Difference between revisions of "Acacia baileyana"
(→Links) |
(→Geographic distribution) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Geographic distribution == | == Geographic distribution == | ||
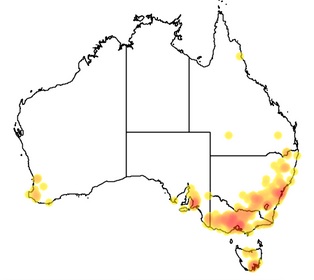
This species has a very limited natural distribution in south-eastern Australia. It is native to the Temora, Cootamundra, Stockinbingal and Bethungra districts in the inland parts of southern New South Wales. | This species has a very limited natural distribution in south-eastern Australia. It is native to the Temora, Cootamundra, Stockinbingal and Bethungra districts in the inland parts of southern New South Wales. | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| + | This species is also found in the Mudgee area of New South Wales | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:baileyana-map.jpg]] | ||
== Identification == | == Identification == | ||
| Line 40: | Line 43: | ||
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acacia_baileyana | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acacia_baileyana | ||
[[Category:Botanicals]] | [[Category:Botanicals]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 06:50, 27 January 2015
| Acacia baileyana |
|
|---|---|
|
Contents
General Plant Info
Acacia baileyana or Cootamundra wattle, is a shrub or tree in the genus Acacia. The scientific name of the species honours the botanist Frederick Manson Bailey. It is indigenous to a small area of southern New South Wales in Australia, but it has been widely planted in other Australian states and territories. In many areas of Victoria, it has become naturalised and is regarded as a weed, out-competing indigenous Victorian species. Almost all wattles have cream to golden flowers. The small flowers are arranged in spherical to cylindrical inflorescences, with only the stamens prominent. Wattles have been extensively introduced into New Zealand.
Geographic distribution
This species has a very limited natural distribution in south-eastern Australia. It is native to the Temora, Cootamundra, Stockinbingal and Bethungra districts in the inland parts of southern New South Wales.
This species is also found in the Mudgee area of New South Wales
Identification
Alkaloid content
Less than 0.02% alkaloids were found in a chemical analysis of Acacia baileyana.[1]
Trace amounts in seeds, Unconfirmed (tlc by J. Apleseed, ref. Trout's Notes). tryptamine and βcarbolines, in the leaf, Tetrahydroharman (TIHKAL)
Extraction
Other uses
A. baileyana is used in Europe in the cut flower industry. It is also used as food for bees in the production of honey.[2]
Cultivation
This plant is adaptable and easy to grow. It has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. Unfortunately it has an ability to naturalise (i.e. escape) into surrounding bushland. Also, it hybridises with some other wattles, notably the rare and endangered Sydney Basin species Acacia pubescens. A prostrate weeping form is in cultivation. Its origin is unknown, but it itself is a popular garden plant, its cascading horizontal branches good for rockeries. The fine foliage of the original Cootamundra wattle is grey-green, but a blue-purple foliaged form, known as 'Purpurea' is very popular.
Suppliers
http://apps.rhs.org.uk/rhsplantfinder/pfregions.asp?ID=23323
Links
http://keyserver.lucidcentral.org/weeds/data/03030800-0b07-490a-8d04-0605030c0f01/media/Html/Acacia_baileyana.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acacia_baileyana