Difference between revisions of "Dissociative"
Mindlusion (Talk | contribs) |
(→Arylcyclohexylamines) |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ==What is it?== | ||
| + | |||
Dissociatives are a class of hallucinogen, which distort perceptions of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment - dissociation - from the environment and self. This is done through reducing or blocking signals to the conscious mind from other parts of the brain. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include sensory deprivation, dissociation, hallucinations, and dream-like states or trances. Some, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria. Many dissociatives have general depressant effects and can produce sedation, respiratory depression[citation needed], analgesia, anesthesia, and ataxia, as well as cognitive and memory impairment and amnesia. | Dissociatives are a class of hallucinogen, which distort perceptions of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment - dissociation - from the environment and self. This is done through reducing or blocking signals to the conscious mind from other parts of the brain. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include sensory deprivation, dissociation, hallucinations, and dream-like states or trances. Some, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria. Many dissociatives have general depressant effects and can produce sedation, respiratory depression[citation needed], analgesia, anesthesia, and ataxia, as well as cognitive and memory impairment and amnesia. | ||
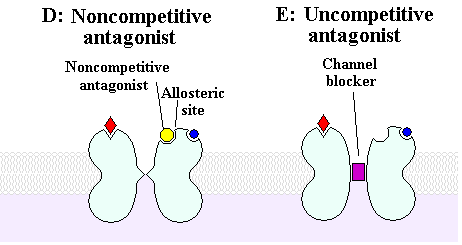
The primary area of activation for dissociatives is blockade of the Ca++ ion in the NDMA receptor. Also known as '''uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists'''. | The primary area of activation for dissociatives is blockade of the Ca++ ion in the NDMA receptor. Also known as '''uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists'''. | ||
| − | + | Noncompetitive antagonists result in the same effect on the receptor, but achieve it in a slightly different way. | |
| − | See images D & E | + | See images D & E [[File:NewNMDA.PNG]] |
| − | + | Dissociatives can also be classified by molecular structure. The most well known dissociatives used recreationally and in medicine are known as '''arylcyclohexylamines''' [[File:Arylcyclohexylamine.gif]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | Dissociatives can also be classified by molecular structure. The most well known dissociatives used recreationally and in medicine are known as '''arylcyclohexylamines''' | + | |
Another well known dissociative Dextromethorphan (DXM) has a very opioid like structure. It is classified as a '''morphinan''' | Another well known dissociative Dextromethorphan (DXM) has a very opioid like structure. It is classified as a '''morphinan''' | ||
| + | ==NMDA receptor antagonists== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Safety_profile | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * NMDA receptor antagonists | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Dissociation, Anesthesia, Analgesia(neuropathic pain), Euphoria, immersive out of body experiences (The Hole), auditory hallucinations | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Raised blood pressure (Hypertension), loss of motor coordination (Ataxia), Confusion and disorientation, increase in heart rate, slurred speech | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Addiction (psychological dependency), delusions of grandeur, risk of accidental self-injury due to analgesic effects (high doses), chronic exposure [<5g per day] causes urinary tract and bladder damage (ketamine) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Dissociatives can seem like they are too good to be true in comparison with serotogenic hallucinogens because they ARE! They carry serious longterm mental and physical risks with their usage. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | ===Adamantanes=== | |
| − | |||
Amantadine | Amantadine | ||
| + | |||
Memantine | Memantine | ||
| + | |||
Rimantadine | Rimantadine | ||
| − | Arylcyclohexylamines | + | |
| + | ===Arylcyclohexylamines=== | ||
| + | |||
Dieticyclidine | Dieticyclidine | ||
| + | |||
Esketamine | Esketamine | ||
| + | |||
Eticyclidine | Eticyclidine | ||
| + | |||
Gacyclidine | Gacyclidine | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [http://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/Ketamine Ketamine] | ||
| + | |||
Metaphit | Metaphit | ||
| − | Methoxetamine | + | |
| + | [http://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/MXE Methoxetamine (MXE)] | ||
| + | |||
Neramexane | Neramexane | ||
| − | Phencyclidine (PCP) | + | |
| + | [http://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/PCP Phencyclidine (PCP)] | ||
| + | |||
Phenylhexylcyclopyrrolidine | Phenylhexylcyclopyrrolidine | ||
| + | |||
Rolicyclidine | Rolicyclidine | ||
| + | |||
Tenocyclidine | Tenocyclidine | ||
| + | |||
Tiletamine | Tiletamine | ||
| + | |||
Methoxydine (4-MeO-PCP) | Methoxydine (4-MeO-PCP) | ||
| + | 3-MeO-PCP | ||
| + | 3-MeO-PCE | ||
| + | 3-MeO-PCPr | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3-MeO-PCPy | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Morphinans=== | ||
| − | |||
Dextromethorphan | Dextromethorphan | ||
| + | |||
Dextrorphan | Dextrorphan | ||
| + | |||
Methorphan | Methorphan | ||
| + | |||
Morphanol | Morphanol | ||
| − | Others | + | |
| + | |||
| + | ===Others=== | ||
2-MDP | 2-MDP | ||
| + | |||
8A-PDHQ | 8A-PDHQ | ||
| + | |||
Aptiganel | Aptiganel | ||
| + | |||
Dexoxadrol | Dexoxadrol | ||
| + | |||
Diethyl ether | Diethyl ether | ||
| + | |||
Dizocilpine | Dizocilpine | ||
| + | |||
Etoxadrol | Etoxadrol | ||
| − | + | ||
Midafotel | Midafotel | ||
| + | |||
NEFA | NEFA | ||
| + | |||
Nitrous oxide | Nitrous oxide | ||
| + | |||
Noribogaine | Noribogaine | ||
| + | |||
Perzinfotel | Perzinfotel | ||
| + | |||
Remacemide | Remacemide | ||
| + | |||
Selfotel | Selfotel | ||
| + | |||
Xenon | Xenon | ||
| + | == κ-opioid agonists== | ||
| + | kappa-opioid agonists are an entirely different type of drug that can have dissociative effects. | ||
| + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%CE%9A-opioid_receptor κ-opioid wikipedia page] | ||
| − | + | Very little is known about this receptor and its effects on the body. Evidence points towards dynorphin, the endogenous κ-opioid agonist, to play a major role in substance addiction. | |
| − | + | {{Safety_profile | |
| + | | | ||
| + | * κ-opioid receptor agonists | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Dissociation, Dysphoria (occasional euphoria), immersive out of body experiences, strong visual and auditory hallucinations, potential to aid addiction recovery | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Strange, uncomfortable body sensations (physical pressures), loss of motor coordination (Ataxia), Confusion and disorientation, increase in heart rate, temporary paralysis, extreme fear | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * Risk of accidental self-injury due to intense dissociation (deleriant effects), (READ DANGEROUS OF [[Ibogaine]]) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * [[Ibogaine]] has some serious health risks and should be researched further before dosing. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | [http://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/ | + | 2-EMSB |
| + | |||
| + | 2-MMSB | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alazocine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bremazocine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Butorphanol | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cyclazocine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cyprenorphine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dezocine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enadoline | ||
| + | |||
| + | Herkinorin | ||
| + | |||
| + | HZ-2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/Ibogaine Ibogaine] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ketazocine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Metazocine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nalbuphine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nalfurafine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nalorphine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Noribogaine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Phenazocine | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pentazocine | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://wiki.dmt-nexus.me/Salvinorin Salvinorin A] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Spiradoline | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tifluadom | ||
| + | |||
| + | U-50488 | ||
Latest revision as of 00:15, 3 May 2013
Contents
What is it?
Dissociatives are a class of hallucinogen, which distort perceptions of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment - dissociation - from the environment and self. This is done through reducing or blocking signals to the conscious mind from other parts of the brain. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include sensory deprivation, dissociation, hallucinations, and dream-like states or trances. Some, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria. Many dissociatives have general depressant effects and can produce sedation, respiratory depression[citation needed], analgesia, anesthesia, and ataxia, as well as cognitive and memory impairment and amnesia.
The primary area of activation for dissociatives is blockade of the Ca++ ion in the NDMA receptor. Also known as uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists.
Noncompetitive antagonists result in the same effect on the receptor, but achieve it in a slightly different way.
Dissociatives can also be classified by molecular structure. The most well known dissociatives used recreationally and in medicine are known as arylcyclohexylamines 
Another well known dissociative Dextromethorphan (DXM) has a very opioid like structure. It is classified as a morphinan
NMDA receptor antagonists
Adamantanes
Amantadine
Memantine
Rimantadine
Arylcyclohexylamines
Dieticyclidine
Esketamine
Eticyclidine
Gacyclidine
Metaphit
Neramexane
Phenylhexylcyclopyrrolidine
Rolicyclidine
Tenocyclidine
Tiletamine
Methoxydine (4-MeO-PCP)
3-MeO-PCP
3-MeO-PCE
3-MeO-PCPr
3-MeO-PCPy
Morphinans
Dextromethorphan
Dextrorphan
Methorphan
Morphanol
Others
2-MDP
8A-PDHQ
Aptiganel
Dexoxadrol
Diethyl ether
Dizocilpine
Etoxadrol
Midafotel
NEFA
Nitrous oxide
Noribogaine
Perzinfotel
Remacemide
Selfotel
Xenon
κ-opioid agonists
kappa-opioid agonists are an entirely different type of drug that can have dissociative effects. κ-opioid wikipedia page
Very little is known about this receptor and its effects on the body. Evidence points towards dynorphin, the endogenous κ-opioid agonist, to play a major role in substance addiction.
| Safety profile | |
|---|---|
Category:
|
|
Main effects:
|
|
Side effects:
|
|
Health risks:
|
|
Important safety remarks:
|
|
2-EMSB
2-MMSB
Alazocine
Bremazocine
Butorphanol
Cyclazocine
Cyprenorphine
Dezocine
Enadoline
Herkinorin
HZ-2
Ketazocine
Metazocine
Nalbuphine
Nalfurafine
Nalorphine
Noribogaine
Phenazocine
Pentazocine
Spiradoline
Tifluadom
U-50488