Acacia maidenii
Contents
General Plant Info
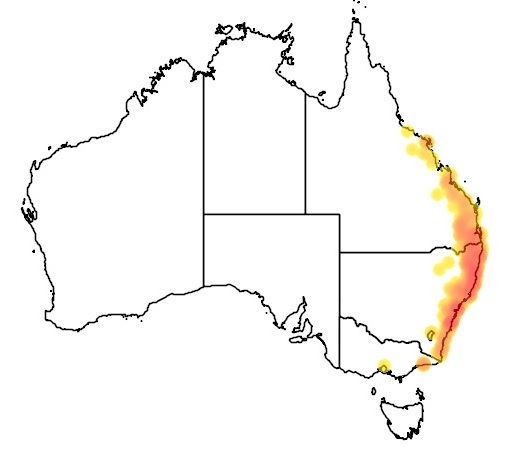
Geographic distribution
Identification
Alkaloid content
Bark of A. maidenii contains 0.24% of N-methyltryptamine and 0.36% DMT[1]
0.6% tryptamines found in bark [2]
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine and other N-methylated tryptamines found in the bark[3]
Phyllode alkaloids up to 0.7% (average 0.4%) - Ref: Trying to Improve Acacia information, DMT Nexus
Extraction
Other uses
It makes an attractive ornamental tree along streets and in parks. It is very good for reforestation in suitable areas. The exudates from the trunk (like gum or pitch) have been used in the past for food by indigenous Australians
Cultivation
USDA Zone 9 is recommended. Acacia maidenii does well in all types of soil, except those that are waterlogged for lengthy periods of time.The tree's seeds number about 65 seeds/g. Acacia maidenii can be propagated from seed, but, in order to increase the germination rate, the seed should be treated first. It can be soaked in hot water or the seed can be nicked or otherwise mechanically scarified, so that water will penetrate the seed's hard coating and induce germination.
Germination is highest at temperatures between 21-27°C