Difference between revisions of "CIELO"
(→Salt) |
(Big update to use chilled ethyl acetate) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| − | In this TEK, aqueous alkaline cactus paste is extracted with ethyl acetate. | + | In this technique (TEK), aqueous alkaline cactus paste is quickly extracted with chilled ethyl acetate (sometimes sold as "MEK Substitute" in hardware stores). Dissolving excess citric acid in the extract precipitates mescaline citrate crystals. |
| − | This process was developed in a loving collaboration at the DMT nexus. Deep thanks and gratitude to everyone who contributed or provided support: someblackguy, Benzyme, shroombee, Metta-Morpheus, Downwardsfromzero, Kash, grollum, Mindlusion, Doubledog, Loveall, and others. | + | This process was developed in a loving collaboration at the DMT nexus. Deep thanks and gratitude go to everyone who contributed or provided support: someblackguy, Benzyme, shroombee, Metta-Morpheus, Downwardsfromzero, Kash, grollum, Mindlusion, Doubledog, Loveall, and others. |
= Safety = | = Safety = | ||
| − | Review ethyl acetate's safety information<ref>Ethyl acetate safety[https://www.msdsonline.com/2015/04/10/ethyl-acetate-a-sweet-smelling-safety-hazard/#:~:text=Ethyl%20acetate%20is%20highly%20flammable,with%20the%20eyes%20or%20skin.]</ref> and check the manufacture's MSDS to verify you have pure ethyl acetate. | + | Review ethyl acetate's safety information<ref>Ethyl acetate safety[https://www.msdsonline.com/2015/04/10/ethyl-acetate-a-sweet-smelling-safety-hazard/#:~:text=Ethyl%20acetate%20is%20highly%20flammable,with%20the%20eyes%20or%20skin.]</ref> and check the manufacture's MSDS to verify you have pure ethyl acetate. Make sure any plastic you use is compatible with ethyl acetate and verify your ethyl acetate evaporates cleanly. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | Make sure any plastic you use is compatible with ethyl acetate and verify your ethyl acetate evaporates cleanly. | + | |
| Line 21: | Line 18: | ||
= Materials = | = Materials = | ||
| − | |||
* 300g water | * 300g water | ||
| − | * 25g | + | * 25g lime |
| − | * 100g | + | * 100g dry cactus powder |
| − | * | + | * ~1200g ethyl acetate |
* Coffee filters | * Coffee filters | ||
| − | * | + | * 5g of citric acid |
| − | * | + | * Non-consumables: Scales (g and mg), jars (~32oz, and ~64oz), french press (optional), funnel, and coffee filter support. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <center>''Fig. 1: Materials used in the CIELO Tek.</center> | ||
= Process = | = Process = | ||
| − | == Paste == | + | == Make Alkaline Paste == |
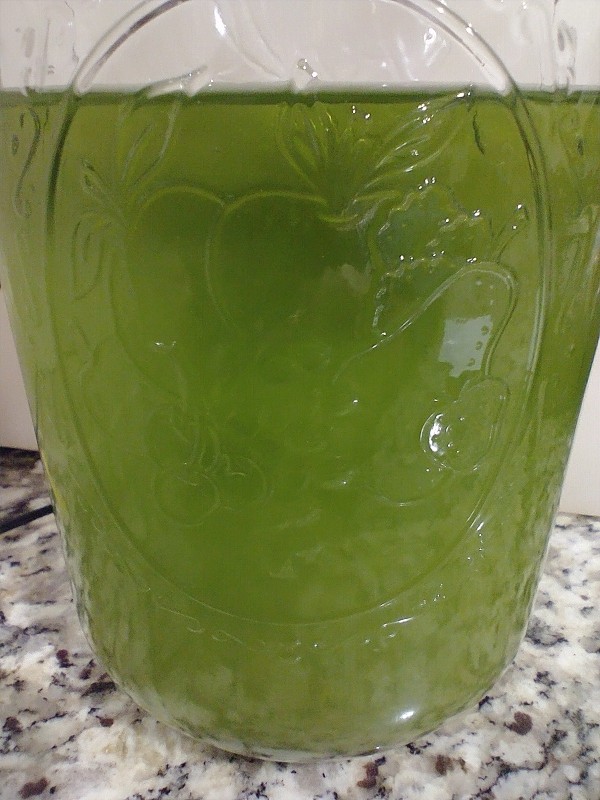
| − | Mix water and lime in a | + | Mix water and lime in a medium (~32 oz) jar, or optionally a french press, to make milk of lime. Incorporate cactus while stirring and continue stirring for at least 10 minutes to a smooth paste. Allow paste to react for 24 hours and mix again for a few minutes. |
[[File:Screenshot_20210311-161134.png|center]] | [[File:Screenshot_20210311-161134.png|center]] | ||
| + | <center>''Fig. 2: Reacted alkali cactus paste thoroughly stirred.</center> | ||
| − | == Pull == | + | == Pull Alkaline Paste== |
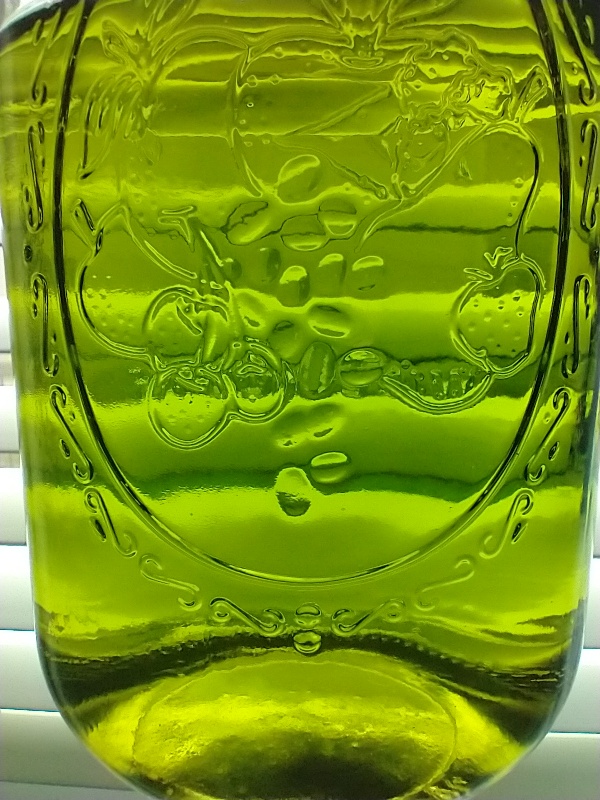
| − | Add ~ 300g of ethyl acetate to | + | Add ~ 300g of freezer chilled ethyl acetate (~0 F) to the paste, mix for 60 seconds, and decant/filter to a large jar (~64 oz). If using a french press squeeze very gently to avoid pulling water. Immediately pull 5 more times with ~150g of ethyl acetate stirring for 60 seconds each time. Final extract should be clear with no droplets or particles (see Fig. 3). |
| − | + | [[File:IMG_20210601_122315740_copy_600x800.jpg| center]] | |
| + | <center>''Fig. 3: Clear ethyl acetate extract from cactus alkaline paste.</center> | ||
| + | == Crystalize Extract == | ||
| − | + | Verify no particles or droplets are in the extract. If any are present, decant/filter to remove them. | |
| − | + | Dissolve ~ 5g of citric acid into extract. Solution will become cloudy (Fig. 4). Move cloudy extract to the fridge overnight to form mescaline citrate crystals (Fig. 5). | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:IMG 20210601 122626621 copy 600x800 1.jpg|center]] | |
| + | <center>''Fig. 4: Cloudy extract after citric acid addition.</center> | ||
| − | + | [[File:IMG 20210603 090359363 copy 600x800.jpg|center]] | |
| + | <center>''Fig. 5: Mescaline citrate crystals in salted extract.</center> | ||
| − | == | + | == Collect Crystals == |
| − | + | Swirl extract to suspend crystals and catch them in a coffee filter. Repeat with a small amount of fresh ethyl acetate until green color is removed and all crystals are in the filter (2-3 times). Allow crystals to dry and collect them. This is the final product (Fig. 6). | |
| − | + | Mass spectrometry (MS) results from solaris analytical<ref>Solaris analytical service[https://www.solarisanalytical.com/]</ref> indicate the product is very clean mescaline (Fig. 7). Yield is highly dependent on cactus material, typically from 0.2% to 2% <ref>Cactus analysis thread[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&t=71353]</ref>. | |
| − | |||
| + | [[File:IMG 20210603 130102387 copy 600x800.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | <center>''Fig. 6: Final product.</center> | ||
| − | |||
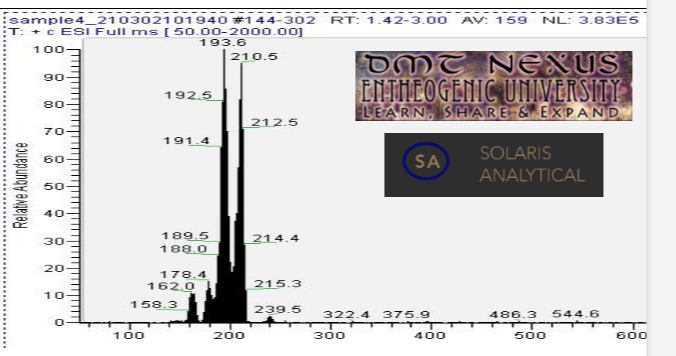
| + | [[File: Screenshot_20210310-062431.png|center]]''<center>Fig. 7: Mass spectrometry result. Peak near 210.5 is mescaline. Peaks at and 193.6, 178.4, and 162.0 are mescaline with amine/methyl/methoxy groups cleaved giving the lower mass spectrum in multiples of ~16 au (16.9, 32.1, and 48.5 respectively). The small peak at 239.5 is not attributed to mescaline. </center> | ||
| − | + | = Appendix: Development Notes = | |
| + | == What worked == | ||
| − | |||
| + | Chilled ethyl acetate was found to make the process robust experimentally, presumably by minimizing water and plant material while remaining efficient with mescaline. By minimizing plant matter in the pull, in situ crystallization is improved across different cacti sources, which is important when skipping the classic liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) steps. | ||
| − | |||
| + | It is also possible to obtain good results with 3 minute room temperature pulls, but the results may not be as consistent between users as with chilled ethyl acetate. [https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1105396#post1105396 Sometimes] it can take longer for crystals to form, while [https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1098483#post1098483 other times] crystalization can be very quick when using a magnetic stirrer. With room temperature solvent 5mg/g of citric acid can be enough when working with outer cactus skin, but not when working with the [https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&m=1102283#post1102283 whole plant]. | ||
| − | + | == What didn't work == | |
| − | + | Paste modifications: No improvements seen with microwaving, partially drying, adding NaCl, or extending the reaction time beyond 24h. Completely drying the paste made the process not work, apparently some water is needed in this process. | |
| − | |||
| + | Pull modifications: Long room temperature pulls made the paste congeal and resulted in lower yield. Heating during the pull did not improve yields. In general the crystalization is more difficult and the product can aquire a tan color if the pulls are more aggressive with no improvement to yield. | ||
| − | |||
| + | Extract modifications: Chemically drying the extract with a drying agent such as anhydrous MgSO4 before salting had no yield benefit. In one example, drying the extract with CaCl2 resulted in a more difficult crystalization and a 40% yield loss. In general, any water content in ethyl acetate directly from the pulls is already in a good range experimentally. | ||
| − | |||
| + | Note: Droplets or debris not decanted/filtered before salting will result in crystalization issues. It is very important to verify the extract is clean before salting. | ||
| − | + | == Crystalization details == | |
| − | + | During crystallization, every 10mg of citric acid ('''H3Cit''') reacts with free base mescaline ('''Mes''') to form to 43mg of mescaline citrate (or slightly more if a hydrate form is precipitating): | |
| − | During | + | |
| Line 102: | Line 106: | ||
| − | + | The TEK calls for a lot more citric acid than would be needed for titration. The reason is that excess citric acid induces crystalization to overcome any water or plant material that would otherwise keep mescaline citrate in solution. '''This is a simple but very important lab observation''', compatible with Le Chatelier's principle. There is a lot room for excess citric acid in ethyl acetate since its solubility is 50mg/g (and water in the solvent from the pulls may increase this solubility further). The TEK recommends 5mg/g since this was found to be enough to crash mescaline for most users when using chilled ethyl acetate, buy going above this recommendation is OK if issues are encountered to try to force crystalization due to plant variability and/or technique issues. | |
| − | + | Finally, other dry solid organic acids could work. Fumaric, Malic, Tartaric, Ascorbic, Succinic, etc can be tested in future investigations. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | == Disclaimer == | ||
It is possible that some of the assumptions and conclusions in these lab notes are incorrect or incomplete. The process was tested in several ways, but the search was not exhaustive<ref>Ethyl acetate approach[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&t=96262]</ref>. There could be ways to improve this process. | It is possible that some of the assumptions and conclusions in these lab notes are incorrect or incomplete. The process was tested in several ways, but the search was not exhaustive<ref>Ethyl acetate approach[https://www.dmt-nexus.me/forum/default.aspx?g=posts&t=96262]</ref>. There could be ways to improve this process. | ||
| Line 118: | Line 117: | ||
= References = | = References = | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 18:40, 3 June 2021
Contents
Introduction
CIELO stands for Crystals In Ethyl-acetate Leisurely OTC (Over The Counter).
In this technique (TEK), aqueous alkaline cactus paste is quickly extracted with chilled ethyl acetate (sometimes sold as "MEK Substitute" in hardware stores). Dissolving excess citric acid in the extract precipitates mescaline citrate crystals.
This process was developed in a loving collaboration at the DMT nexus. Deep thanks and gratitude go to everyone who contributed or provided support: someblackguy, Benzyme, shroombee, Metta-Morpheus, Downwardsfromzero, Kash, grollum, Mindlusion, Doubledog, Loveall, and others.
Safety
Review ethyl acetate's safety information[1] and check the manufacture's MSDS to verify you have pure ethyl acetate. Make sure any plastic you use is compatible with ethyl acetate and verify your ethyl acetate evaporates cleanly.
Following this advice does not guarantee safety. It is up to each adult individual to make their own decision on proceeding with this process.
Materials
- 300g water
- 25g lime
- 100g dry cactus powder
- ~1200g ethyl acetate
- Coffee filters
- 5g of citric acid
- Non-consumables: Scales (g and mg), jars (~32oz, and ~64oz), french press (optional), funnel, and coffee filter support.
Process
Make Alkaline Paste
Mix water and lime in a medium (~32 oz) jar, or optionally a french press, to make milk of lime. Incorporate cactus while stirring and continue stirring for at least 10 minutes to a smooth paste. Allow paste to react for 24 hours and mix again for a few minutes.
Pull Alkaline Paste
Add ~ 300g of freezer chilled ethyl acetate (~0 F) to the paste, mix for 60 seconds, and decant/filter to a large jar (~64 oz). If using a french press squeeze very gently to avoid pulling water. Immediately pull 5 more times with ~150g of ethyl acetate stirring for 60 seconds each time. Final extract should be clear with no droplets or particles (see Fig. 3).
Crystalize Extract
Verify no particles or droplets are in the extract. If any are present, decant/filter to remove them.
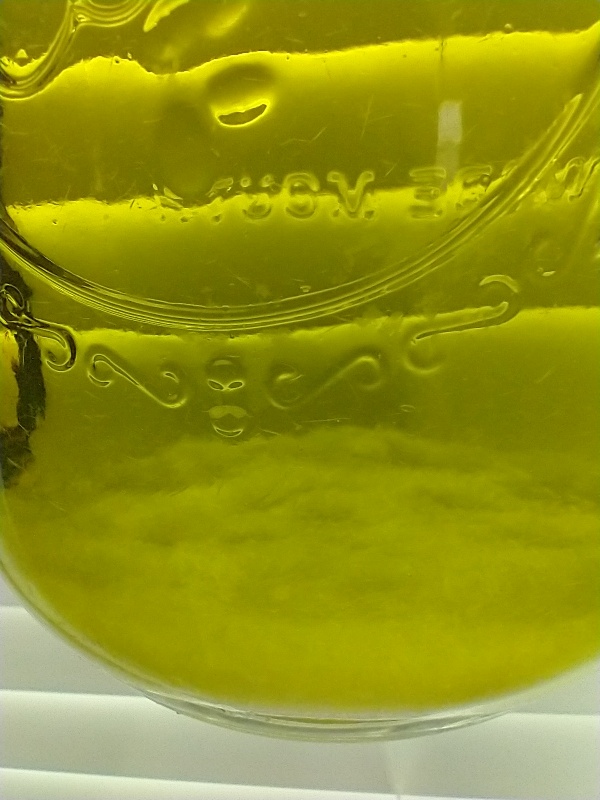
Dissolve ~ 5g of citric acid into extract. Solution will become cloudy (Fig. 4). Move cloudy extract to the fridge overnight to form mescaline citrate crystals (Fig. 5).
Collect Crystals
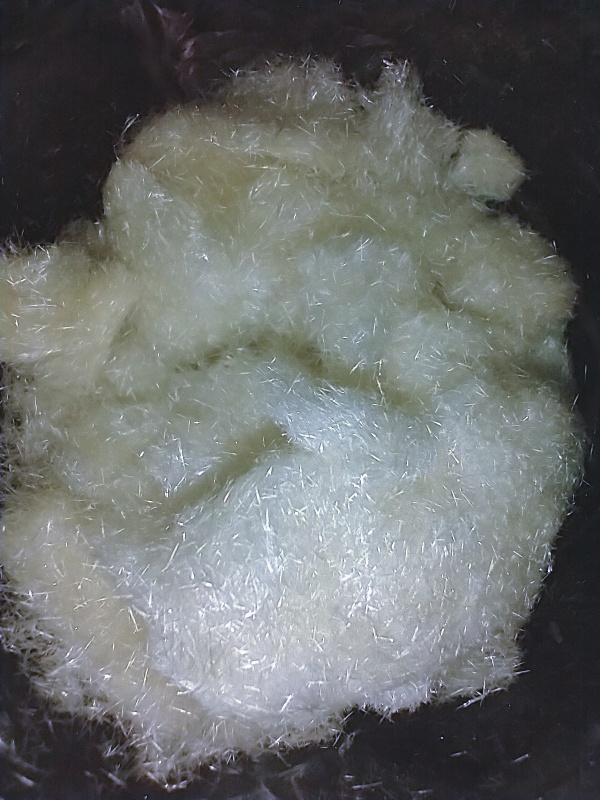
Swirl extract to suspend crystals and catch them in a coffee filter. Repeat with a small amount of fresh ethyl acetate until green color is removed and all crystals are in the filter (2-3 times). Allow crystals to dry and collect them. This is the final product (Fig. 6).
Mass spectrometry (MS) results from solaris analytical[2] indicate the product is very clean mescaline (Fig. 7). Yield is highly dependent on cactus material, typically from 0.2% to 2% [3].
Appendix: Development Notes
What worked
Chilled ethyl acetate was found to make the process robust experimentally, presumably by minimizing water and plant material while remaining efficient with mescaline. By minimizing plant matter in the pull, in situ crystallization is improved across different cacti sources, which is important when skipping the classic liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) steps.
It is also possible to obtain good results with 3 minute room temperature pulls, but the results may not be as consistent between users as with chilled ethyl acetate. Sometimes it can take longer for crystals to form, while other times crystalization can be very quick when using a magnetic stirrer. With room temperature solvent 5mg/g of citric acid can be enough when working with outer cactus skin, but not when working with the whole plant.
What didn't work
Paste modifications: No improvements seen with microwaving, partially drying, adding NaCl, or extending the reaction time beyond 24h. Completely drying the paste made the process not work, apparently some water is needed in this process.
Pull modifications: Long room temperature pulls made the paste congeal and resulted in lower yield. Heating during the pull did not improve yields. In general the crystalization is more difficult and the product can aquire a tan color if the pulls are more aggressive with no improvement to yield.
Extract modifications: Chemically drying the extract with a drying agent such as anhydrous MgSO4 before salting had no yield benefit. In one example, drying the extract with CaCl2 resulted in a more difficult crystalization and a 40% yield loss. In general, any water content in ethyl acetate directly from the pulls is already in a good range experimentally.
Note: Droplets or debris not decanted/filtered before salting will result in crystalization issues. It is very important to verify the extract is clean before salting.
Crystalization details
During crystallization, every 10mg of citric acid (H3Cit) reacts with free base mescaline (Mes) to form to 43mg of mescaline citrate (or slightly more if a hydrate form is precipitating):
The TEK calls for a lot more citric acid than would be needed for titration. The reason is that excess citric acid induces crystalization to overcome any water or plant material that would otherwise keep mescaline citrate in solution. This is a simple but very important lab observation, compatible with Le Chatelier's principle. There is a lot room for excess citric acid in ethyl acetate since its solubility is 50mg/g (and water in the solvent from the pulls may increase this solubility further). The TEK recommends 5mg/g since this was found to be enough to crash mescaline for most users when using chilled ethyl acetate, buy going above this recommendation is OK if issues are encountered to try to force crystalization due to plant variability and/or technique issues.
Finally, other dry solid organic acids could work. Fumaric, Malic, Tartaric, Ascorbic, Succinic, etc can be tested in future investigations.
Disclaimer
It is possible that some of the assumptions and conclusions in these lab notes are incorrect or incomplete. The process was tested in several ways, but the search was not exhaustive[4]. There could be ways to improve this process.