Difference between revisions of "CIELO"
(→Pull) |
(→Salt) |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
| − | Move extract to fridge for 12-72h. White xtals should form towards the bottom of the jar | + | Move extract to fridge for 12-72h. White xtals should form towards the bottom of the jar. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Screenshot_20210311-162001.png|center]] | ||
Revision as of 22:27, 11 March 2021
Contents
Introduction
CIELO stands for Crystals In Ethyl-acetate Leisurely OTC (Over The Counter).
In this TEK, aqueous alkaline cactus paste is extracted with ethyl acetate. The extract is salted with citric acid to precipitate mescaline citrate crystals directly in the solvent.
Materials
- Quart jars with LDPE or PP plastic lids (e.g. below)
- Food scale
- 300g water
- 25g Ca(OH)2 (lime)
- 100g powdered dry cacti
- ~ 1000g ethyl acetate ("MEK substitute")
- pH paper
- Citric acid
- Filter (optional)
- Shallow baking dish
- Scraping tool (e.g. razor blade)
Safety
Review ethyl acetate's safety information[1] and check the manufacture's MSDS to verify you have pure ethyl acetate.
Each adult individual needs to find and review any other relevant safety information throughly and make their own personal decision on proceeding.
Process
Paste
Mix water and lime. Add cactus powder and mix to a homogeneous paste for a few minutes.
Pull
Add ~ 200g of ethyl acetate to the paste. Extract passively or by mixing very gently for 10 minutes and decant to a second jar.
It is important to never shake or stir quickly so solvent does not bind to the paste.
Pull three more times. Progress can be monitored with pH paper (green color indicates free base presence). Paste will change during the pulls and become more gunky.
Combined pulls will give ~a quart of deep green extract (see image below). Optionally, more pulls can be done into a different jar for a modest yield improvement.
Salt
Dissolve ~250mg (~1/16 tsp) of citric acid into the extract making it cloudy. Test with pH paper, salting is complete when pH paper is acidic. If needed, add more citric acid in small increments of ~100mg until salting is complete.
Move extract to fridge for 12-72h. White xtals should form towards the bottom of the jar.
If there are issues with chrystalization, it should still be possible to recover any product present with water pulls followed by evaporation and ethyl acetate washes.
Finish
Decant ethyl acetate into a storage jar for reuse, using a filter to catch any loose crystals. Rinse chrystals with fresh ethyl acetate at least once or until green color is removed to personal cosmetic satisfaction. Dissolve crystals in minimal warm water and passively evaporate undisturbed in a shallow baking dish. Finally, scrape up the resulting long crystal needles.
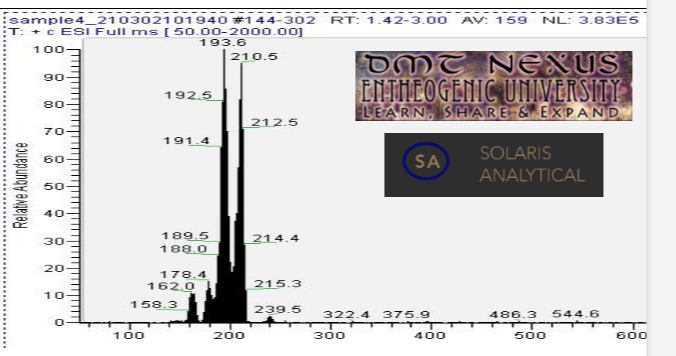
Mass spectrometry (MS) results from solaris analytical[2] indicate the product is very clean mescaline after only two ethyl acetate rinses with some minor discoloration remaining. See MS spectrum below, peak near 210.5 is mescaline. Peaks at and 193.6, 178.4, and 162.0 are believed to be mescaline with amine/methyl/methoxy groups cleaved to generate the lower mass mescaline spectrum in multiples of ~16 au (16.9, 32.1, and 48.5 respectively). The small peak at 239.5 is not attributed to mescaline.
Lab Notes
It is possible to chemically dry the extract with a drying agent such as anhydrous MgSO4. However, no clear yield benefit was observed by performing this step. Surprisingly, solutions carefully dried with anhydrous CaCl2 followed by K2CO3 had difficulty crystalizing after salting, indicating that a some water is desirable for crystalization. This points to the precipitate from this TEK maybe being hydrate salt. Regardless of the reason, the water content in ethyl acetate directly from the pulls is in a good range experimentally.
During salting, every 10mg of citric acid (CitH3) reacts with enough free base mescaline (Mes) to precipitate up to 43mg of mescaline citrate (or slightly more if a hydrate form is precipitating):
250mg of citric acid are enough for the typical cactus (up to 1% yield). However, and outlier like the legendary Ogun would need ~1100mg of citric acid for a 4.7% yield.
Over acidifying is not a big concern. There is room for excess citric acid in solution since several grams can dissolve in a quart of ethyl acetate even when chilled. The vast majority of excess acid would be poured off after salting, and any traces removed when washing the crystals.
Other solid organic acids could work. Fumaric acid was tested and gave wispy tiny crystals (not ideal). Malic was tested and slowly crystalized from a dry solution. Tartaric could not crystalize well from dry a dried extract, but began to crystalize with some water added (similar to citric acid). There are many other solid organic acids soluble in ethyl acetate that can be tested (ascorbic, succinic, etc).
It is possible that some of the assumptions and conclusions in these lab notes are incorrect or incomplete. The process was tested in several ways, but the search was not exhaustive[3]. There could be ways to improve this process.
References
Shroombee's Notes
Experiment #1
March 9, 2021
6:42 pm
100 grams Peruvian Torch chips
298 grams purified water
Blended cactus chips in the Vitamix dry container so it becomes a fine powder.
6:58 pm Mixed cactus powder and water in a plastic mixing bowl rather than a mason jar because it seems easier. Product is a fluffy texture, olive green color. There is no excess water.
The bowl plus cactus plus silicone mixing spoon weighs 826.5 grams. Microwave on high for 30 seconds, mix, then weigh. This is pretty easy. I wouldn't want to do this in a mason jar. The cactus does not bubble and there is no issue at 30 seconds with anything bubbling over. Weight after each 30 second cycle:
825.6 grams
823.9 grams
820.2 grams
816.0 grams
808.7 grams
800.7 grams
791.3 grams
783.2 grams
775.8 grams
765.8 grams
DONE
After a couple of the microwaving cycles, the cactus lost its fluffiness and became like light bread dough, not sticking much to the bowl.
7:25 pm Begin slowly mixing in 25 grams pickling lime. Started with the plastic bowl but switched to a ceramic bowl after a minute, not knowing how the plastic would react to the base. Bowl appears fine after washing it out.
7:39 pm I'm using a fork to try to get the lime mixed evenly. I figure my Kitchenaid stand mixer will be easier so I break that out.
7:45 pm Letting the Kitchenaid stir the cactus for me. Much easier!
7:53 pm Added 25 grams calcium chloride. Before adding, the cactus paste was fluffy and stuck to the sides of the stainless steel bowl. After adding the calcium chloride, the cactus became like clumpy sand and hardly stuck to the sides of the bowl.
7:58 pm Stopped mixing.
8:05 pm Transferred cactus to a wide mouth quart mason jar and added 220 ml of ethyl acetate (weighing 199.9 grams). The ethyl acetate came up to approximately 540 ml on the side of the mason jar. After shaking, the cactus looked like fluffy beach sand.
8:28 pm Shake for a minute.
9:00 pm Shake for a minute.
9:22 pm No shaking, I notice the ethyl acetate is light green.
10:30 pm Shake for a minute. The cactus is starting to get a little stickier, leaving streaks on the glass.
11:00 pm Ethyl acetate comes up to exactly 500 ml on the side of the mason jar. Versus ~540 ml at 8:05 pm when the ethyl acetate was first added. What accounts for this 40 ml difference?
12:00 am Shake for a minute.
1:06 am Weighed mason jar with cactus: 1001.4 grams.
March 10, 2021
7:57 am Weighed mason jar with cactus: 1001.1 grams.
Ready to decant ethyl acetate. Large pyrex beaker with metal coffee filter weighs 342.3 grams. Ethyl acetate is a medium, emerald green. Definitely not light green and not yellow.
Using a small ladle to decant, which gets most of the ethyl acetate with no plant matter. Beaker weighs 427.2 grams meaning we recovered 84.9 grams of ethyl acetate. Not too good.
I transferred the cactus to a french press to see if I could recover more ethyl acetate. The sticky paste does not compress and I recovered an additional ~6 grams ethyl acetate. French press is obviously not worth the effort!
8:21 am Done with decanting, transferring, french pressing, weighing, et cetera. Total recovery for this pull is 90.6 grams ethyl acetate.
8:23 am Added 90.7 grams of fresh ethyl acetate to the mason jar. Stirred ethyl acetate into the sticky cactus, did not shake. Ethyl acetate is already changing to green color.
8:33 am Photo of pH paper. Paper is dark green. pH 10 or 11? Also tested using the 4 color pH strips. More difficult to judge the pH with these.
8:34 am Photo of recovered ethyl acetate showing it is an emerald green color.
8:45 am Poured 10 ml of ethyl acetate into a small beaker. Added 13 mg of citric acid. Lower half of the beaker turned milky, cloudy. Checked pH and it's basically the same as the rest of the solvent. So the small amount of citric acid didn't change the pH much. I used a disposable pipette and pulled from the top of the solvent, so perhaps the top layer didn't have a chance to react yet.
8:49 am Photo showing cloudy 10 ml in small beaker.
8:50 am Poured the 10 ml and the rest of the solvent into a mini Pyrex baking dish, using the larger volume of solvent to rinse out of the small beaker. I probably should have left the solvent in a mason jar or beaker rather than adding to the baking dish. Added 95 mg of citric acid. Stirred a little because I wanted to get a more accurate pH. pH was about 7. Added an additional 61 mg citric acid. pH went to about 6. Total citric acid added to the 90.6 grams ethyl acetate is 169 mg. Even after rinsing with the main solvent, the bottom of the small beaker has some spots that look like something crystalizing. I don't know if it's just sticky citric acid or ???
9:07 am Photo of 3 pH test strips.
3:42 pm Moving the dish to the freezer. Solvent is clear (and has been clear for at least a few hours). Initially I thought there were droplets on the bottom of the dish (around 11:00 am). Then tried to scrape at them with a knife and not seeing any movement, I figured they were a reflection from the surface because I noticed some tiny droplets on the surface if I caught the light at the right angle. Then as I tipped the dish at 3:42pm to move it into the freezer, I now see the droplets really are at the bottom of the dish. Sort of an oily substance. There are no crystals.
8:00 pm Retrieving pull #2. Beaker plus metal coffee filter weigh 342.3 grams. Weighs 407.5 grams after decanting. Recovered 65.2 grams. Looks like the cactus sucked up more solvent even though I didn't shake. pH is basic, although the pH paper is not as dark green as pull #1.
8:09 pm Removed a few tablespoons of sticky slimy cactus and put it into a separate bowl. Mixed in 5.4 grams of calcium chloride (which is a lot relative to the amount of cactus). Even waiting more than 30 minutes, no additional solvent is released. The cactus is drier though, more clumpy, and lost some gooey sliminess.
8:27 pm Since only 65.2 grams of solvent was retrieved, I decided adding this amount of fresh solvent for pull #3 would be too inefficient. I added 197.6 grams fresh ethyl acetate and stirred for 1-2 minutes. Solvent turned a light green fairly quickly.
8:38 pm Added 49 mg citric acid to the recovered solvent. Bottom of jar got milky. Tested pH with 3 strips. (1) Took a solvent sample towards the bottom of the jar at the clouds: pH about 5. (2) Solvent sample at the surface: pH about 7. (3) Swirled the jar around then took a solvent sample. pH about 6.
8:45 pm Put jar into freezer.