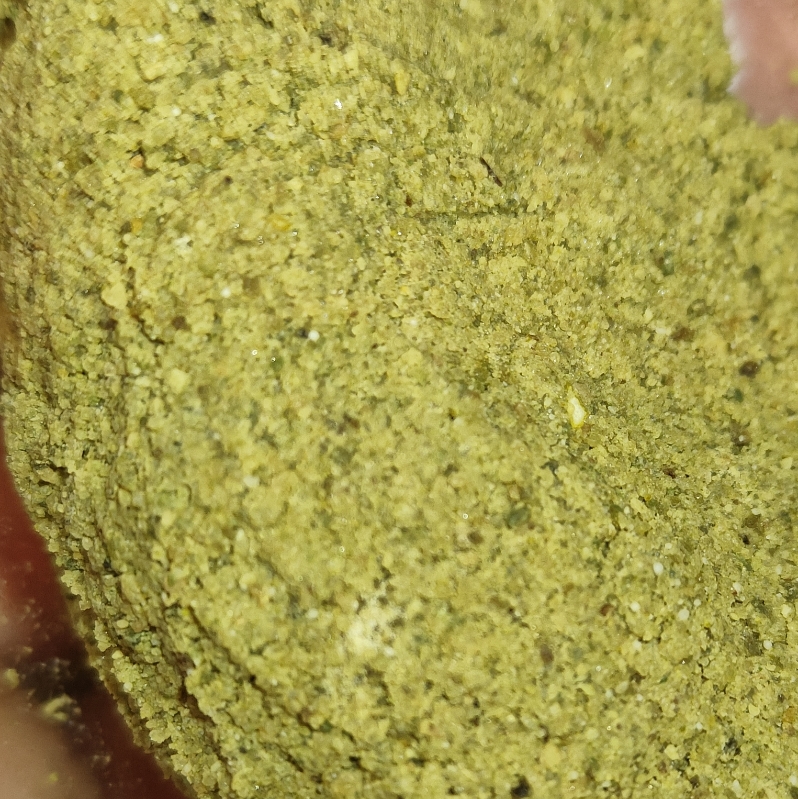
Run the powder through a flour sifter and regrind any course material caught by the sifter. It is very important to make a uniform cactus powder that is dry and finely ground. The fine grind enables good yields and proper crystallization. Clouds of fine dust fly into the air when handling a good powder, reminiscent of flour (but green). Store powder in a sealed container to avoid moisture absorption over time. Old cactus powder may change to a tan color because chlorophyll slowly breaks down over time, and still works well in this process, however same as with tan powder from excessive dry heat, the tan color may make it to the product. No differences in subjective effects have been noticed for different off-white product colors (green/yellow/tan).
Wet Crumb Mix 🟢
Mix the finely ground cactus powder and lime together until uniform. Add ~130ml of water, mix well for at least 10 minutes. Mixing can be done with a spoon or gloved hands. Alternatively, a stand mixer at low speed and is a great upgrade.
Mix well enough to have a uniform
mix with no dry spots. If dry spots remain after thoroughly mixing, add small amounts of water until no dry spots remain. Mix well after the last water addition to make sure there are no pockets of wet spots either.
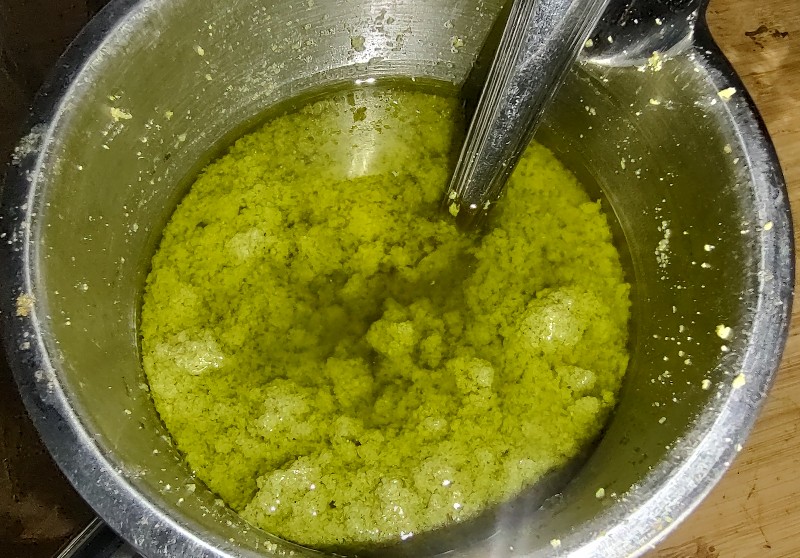
A "wet crumb" consistency should be reached (see Fig 3. Top). These wet crumbs are wet enough to stick together when cupped (see Fig 3. Bottom), and dry enough to crumble back to crumbs when broken apart.
If by mistake the mix becomes too wet the crumbs will congeal into a dough or even a paste. The extraction process will still work for wetter mixes, but excess water requires a water removal step from the solvent: See the sodium carbonate fridge rest in the appendix.
Extract 🧑🏾🔬
Transfer the wet crumbs to a french press. A food scale is recommended to keep track of the ethyl acetate. Cover wet crumbs with ethyl acetate (~225g = 250ml), stir for three minutes, and rest for one minute (see Fig. 4). The wet crumbs will break up into a sandy consistency allowing ethyl acetate to easily access all the mescaline in the plant matter. Do not stir too aggressively, such as using an electronic hand mixer, to avoid changing the pull consistency. Press extract into a clean quart jar trough two stacked coffee filters. Do not press too aggressively and watch the final trickle of liquid closely to avoid water from the crumbs being squeezed into the solvent. Some of the solvent will remain trapped in the crumbs matrix, but aim to get back at least 125g (~ 137ml) of Ethyl acetate in the first pull. Since the mix is now saturated with solvent, aim for getting al of the add mass of ethyl acetate back out in subsequent pulls.
It is normal for some plant mass to be caught by the filters, but if loose particles appear in the extract and/or the filter clogs, the wet crumbs had some dry spots from insufficient water mixing. The process will still work after putting in the extra effort to filter/decant all particles in the extract before salting in the next step. Next time, mix the crumbs thoroughly with enough water so they are uniformly sticky and properly hydrated.
Repeat the extraction with ~160g (~175ml) of ethyl acetate until the extraction jar is full (~5 total pulls). All of the added ethyl acetate in these pulls can be recovered. Optionally, the alkaloid content can be roughly tracked with pH paper (see Fig 4b.).
All of the extraction pulls should be completed within 45 minutes and combined (see Fig. 4b). After ~45 minutes the sandy plant matter will begin to congeal, making solvent penetration and recovery more difficult. Hours after the last standard pull, the congealed plant matter will have released a few ml of solvent which can be optionally added to the extraction for a minimal yield boost and increased solvent recovery. Over 90% of the solvent should be recovered.
The spent wet crumbs can be dumped in a compost pile when not raining (avoid introducing ethyl acetate into waterways). Alternatively, allow the spent plant material to dry in a ventilated area and dispose of it in the trash.
Crystallize ✨
Drop fumaric acid (~3 grams) in the extract. Alternatively, 5g of citric acid cam also be used. Extract will cloud as the dissolved organic acid reacts with mescaline freebase to form an insoluble monomescaline salt. Cloudiness may be hard to see in darker extracts (a backlight may help).There are two recommended options to complete the crystallization:
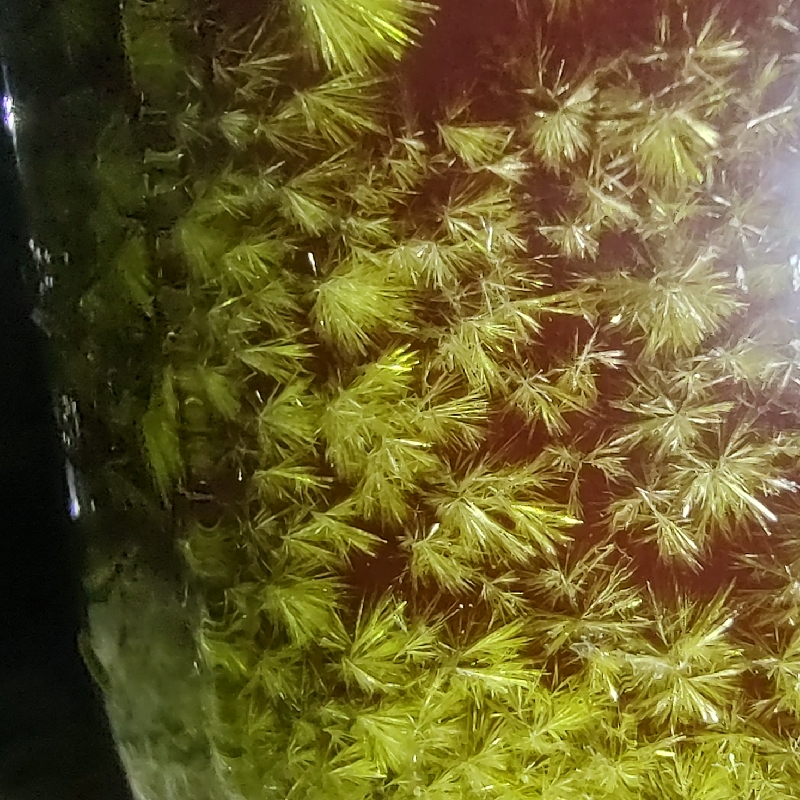
- Slow crystallization option: Allow the organic acid to dissolve by diffusion without stirring. Leave cloudy extract undisturbed and sealed with a lid. Crystals of monomescaline fumarate (or citrate) should begin to appear after a few hours, and take a few days to completely crash out (at least 3 days of wait is recommended). Crystals will sometime grow large with this method (>2mm, see Fig. 5), but not always.
- Fast crystallization option: Turn on the magnetic stirrer for faster crystallization. Monomescaline fumarate crystalizes will form quickly (typically in 30 minutes or less), while monomescaline citrate will take more time (up to two hours). The crystals will be very small and will form a powder.
The crystallization time can vary a lot, especially for beginners, so give extra time to ensure the crystallization is complete until familiar with the process. See appendix for other crystallization options.
The mescaline salt crystals cam sometimes look like undissolved organic acid to beginners. However, all the acid granules are reliably dissolved. The mescaline salt floats in the extract long enough to make a "snow globe" when shaken/stirred. Organic acid will not.
If citric acid was used and no crystals form and goo appears, the ethyl acetate contained too much water. See FAQ below for simple recovery options. If goo still results after taking the FAQ suggestions into account, please report this on the DMT nexus or the reddit forum r/mescaline.
Collect 💖
Swirl ethyl acetate to knock crystals loose. Citrate crystals that cling to the wall can sometimes be dislodged by shaking or with a knife/spoon. Fumarate crystals do not tend to stick to the wall and are easier to pour out. Send solvent through a coffee filter to catch crystals (note: do not store the filtered salted solvent in a metal can because excess acid can corrode metal). Rinse any crystals remaining on jar walls with a small amount of fresh ethyl acetate and send wash through the collection filter (a good practice to protect the metal filters basket from corrosion). Repeat ~1-2x until off color is mostly removed).
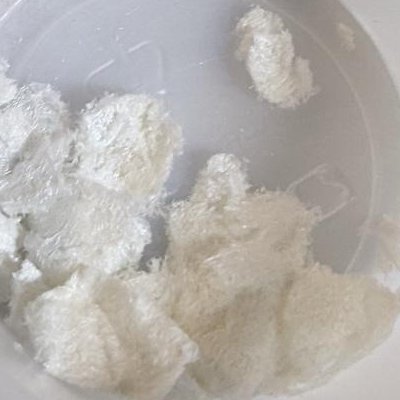
Let the filter dry and collect crystals by sliding them off the filter. Folding and rubbing the inside of the filter against itself with the palms of the hands can help loosen the last bit of crystals. This is the final product (Fig. 6).
Yield depends on the cactus and is usually between 0.3% to 3% with ~0.6% to 1.5% being common[15]. However, yields up to 8.2%[16] (5.0% mescaline HCl equivalent) have been reported. The large mescaline variability cannot be explained by genetics alone and understanding the environmental factors is a fertile scientific question waiting for new discoveries to be made. In general, healthy home grown bridgesii cacti tend to yield more than pachanoi, while peruvians have a wide range of yields and less data.
Depending on the organic acid used, the product is (1) monomescaline fumarate (anhydrous), or (2) hydrated monomescaline citrate with 1.5 molecules of water per molecule of salt (see fig 6a).
The monomescaline fumarate contains 645mg/g of mescaline and is 76% as strong as mescaline HCl. In previous versions of the TEK before we had more analysis, the dimescaline salt was believed to form. However, titration showed that product was much more consistent with the monomescaline salt.
The citrate hydrated salt has been analyzed well, since it was used in the early TEK before the benefits of fumaric were known. It contains 491mg/g of mescaline which was verified separately by Altitude Consulting measuring 492mg/g of mescaline (anonymous source). The rest of the hydrated salt is 447mg/g citric acid 63mg/g of water. The product is therefore ~58% as strong as Mescaline HCl which contains 853mg/g mescaline.
Attempting to smoke the product is not recommended as potentially unwanted compounds can form [17], [18].
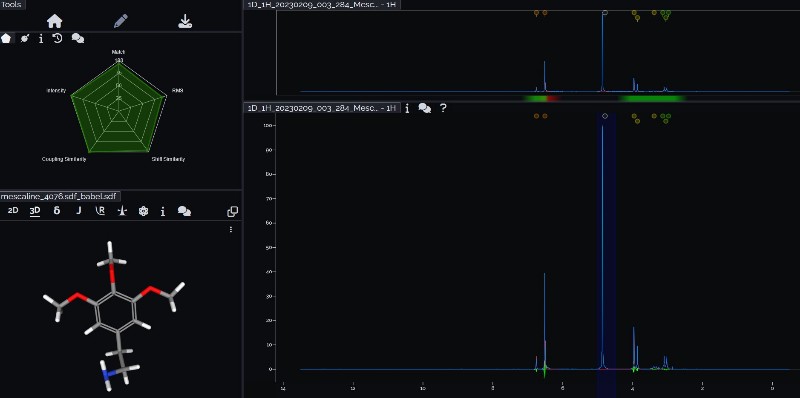
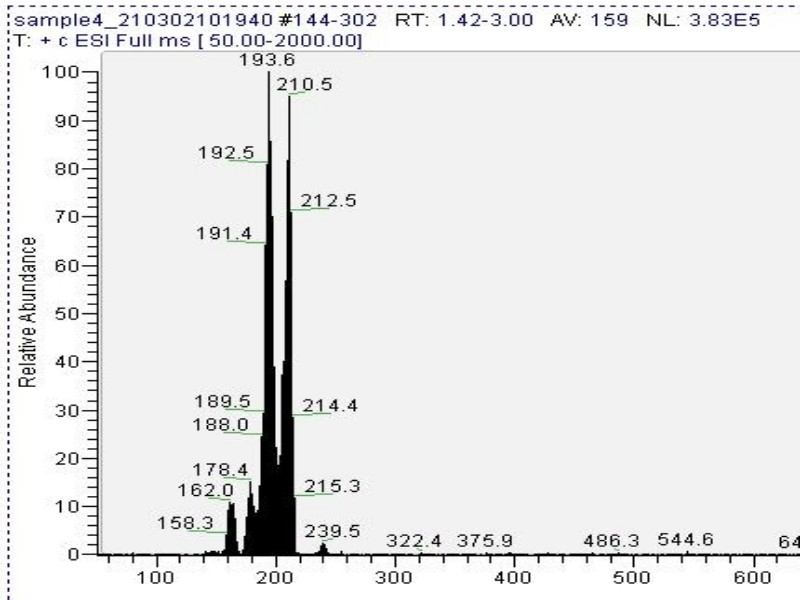
Mass spectrometry (MS) results from Solaris analytical[19] indicate the product is very clean mescaline (Fig. 7a) in one example where pachanoi was used. It is unknown if cacti with different starting starting alkaloid profiles would give the same result, and more data is needed to make that claim.
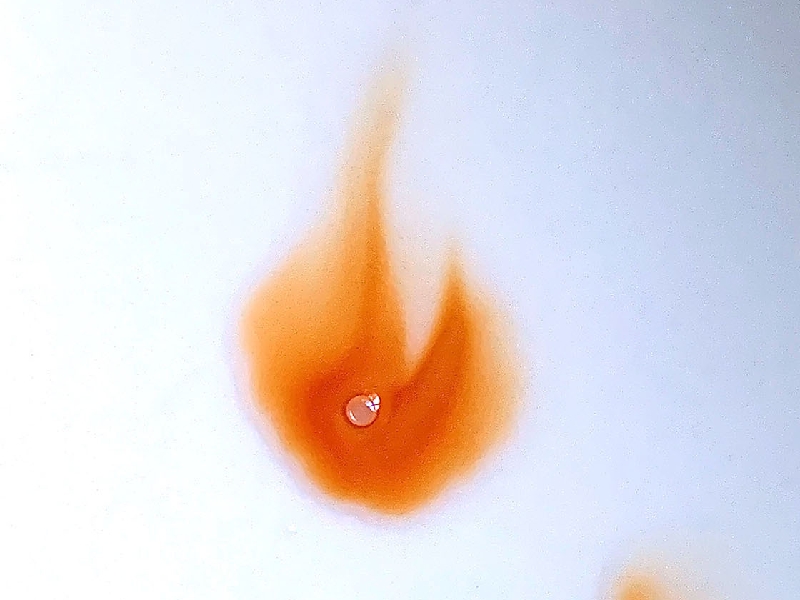
Testing the product with fresh or well stored marquis reagent gives a bright orange color as expected[20] (see Fig. 7b). Several reagent results for the product from this TEK have been published by _Trip_[21]. Note that marquis reagent may expire after a few months depending on storage conditions after which the reaction color is invalid/brownish.

Tip: The coffee filter used to collect the crystals can be re-used upside-down before salting the next extract. Any small crystals not collected may be forced into the extract and subsequently act as seed crystals for the next extraction[22].
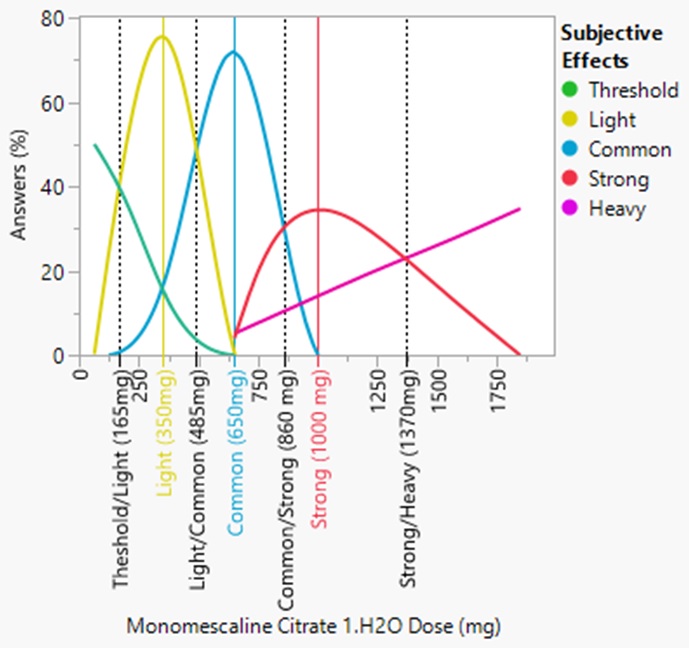
Dosage ⚕️
The mescaline experience is subjective. It can vary by individual and can be affected by the environment. Natural settings usually go well with the mescaline experience. A small group of trusted loved ones or close friends also goes well with the experience. When deciding on a dose for a desired experience classification[23], the results of several non-scientific poll results indicate the following for monomescaline citrate 1.5H2O (see Fig 7c):
- Threshold: 100 - 165 mg, average 133mg
- Light: 165 - 485 mg, typically 350mg
- Common: 485 - 860 mg, typically 650mg
- Strong: 860 - 1370 mg, typically 1000mg
- Heavy: >1370mg
For monomescaline fumarate, divide these doses by a factor of 1.3.
Reuse 💚
Reusing solvents is simple, environmentally friendly, economical, and highly encouraged[24] at the DMT nexus.
To reuse, the excess organic acid will be removed. The green chlorophyll does not interfere with the process and will remain. There is no limit to the number of reuses.
Before washing solvent, check for new crystal grown and collect any new product if present. Sometimes, a small amount of product precipitates after the main collection.
It is not necessary to remove the green/dark color present in the solvent because it does not affect the TEK and remains stable after many reuses (chlorophyll saturation). Also, any mescaline that does not crystallize in the main extraction will mostly remain in the ethyl acetate during regeneration.
Do not store salted solvent in metal cans. The excess citric acid can make them rust. It is ok to store neutralized/washed solvent back in the original metal can long term. Another long term storage solution is a mason jar sealed with a plastic lid resistant to ethyl acetate[25].
There are two options to regenerate the solvent. The option that uses a magnetic stirrer is a lot less work and is recommended.
With Magnetic Stirrer
Add a tablespoon of sodium carbonate and a teaspoon of water to the solvent, cover loosely, and magnetically stir until pH strips roughly match fresh EA after. The reaction is very quick for fumaric acid (seconds), but can take up to half a day for citric acid. If no pH strips are available, 12 hours of magnetic stirring should be enough.
If citric acid is being removed, a cloudy haze of sodium citrate from the neutralization reaction will appear over time (best seen by shining a light). If the solvent has enough water, hydrated sodium citrate subsequently forms and drops out of solution as a wet white solid layer. If cloudiness persists after 12 hours, remove the washing soda, add a tablespoon of water, and check again after another 12 hours. Repeat until cloudiness disappears.
Once the neutralized extract is clear (a backlight can be seen through the solvent), stop the magnetic stirrer, rest the solvent for a few minutes, and pour off the neutralized clear extract from the wet clumped up solids (sodium carbonate and sodium fumarate/citrate) through a coffee filter. Wet salts can be sticky and that is normal. The solvent is now reclaimed and ready to use.
Note: if the xtalization during the main TEK did not completely finish (impatience, mistake, etc), the reclaimed solvent will carry any residual mescaline to the next extraction and pH paper could be slightly green (see Fig. 4b).
Without Magnetic Stirrer
Are you sure you don't want a magnetic stirrer? Regeneration of one quart of solvent is done in two steps:
1) Add a tablespoon of sodium carbonate and 50ml of water to the extract. Shake vigorously, releasing CO2 gas as citric acid reacts with sodium carbonate. Neutralization can be verified with pH paper matching fresh EA and/or the absence of pressure buildup. If excess citric acid is used (above the TEK's main recommendation) more sodium carbonate may be needed for neutralization (0.83 parts sodium carbonate neutralize 1 part citric acid). It is important to remove all the citric acid and it can take 5 minutes or more of shaking to fully neutralize the extract. A water layer may form above the excess sodium carbonate and the extract will cloud. After resting for at least an hour, decant neutralized extract into new jar (you may need to leave a small amount of solvent behind when decanting: it can be added to the next extraction's neutralization). Optionally, use a separatory funnel to recover all of the neutralized extract.
2) Wash neutralized solvent with a tablespoon of salt and ~50ml of water. The solvent cloudiness will change after shaking for a few minutes. Rest the solvent in the fridge for a few hours until a backlight shines through clearly. Decant into a long term storage container (e.g. original solvent can if empty). As before, you will need to leave some solvent behind which can be added to the next brine wash). Optionally, use a separatory funnel to recover all of the washed extract.
Frequently Asked Questions ❓
Q: I froze my cuttings on the freezer, is ok to proceed with the TEK?
A: Probably not. Fully freezing the cuttings will change the consistency of the cactus/lime/water mix during the pull, resulting in a pancake-like batter mixture and low yield [26]. If you can still produce a fine powder and find a way to make the process work please share your result with the community on the dmt nexus.
Q: My plants died. Can I extract them with this process?
A: Dead dry plants have been used successfully as long as they can be dried well and ground to a fine powder. Moldy parts have also worked with no apparent issue, but users need to assess the possibility of mycotoxins for their case. In extreme cases such as a deep freeze to the core they may not be usable (see previous FAQ).
Dead plants will have some chlorophyll degradation which can give the final product a tan color. This is only cosmetic.
Q: I bought cactus powder only and I'm getting a low yield, is this normal?
A: Yes. Online powders typically yield below 1%, with 0.5% or less being common. Buying powders online is strongly discouraged as it can finance poaching and plant destruction in natural habitats. Instead, grow your own cacti if possible. If not possible, go out there and make it possible. However, be warmed that mescaline is a gateway drug to gardening.
Q: Does increasing the basing time increase the yield?
A: No. Shroombee has tested 15 minute, 24 hour, and 72 hour basing times and there was no difference in yield. Other process variables were 8 minutes incorporating milky water with cactus, 6x3 minute pulls, and 15 mg/gram citric acid added with the fast crystallization method. Loveall has confirmed in his experiments that 10 minute and 24 hour basing times produce the same yield. So we assume that any basing time from 10 minutes through 72 hours will produce the same yield. See a detailed explanation in this post.[27]
Q: I got an emulsion while pulling, what do I do?
A:If an emulsion forms, the cactus/lime/water mix was too watery. Add lime, dry magnesium sulfate, and more ethyl acetate until solvent is released. Keep the lime to magnesium sulfate ratio above 1 to ensure cactus mix remains alkaline[28]. Next time, use less water to make the cactus mix.
Q: Why is fumaric acid recommended over citric acid?
A: The main reason is that fumaric acid is leas sensitive the water in the EA. The process window for water content is much larger. Other benefits include:
- Faster crystallization - Less sticking of the salt to the jar walls - More complete precipitation of the last traces of mescaline salt (needs analytical confirmation a - Less likely to keep the color of brown powder from chlorophyll breakdown (but this is only cosmetic) - Stronger by weight than the citrate salt by a factor of 1.3 - Faster regeneration reaction
Downsides are (1) fumaric is more difficult to find in stores than citric, but homebrew shops do carry it sometimes, and (2) there is less analytical data confirming purity and stoichiometry.
Q: I have a bottom separate layer in my pulling jar. What is it and what do I do?
A: It is a gunky water layer. This can happen if you squeeze the French press aggressively and/or the initial cactus mix is too wet. Remove the bottom layer using a pipette/syringe, separatory funnel, or decanting. Do a sodium carbonate partial dry, and continue the TEK.
Q: I have citric acid which contains <2% SiO2 anti-caking agent. Can I use it in the TEK?
Yes, it should work despite the unwanted additional chemical. It is usually a lot less than 2% SiO2.
If used as is, there will have a small amount of SiO2 in the product, <100mg if 5g were used for salting <2%), but it is probably a lot less.
Alternatively, the adulterated citric acid can be dissolved in water. Any SiO2 won't dissolve and can be separated out. Evaporate the water to recover purer citric acid. Note that this citric acid will be hydrated and mass may increase slightly, but that is not an issue.
Q: I heard of people using more citric acid and shaking. What’s the difference between the two crystallization methods?
A: In general, adding more citric acid and aggressively stirring or shaking will:
- Force crystals to form faster
- Form smaller and denser crystals (can be powdery in appearance) less likely to stick to the jar walls
- Cause a negligible amount of tiny crystals to drop through the coffee filter.
Q: What is the upper limit of citric acid that can be added to the extract?
A: The solubility of citric acid monohydrate in ethyl acetate is over 50 mg per gram of ethyl acetate[29]. Note that plant matter or other unwanted extraction products (such as water) may affect the solubility. Stay well under 50 mg/gram limit and do not chemically dry the extract to ensure no undissolved citric acid is mixed in with the mescaline citrate. Under mostly anhydrous conditions the solubility of anhydrous citric acid in ethyl acetate has been measured as low as 10mg/g [30].
Q: After adding citric (or fumaric) acid, I saw clouds followed by precipitation, but the precipitate reminds me of citric (or fumaric) acid. How do I know a mescaline salt is precipitating and not citric acid?
A: Citric (or fumaric) acid is not part of the precipitate after 3 days. It goes in solution because it is well bellow its solubility limit in wet Ethyl Acetate (~50mg/g for citric and ~10mg/g for fumaric). The white particles that form from the clouds after the organic acid is added and dissolved are mescaline salts.
Only exception to this is if one deviated from the TEK (e.g. by doing a freezer reset or used a chemical drying agent), and dried the Ethyl Acetate too much.
Note that product crystal morphological can vary a lot and sometimes look like acid granules. Do not allow this to confuse you.
Some beginners still doubt that all the solid organic acid dissolves. To verify solubility directly, add 1mg/g of acid to the used extract after product collection and verify it all dissolves.
Q: After adding citric acid, nothing precipitated, what gives?
A: Some water is needed for the salting crystals to form. Add a few drops of water and check for clouding.
If the drops of water initiate clouding, add 0.5% water and check for xtalization after a few days. If no xtalization repeat the drop test and add another 0.5% water if new clouds form. Next time you perform the TEK, think about how you may have made the extract too dry or ask on the online forums.
If clouds do not form, check the jar walls, a transparent product may have precipitated there (e.g. this has been reported for whole bridgesii[31]).
If product did not precipitate on walls as a transparent film, bring up the citric acid concentration up to 20mg/g and wait a few days. Higher citrate concentration can help a initiate xtalization, but this borderline case is rare.
If your cactus does not contain mescaline, no mescaline citrate will form. It is possible to have bunk cactus, especially if bought as powder online (which should never be done). Under certain conditions, PC cacti can struggle to yield anything significant.
Q: After adding citric acid, goo/oil precipitated instead of crystals, what gives?
There was an issue with the citric/water/mescaline ratio in the solvent when salting. For most people, too much water was their issue, but too little citric acid or not enough water can also cause problems. Low yielding plants have narrower process windows for xtalization. However, an issue with ratios can be reliability avoided with good cacti (>0.4% mescaline) and good TEK execution.
In one example from Cheelin the goo was 65% mescaline citrate[32]. In another example, goo was measured to be roughly equal parts water, citric acid, and mescaline citrate [33].
Tips to reduce changes of goo:
- Ensure you are using an active cactus (>0.4% mescaline). Low mescaline concentrations can fall outside the proper crystallization process window. People may encounter this when using low potency PC plants (note that not all PC plants are low potency for unknown reasons).
- Good wet crumb consistency
- Not excessively squeezing the French press
- Perform the sodium carbonate partial dry.
Before salting it is important to ensure water and debris are not present. Tilting the extract and shining a flashlight are needed for a good check. Take your time, especially the first time you try the TEK.
Alternatively, to reduce the water percentage before salting, , Shroombee suggests to add fresh ethyl acetate (usually relatively dry from the manufacturer) to the extract [34]. This can increase robustness if any water is missed by a novice. For example, by adding ~100g of fresh ethyl acetate to a quart of extract.
Some people recommend a freezer rest followed by filtering off the ice crystals that form. This is very effective at removing large amounts
of water if the TEK has not been done properly. However, if a lot of water is removed with this technique, about 1% water needs to be added back before salting for good crystallization dynamics. This is a gross sledgehammer for water removal, and may be useful for those who don't trust their cactus mix skills or have fridge/ambient temperature issues (e.g. fridge is set to warm and/or crystallization environment is set too cold).
If you continue to encounter goo even after taking all this information into account, please report it on the forum.
Q: I recovered the goo/oil precipitate instead of crystals, what do I do?
A: A simple recrystallization with 99% IPA is recommended.
- Dissolve the goo in minimal heated 99% IPA (using a hot water bath and a covered but unsealed small mason jar jar) until only white solid mescaline citrate remains undissolved (will look like small fine particles). Note: If a lot of IPA is used all the mescaline citrate may dissolve, while unnecessary, this is not detrimental.
- Seal/tighten the bar and move the IPA to the freezer for 24h where more mescaline citrate will precipitate.
- Collect the precipitate in a filter and rinse with a small amount of freezer cold 99% IPA.
- Immediately press the outsides of the folded collection filter into absorbent paper towels until dry so the cold product does not have a chance to absorb air moisture and liquify.
Q: How quickly can the extraction process be done?
A: With experience, and by skipping the fridge rest step it is possible to go from raw cactus powder to dry crystals in under an hour by choosing a fast crystallization method. The first documented world record is 48 minutes to go from cactus powder to dry mescaline crystals ready to use.[35]. However, there is an increased risk of obtain goo without the fridge rest step. The express process is not recommended for newcomers.
The world record was beat in October 2024 with a time of 32 minutes by an anonymous contributor.
Example CIELO process for record seekers (raw cactus powder to pure mescaline citrate):
- Prepare ingredients for world/personal record and start timer
- Turn on stand mixer with 1 part cactus and add in order 0.22 parts lime until uniform (seconds), 1.33 parts ice cold water (seconds), and finally 2.22 parts fridge cold ethyl acetate. Stand mix for a few minutes
- Strain/filter mixing bowl solvent into jar over mag stirrer with mag stirrer rod (a fine metal pasta strainer pushed down into the mixing bowl can be helpful)
- Add another 2.22 parts fridge cold ethyl acetate to sand mixer for second pull for a few minutes (go to next step before this one finishes)
- While stand mixer runs with second pull, turn on magnetic stirrer with first pull and add 0.055 parts of citric acid
- Strain second pull into xtalizing extract
- Decide if any more pulls are needed
- Decide when to stop the xtalization
- Collect xtals in coffee filter, rinse with fresh EA, and dry quickly (e.g. with a paper towel press followed by hot hair from a hair dryer).
To make the record official the following conditions must be met:
1) Total yield must be above 1.1%
2) Another pull needs to done after the timer stops and must yield less than 0.06%
3) Original dry yield must be measured again after two hours with no weight loss detected from solvent evaporation
4) Magnetically stir the salted extract for two more hours. Any new mescaline citrate must be below 0.06% yield.
Q: The cactus mix congealed in ethyl acetate very quickly and I couldn't finish the timed pulls with a sandy consistency. How can I give myself more time?
A: Try using less water and/or lower temperature ethyl acetate next time.
1) Excess water can accelerate congealing and decrease yield as it is harder to extract.
2) Higher summer temperature pulls in the summer can also accelerate congealing. Keep ethyl acetate in a cool place. Consider using fridge cold ethyl acetate.
Q: Why do I need to neutralize the extract before re-use?
A: Salted extract is acidic due to excess citric acid. The citric acid will react with the lime in the cactus mix releasing small particles of calcium citrate into the extract, making a cloudy mess. While it is possible to rest/settle/decant these particles off with time, neutralizing the extract and washing it is recommended by default.
However, if the operator would rather deal with calcium citrate as part of the extraction process, reclaiming the solvent is not needed. The resulting calcium citrate can be used as a supplement.
Q: I have old resin and/or tea and would like to extract mescaline for a measured dose, can CIELO be used?
A: Yes! Adding resin or even tea to the cactus mix works. Increase the amount of citric acid accordingly (e.g. 50% if 50g of dry cactus is added).
Q: Is there a lingo for this TEK
A: Yes, the clouds formed after salting are called "nubes" and the star shaped crystals growing on the jar walls as they clear "estrellas". These are the Spanish words for clouds and stars. You can practice your Spanish while doing this TEK. For example:
San Pedro vio nubes transformarse en estrellas en el cielo
Translates to
St. Peter saw clouds transform into stars in the sky
Q: Is there a video example of this TEK?
Yes, see for example https://youtu.be/-uQo7Xka8_c. The video does not wash the product with fresh EA, which leaves a light cosmetic green color behind.
Appendix: Development Notes 🔬
Wet Crumbs 🌵
No improvements were seen with longer basing time, oven drying, or increasing the ionic strength with CaCl2. Microwave treatment or boiling water resulted in a small yield loss.
Mix made with sodium carbonate failed. Material congeals very quickly and requires long solvent soaks which are darker and don't crystallize to large loose crystals (small sticky crystals were obtained).
Use of lime and boiling water causes the saponification of chlorophyll over time [36]:
Chlorophyll is soluble in Ethyl Acetate, but Chlorophyllin and Phytol are not[37]. Saponification in hot water gives an extract with less plant matter and lighter color, however yields where slightly lower with this approach.
Extract 👨🏾🔬
Tests with longer/warmer pulls resulted in darker extract, smaller crystals, more solvent absorption by cactus mix, faster congealing of plant mix, stickier crystals and no yield benefit.
Colder ethyl acetate (e.g. fridge temperature) the works fine with no yield loss and less smell. It can be used if desired. It is not mentioned as an option in the main TEK for brevity.
Chemically drying the extract with anhydrous CaCl2 had no benefits, while drying with MgSO4 was problematic. However, depending on the worker and techniques used, a chemical dry with CaCl2 pellets (available commercially as de-icer) could reduce water content in the solvent and possibly make crystallization easier. Washing soda (when sold as Na2CO3 in monohydrate form, or when making the anhydrous form from baking soda with an oven) also dried the extract and can be beneficial in cases where the cactus/lime/water mix was made improperly with too much wetness, and this process is now detailed in the next section.
Ethyl acetate has been shown to not as strong as chloroform in LLE extractions[38]. However, it is great for our purposes here because of wet crumbs penetration and citric acid (or fumaric acid) solubility.
Partial Dry (required if mix became a dough instead of wet crumbs) 🧐
Beginners may use too much water in their cactus/lime/water mix, making it a dough instead of wet crumbs. The additional water can make it into the extract and interfere with xtalization, causing goo (a brown syrupy mix of mescaline citrate, citric acid, and water)
If a dough was made during the mixing step, to ensure water levels are correct, add a tablespoon of washing soda to the extract, shake for a few minutes, and rest overnight in the fridge. The washing soda will absorb some water and partially clump* ♡. Filter the extract and proceed to the next step.
*If all the washing soda clumps up or a water layer forms, the extract is still too wet. You are at a risk of goo. Isolate the extract and repeat the partial dry until some washing soda does not clump. Next time, improve your mixing process (fine grind of well dried cactus and mix thoroughly adding water slowly giving it time to fully incorporate before adding more).
♡If none of the washing soda clumps, congrats! This is an indication that your extract was not excessively wet and you could have salted it directly.
Crystallize ✨
Alternative crystallization options:
- Fast crystallization option: Use a magnetic stirrer to dissolve the citric acid and speed up crystallization. This produces a fast crystallization and minimizes crystals that are stuck to the wall. A stirring vortex will go from visible, to not visible as clouds form, to visible again as mescaline citrate precipitates (see Vid. 1). Crystallization is complete within two hours for almost all situations, but can vary a lot depending on the starting conditions (mescaline percent, water content, temperature, stirring speed, etc). Crystals will be very small with this approach and look like a powder. The crystals should still be large enough to be caught by a filter in almost all situations, but if some are not caught, slowing down the magnetic stirrer will produce larger granules in subsequent runs. The resulting powder is dense and easier to pack in capsules compared to the long needles, but not as pretty to look at (see Fig. 8aa).
- Shaken: After adding the citric acid, shake the sealed jar vigorously. The citric acid will dissolve quickly and small crystals will precipitate as the shaking continues. After 15 minutes, shaking will crystallize most (but not necessarily all) of the product out of solution quickly.
- CASEA: Endlessness has reported success with this method. In his words[39]:
I added 11.1g anhydrous citric acid in 250ml ethyl acetate. It did not dissolve much at all, even after overnight stirring in a magnetic stirrer and some time in the ultrasonic bath.So I decided to add water in small amounts until it all dissolved. It took about 5ml water for the citric acid to dissolve completely.
So I added all the 250ml CASEA, and there was immediate clouding. After 1 hr it looked like this (see Fig. 8a):
During crystallization, excess citric acid (H3Cit) reacts with free base mescaline (Mes) to form to form the monomescaline citrate salt (MesH)H2Cit, which preliminary NMR results indicate could be a hydrate:
By not using excess citric acid, different salt forms can be precipitated[40], but that process is more complex than the simpler excess citric acid approach, and the other salt forms can form goo.
There is a lot room for excess citric acid in solution since its solubility is 50mg/g in ethyl acetate. In extracts with crystallization issues, adding more citric acid can help force precipitation: in one example with whole cactus powder 20mg/g was used [41].
Several factors can make crystals smaller: Reusing ethyl acetate, longer/warmer pulls, higher citric acid concentration, mechanical agitation, and other potential variables. Small crystals can look like a fine powder. Potency does not seem affected by the crystallization appearance, and a powdery precipitate is not a problem unless it becomes difficult to decant/filter.
After the initial crystallization, adding more citric acid and/or moving the extract to the refrigerator does not result in any more precipitation. Moving the extract to the freezer produced ice crystals.
Other dry organic acids have been tested[42],[43]. Fumaric and tartaric crystallized well as and could be a substitute for citric. Malic also crystallized but took longer to do so. Crude mass measurement indicated the anhydrous monomescaline form for the fumarate salt. See Fig. 8b for resulting citrate, tartrate, fumarate, and malate crystals. Succinic also crystallized from a chemically dried extract (without drying crystals did not form[44]) as the monomescaline form (see Fig. 8c). Ascorbic, did not crystalize well. Other organic acids (lactic, oxalic, etc) have not been tested yet at the time of this writing. For the organic acids that crystallized, Mescaline HCl equivalent is:
- Monomescaline Citrate 1.5 H2O: 58%
- Dimescaline Fumarate 92% (Titration analysis from Nov 2025 indicates this is NOT the salt that forma with CIELO [45]
Monomescaline Fumarate:76%
A good alternative to citric acid is fumaric acid, which is also used in the food industry. Since the fumarate salt does not interact with water, it has a larger process window: less prone to form goo or stick in excess water conditions. It is also more concentrated, with 1.60 times more mescaline per gram compared to the citrate salt (monomescaline citrate 1.5H2O).
For a comprehensive reference of mescaline salt weight conversion see orchidist's calculator[46].
10% sulfuric acid was tested and while some crystals formed, a separate liquid layer also appeared making the process not practical. HCl has not been tested as it may break down ethyl acetate, but a careful titration of a dry extract with concentrated HCl may work (however this is not considered lazy or a low hazard and committed from CIELO options).
Collect 💖
Washing crystals in the filter with a splash of fresh ethyl acetate wicks away plant colors very effectively. It is the ultimate lazy purification method.
Any product stuck to the jar walls tends to be small. Minor amounts of xtals on the wall are normal, but if a lot of it sticks to the wall, the cactus mix could have been too wet and/or the ethyl acetate was too warm. The laziest way to collect this small amount of product is to dissolve it in water used in the next extraction.
Reuse 💚
Dark extract can be cleared up with activated carbon (also called activated charcoal). Use dustless pellets (typically rinsed with water and dried before use). Use the pellets statically so they don't release difficult to filter carbon powder. Clearing process takes time, especially for dark solvents used many times and saturated with plant matter. It may take several days to notice a change in very dark solvent, and weeks to completely clear it.
Manually passing the EA through a home made carbon filter a few times won't work. A recirculation system at 1000 GPH would time and pass the quart of EA through the filter thousands of times before beginning to clear the EA.
Any benefit to using activated charcoal to decolor the used solvent is not clear (pun intended). Also, the environmental benefit of regenerating to a colorless solvent is in question since ethyl acetate is easy to produce and activated charcoal requires resources to manufacture. However, if the activated charcoal itself can be regenerated (e.g. in a hot oven) it may be economical to use it if a colorless solvent is wanted. However, there is no benefit to this other than aesthetics since the final product is the same regardless of the color of the starting solvent (provided some fresh ethyl acetate is available for the rinse).
References 🗝️
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sowing Cactus Seeds[1]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cactus growing guide (PDF)[2]
- ↑ Huachuma Collective Talk[3]
- ↑ Huachuma Collective statement 2023 (PDF)[4]
- ↑ Huachuma Collective statement 2024 (PDF)[5]
- ↑ DMT nexus website[6]
- ↑ Reddit community [7]
- ↑ Ethyl acetate safety[8]
- ↑ Citric Acid Safety[9]
- ↑ Al vessel issue[10]
- ↑ Suitable pH strips [11]
- ↑ Paper with vertical signal[12]
- ↑ Dark storage data[13]
- ↑ Result for different cactus parts[14]
- ↑ Cactus analysis thread[15]
- ↑ High bridgesii yield[16]
- ↑ Citric acid heat degradation[17]
- ↑ Direct heat vaporization test[18]
- ↑ Solaris analytical service[19]
- ↑ Marquis reagent result[20]
- ↑ Reagent results[21]
- ↑ Filter reuse[22]
- ↑ Experience Classification[23]
- ↑ On reusing non polar solvent[24]
- ↑ Plastic lid resistant to ethyl acetate[25]
- ↑ Freezing cutting result[26]
- ↑ Basing time tests results[27]
- ↑ Lime and magnesium sulfate ratio vs pH[28]
- ↑ Citric acid solubility[29]
- ↑ Anhydrous citric acid solubility test[30]
- ↑ Whole bridgesii precipitate on jar walls [31]
- ↑ Goo conversion to crystals[32]
- ↑ Goo measurements[33]
- ↑ Fresh ethyl acetate to lower water content before salting[34]
- ↑ Plant to crystal record [35]
- ↑ Hot water saponification with lime[36]
- ↑ Phytol not present in Ethyl Acetate plant extract[37]
- ↑ LLE extractions with Ethyl Acetate[38]
- ↑ Endlessness' CASEA[39]
- ↑ Trimescaline citrate candidate[40]
- ↑ Ethyl acetate approach[41]
- ↑ Organic acid tests[42]
- ↑ Succinic test[43]
- ↑ Wet solvent succinic salting[44]
- ↑ Titration showing monomescaline fumarate[forum.dmt-nexus.me/threads/ethyl-acetate-approach-cielo.363620/post-3975576]
- ↑ Orchidist's mescaline salt calculator[45]