NMT
From DMT-Nexus Wiki
Revision as of 13:16, 7 November 2011 by Endlessness (Talk | contribs)
Contents
- 1 Brief overview - What is Bufotenine?
- 2 Chemical and physical properties
- 3 Effects
- 4 Pharmacology, toxicity and general safety
- 5 Plants containing bufotenine
- 6 Extraction teks
- 7 Dosages and consumption methods
- 8 History of usage
- 9 Analysis of bufotenine
- 10 Scientific publications
- 11 Other links of interest
Brief overview - What is Bufotenine?
Chemical and physical properties
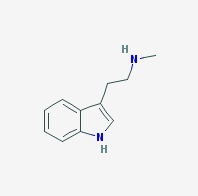
N-Methyltryptamine, monomethyltryptamine
Freebase NMT
 |
- Appearance: Oil, difficult crystallization, eventually forms crystalline stellar aggregates, darkens with exposure to air (Source 1, Source 2)
- Composition: C11H14N2
- Molecular Weight: 174.24226 g/mol
- Melting point: 87-89C (Sigma Aldrich)
- Boiling point: 336.181 °C at 760 mmHg (Chemspider)
- XLogP3: 2.1 (PubChem)
- Colorimetric reagent results: Here
- Stability/Degradation: Darkens over time, but does not seem to form oxides (Source )
- Solubility:
Soluble in methanol, warm ethanol, dichloromethane & choloroform. Soluble to some extent in naphtha (not nearly as much as DMT). It seemed only partially soluble in warm acetic acid. It is likely soluble in xylene. (Source )
Effects
- 1/3 to 1/4 potency of DMT Nen (2001))
- Further info: TIHKAL NMT entry
Pharmacology, toxicity and general safety
- Present in trace amounts as part of normal metabolism (Source)