Harmaline
From DMT-Nexus Wiki
Revision as of 13:23, 7 November 2011 by Endlessness (Talk | contribs)
Contents
- 1 Brief overview - What is Harmaline?
- 2 Chemical and physical properties
- 3 Effects
- 4 Pharmacology, toxicity and general safety
- 5 Plants containing harmaline
- 6 Extraction teks
- 7 Dosages and consumption methods
- 8 History of usage
- 9 Analysis of Harmaline
- 10 Scientific publications
- 11 Other links of interest
Brief overview - What is Harmaline?
Chemical and physical properties
3,4-dihydro-7-methoxy-1-methyl-β-carboline
Freebase Harmaline
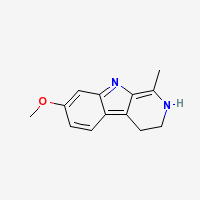 |
- Composition: C13H14N2O
- Melting point: 232-234 °C (Sigma Aldrich)
- Boiling point: 120-140 °C at 0.001 mm/Hg (TIHKAL)
- XLogP: 0.8
- XLogP3: 1.2
- pKa: 9.8
- Colorimetric reagent results: Here
- Solubility:
Slightly soluble in basic water, poorly soluble in distilled water. Reasonably soluble in acetone (at 25°C, acetone can dissolve 4mg/ml mixed harmalas as this test shows)
- Isolation: To separate from harmine, using pKa properties, raise pH of solution containing both alkaloids to pH 8.75 to precipitate 92% of harmine and only 8% Harmaline. Filter to retrieve precipitated alkaloids, and raise the pH further to retrieve the bulk of harmaline. Check the freebase percentage calculator thread and the Harmala Extraction Guide for more info.
Harmaline Hydrochloride
- Solubility:
Soluble in water
Insoluble in salt-saturated water