Difference between revisions of "Acacia colei"
(→General Plant Info) |
Nen888wiki (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | {{botanics_info| | + | {{botanics_info|[[File:Acacia colei var colei copy.png]]|Acacia colei|DMT (Dr. Karl and abc.net.au 2005) 1%+ in bark (different net reports)}} |
</onlyinclude> | </onlyinclude> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
It grows to a height of up to 9 m. ''Acacia colei'' blooms from June through July and the flowers are bright yellow.<ref>[http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/species-bank/sbank-treatment.pl?id=55598 Australian Biological Resources Study]</ref> | It grows to a height of up to 9 m. ''Acacia colei'' blooms from June through July and the flowers are bright yellow.<ref>[http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/species-bank/sbank-treatment.pl?id=55598 Australian Biological Resources Study]</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Consists of 2 variants: | |
| − | + | [[Acacia colei var. colei]] | |
| + | [[Acacia colei var. ileocarpa]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Geographic distribution == |
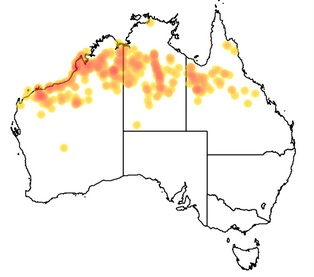
| + | [[File:colei-map.jpg]] | ||
| − | + | == Identification == | |
| − | + | Phyllodes are 10-19 cm long and 20-55 mm wide, usually with three prominent longitudinal nerves. A dense covering of short hairs on the phyllodes gives the plant a characteristic silvery-blue appearance. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | == Alkaloid content == | ||
| + | Claimed to contain 1.8% or more DMT in bark <ref>[https://www.abc.net.au/science/k2/stn/q&a/notes/051027-9.htm Dr. Karl Kruszelnicki ABC Radio]</ref> <ref>[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=992290&#post992290 Seldom/nen888 DMT Nexus]</ref>, 0.2-0.6% in leaf. Needs further research. | ||
== Other uses == | == Other uses == | ||
| + | Its uses include environmental management, [[Fodder|forage]] and wood. The seeds are good-tasting<ref>[http://www.echotech.org/mambo/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=19&Itemid=51 ECHO] Education Concerns for Hunger Organization</ref> and are potentially useful as food for humans. The results of tests in [[Nigeria]] for the feasibility of raising the tree as a drought-resistant food crop came out very positively.<ref>[http://www.worldwidewattle.com/schools/uses.php World Wide Wattle]</ref> | ||
| + | == Extraction == | ||
== Cultivation == | == Cultivation == | ||
| − | |||
== Suppliers == | == Suppliers == | ||
| − | |||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Botanicals]] | [[Category:Botanicals]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:58, 20 February 2023
[[ |center|100x100px]] |center|100x100px]] |
Acacia colei |
|---|---|
| DMT (Dr. Karl and abc.net.au 2005) 1%+ in bark (different net reports) |
Contents
General Plant Info
Acacia colei is a perennial bush or tree native to Australia and southern Asia. A common name for it is Cole's Wattle. It grows to a height of up to 9 m. Acacia colei blooms from June through July and the flowers are bright yellow.[1]
Consists of 2 variants:
Geographic distribution
Identification
Phyllodes are 10-19 cm long and 20-55 mm wide, usually with three prominent longitudinal nerves. A dense covering of short hairs on the phyllodes gives the plant a characteristic silvery-blue appearance.
Alkaloid content
Claimed to contain 1.8% or more DMT in bark [2] [3], 0.2-0.6% in leaf. Needs further research.
Other uses
Its uses include environmental management, forage and wood. The seeds are good-tasting[4] and are potentially useful as food for humans. The results of tests in Nigeria for the feasibility of raising the tree as a drought-resistant food crop came out very positively.[5]
Extraction
Cultivation
Suppliers
Links
References
- ↑ Australian Biological Resources Study
- ↑ Dr. Karl Kruszelnicki ABC Radio
- ↑ Seldom/nen888 DMT Nexus
- ↑ ECHO Education Concerns for Hunger Organization
- ↑ World Wide Wattle